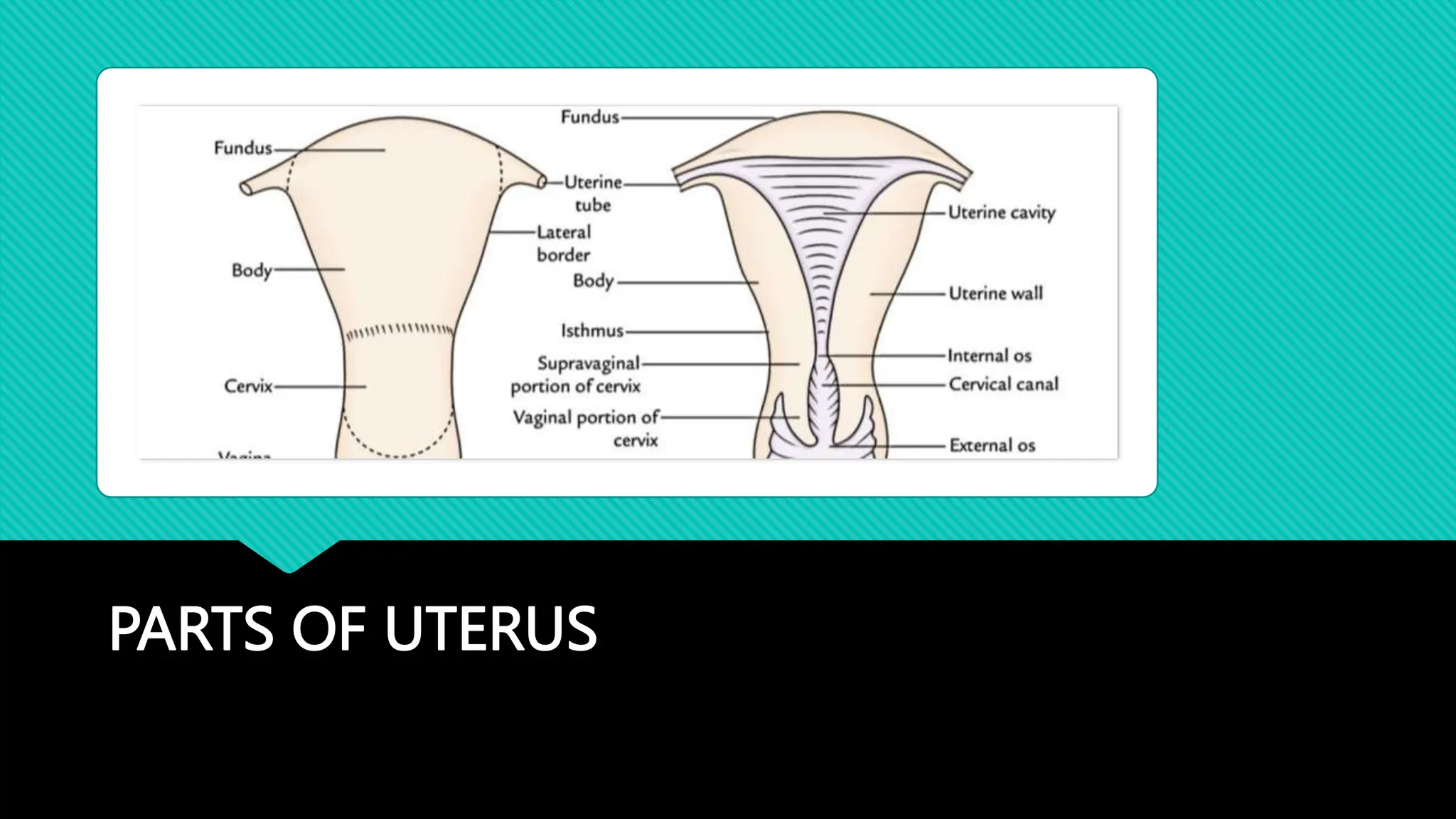
