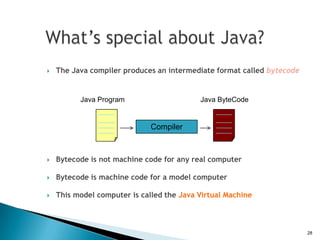
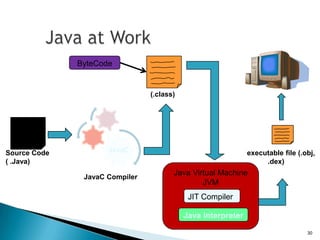
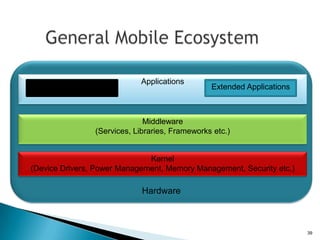
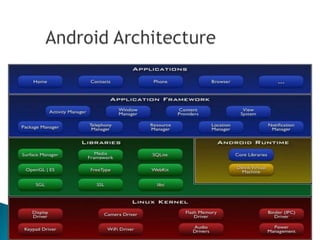
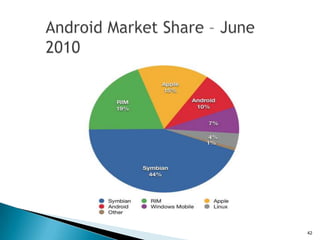
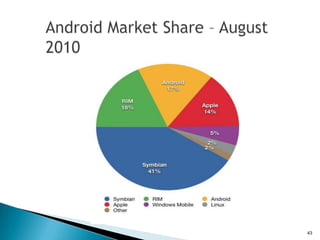
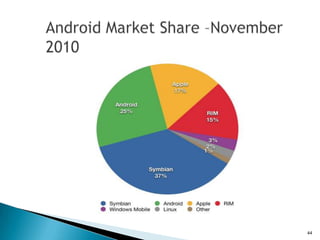
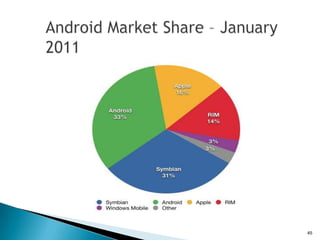
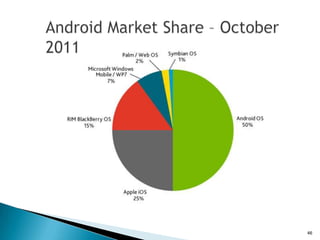
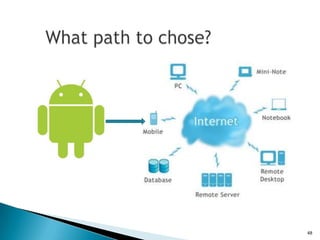
The document provides an overview of mobile application development, differentiating between mobile native and web applications, as well as discussing the Open Handset Alliance's role in advancing mobile standards. It highlights the increasing popularity of mobile apps across various platforms, outlines the benefits and limitations of native and web applications, and details the features of the Android operating system. Additionally, it emphasizes Java's portability and object-oriented nature, alongside the tools available for developing Android applications.