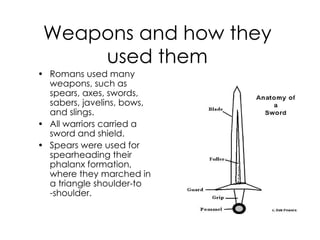
The document provides information about ancient Roman architecture and daily life. It describes architectural structures like aqueducts, bridges, and the Colosseum. It details Roman homes, roads, transportation, food, clothing, and the military. Gladiator fights and Pompeii are also summarized. The document covers many aspects of architecture, infrastructure and culture in ancient Rome.