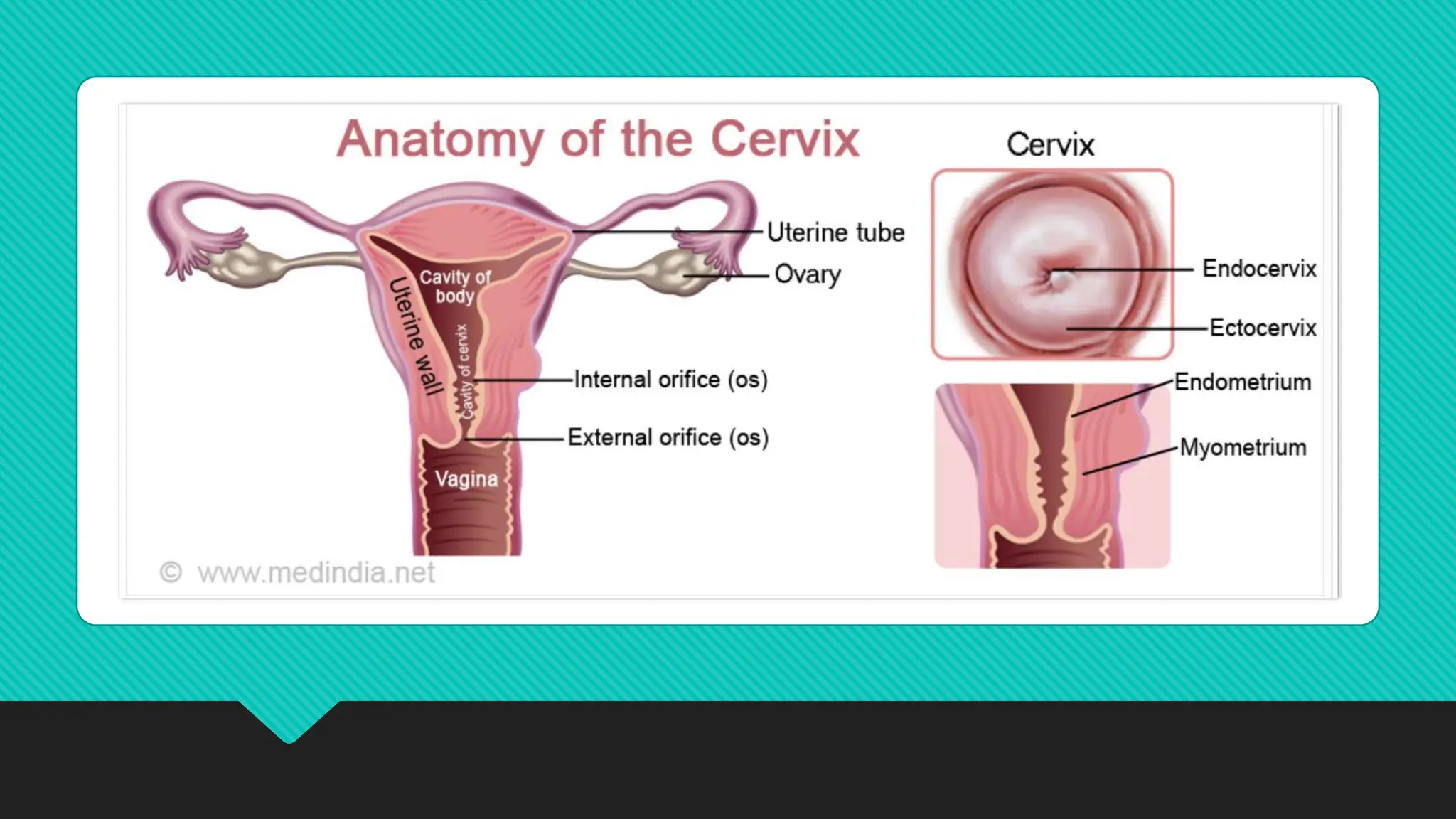
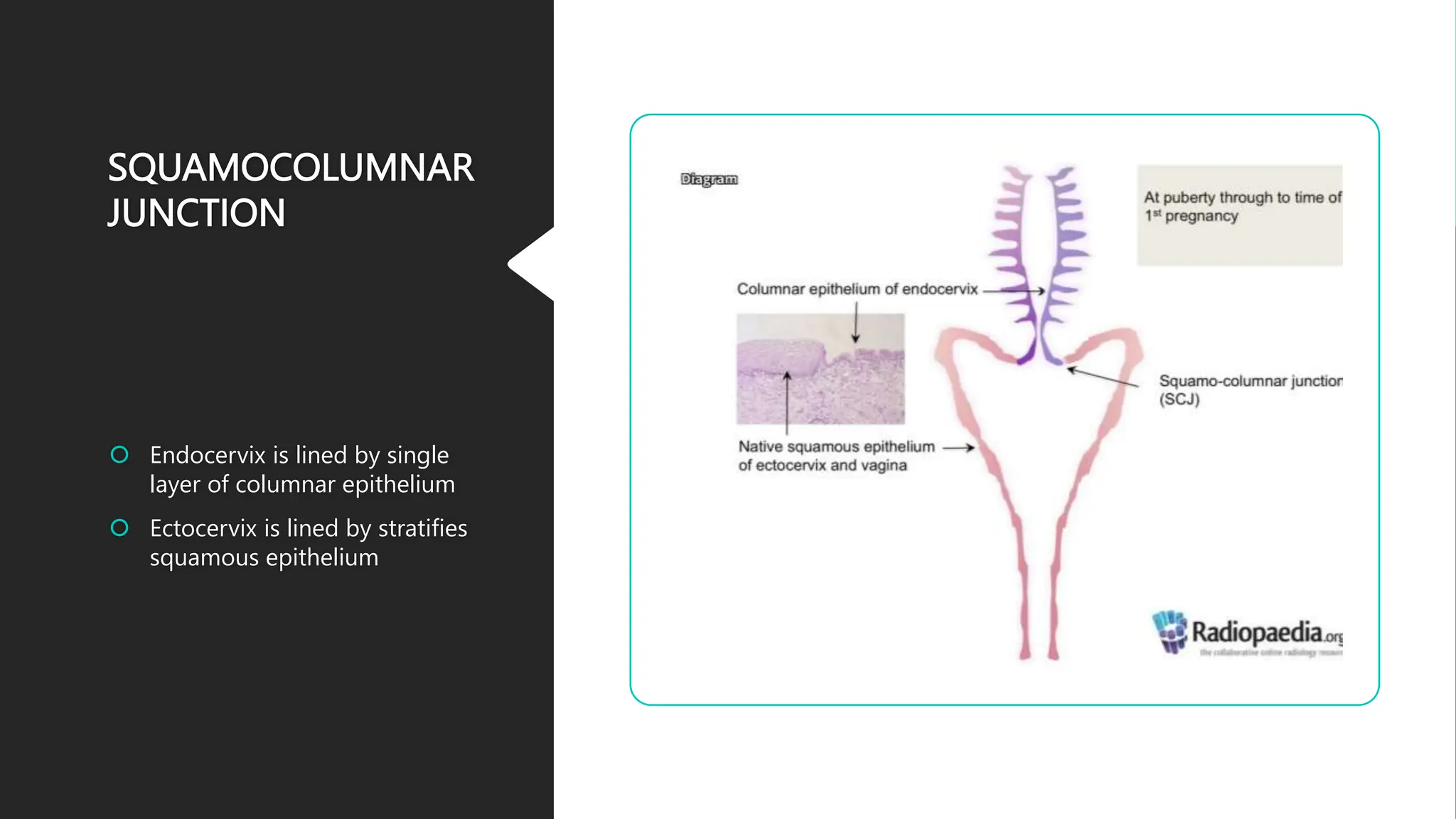
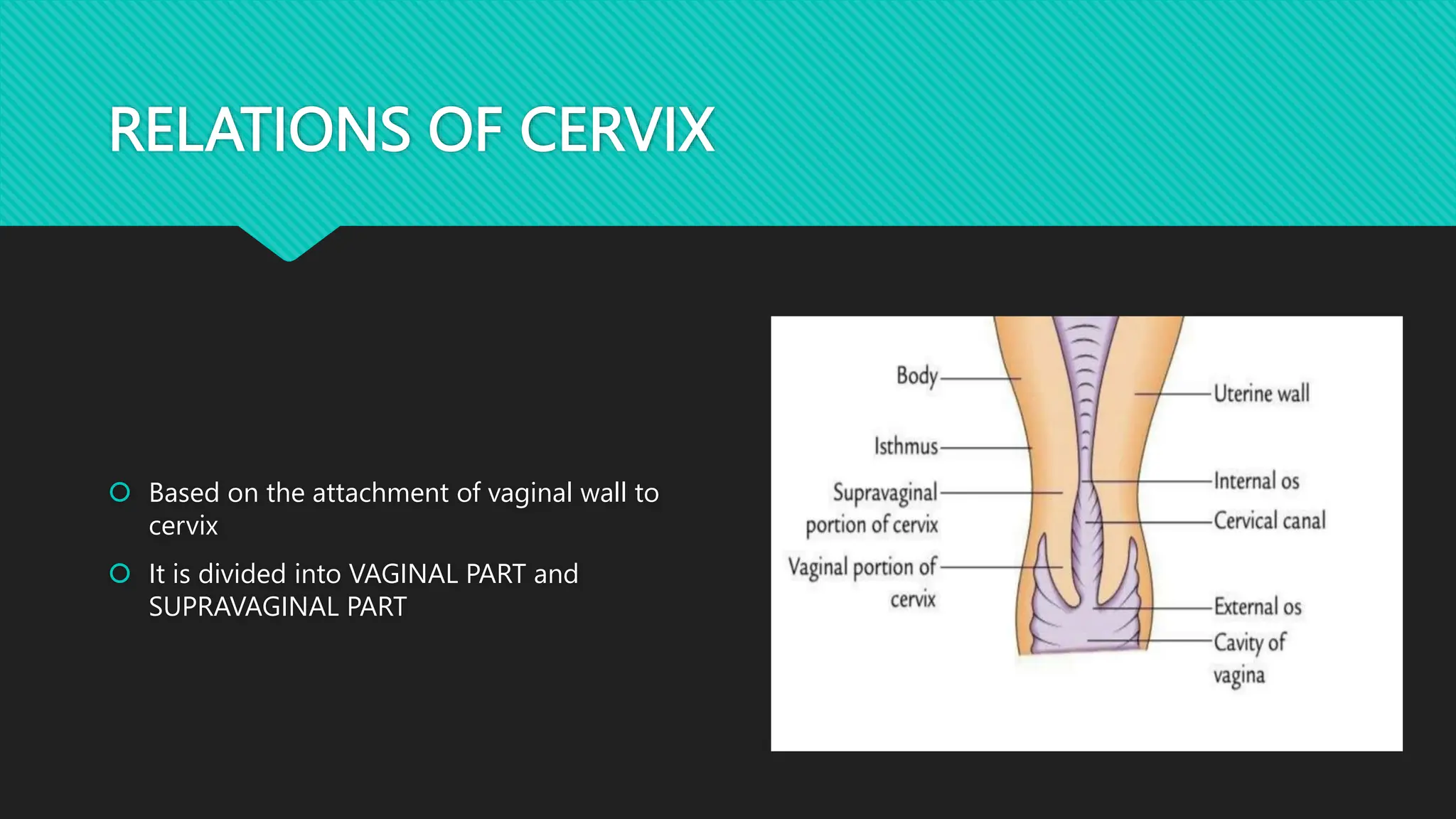
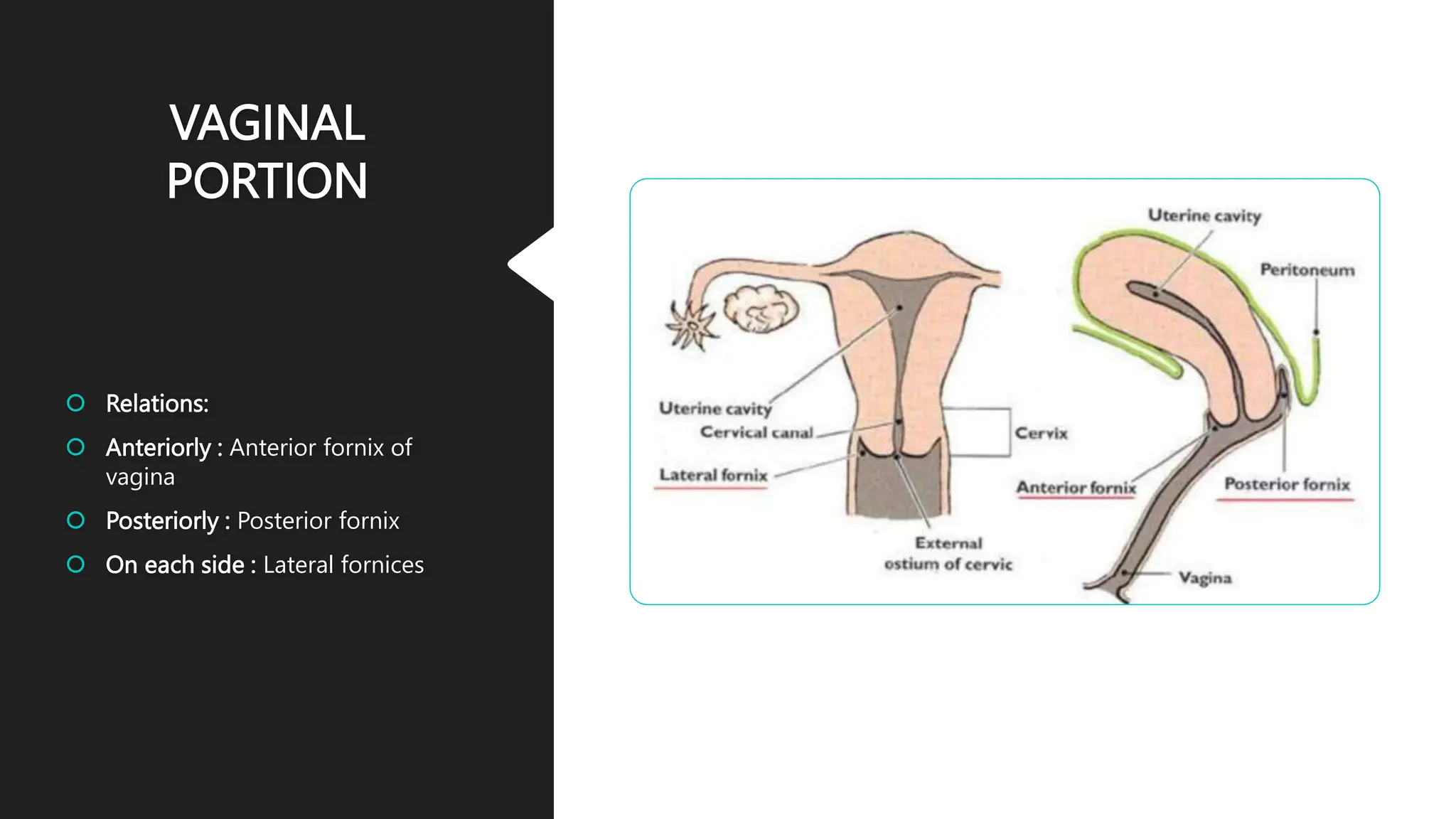
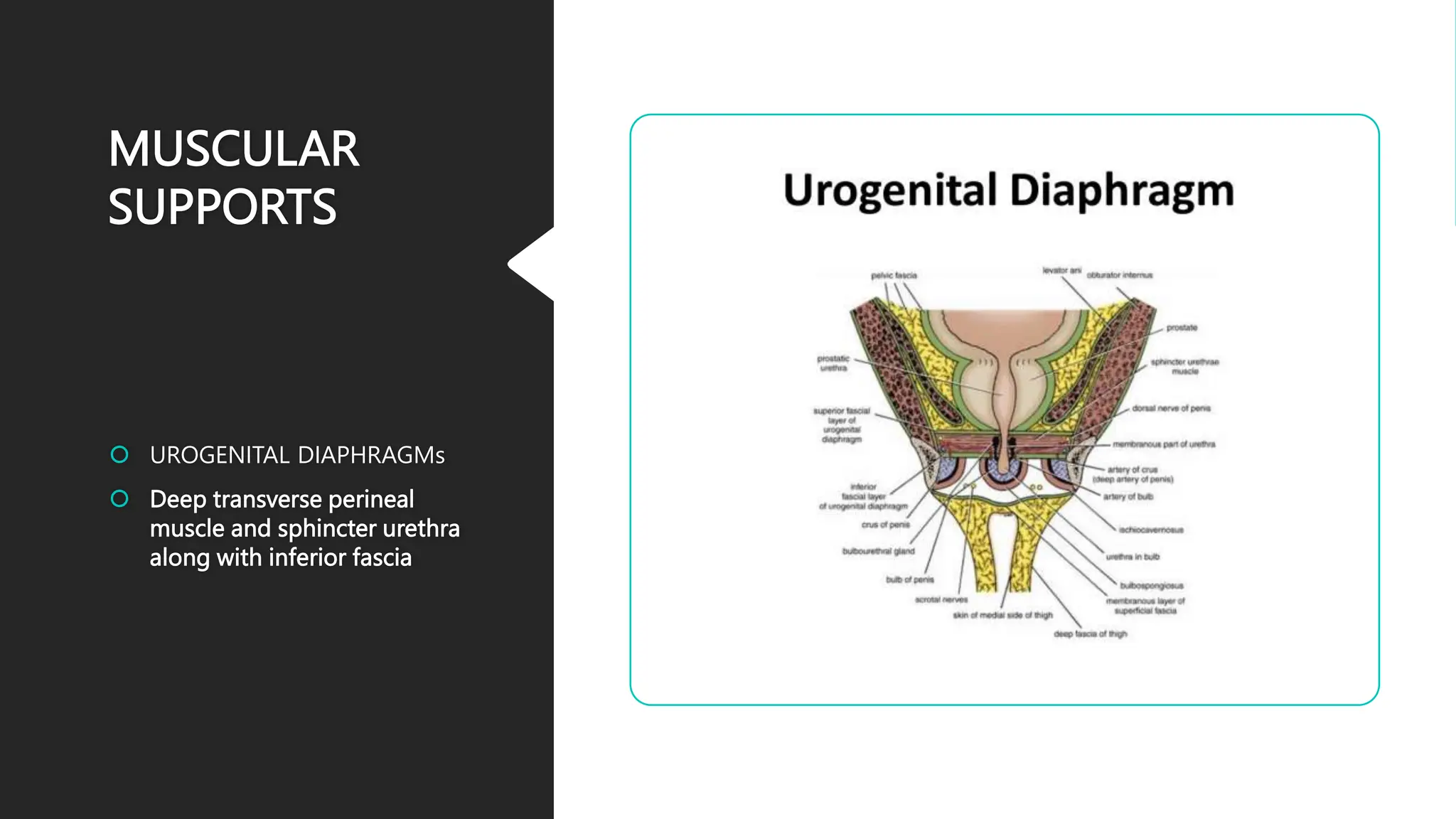
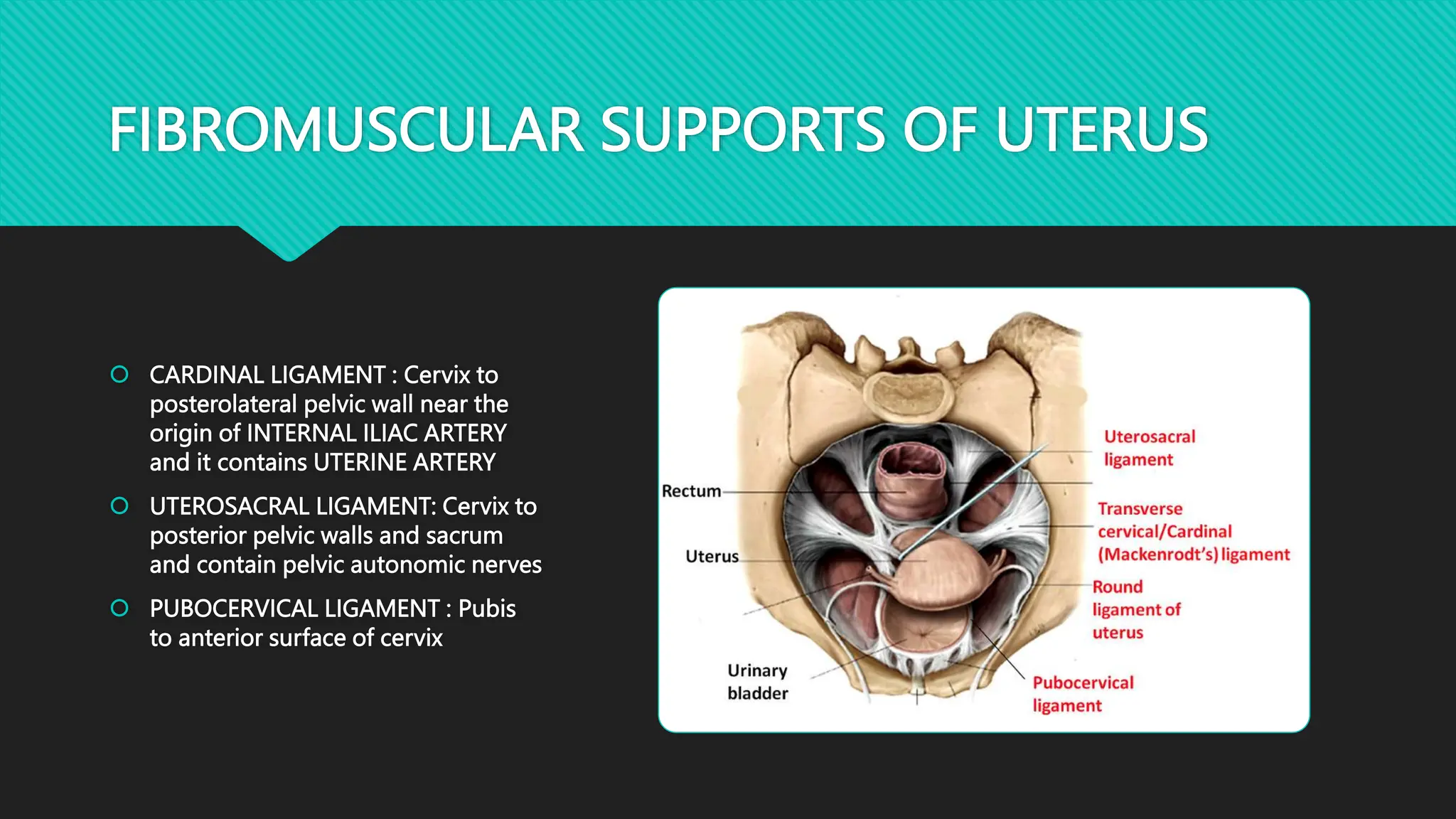
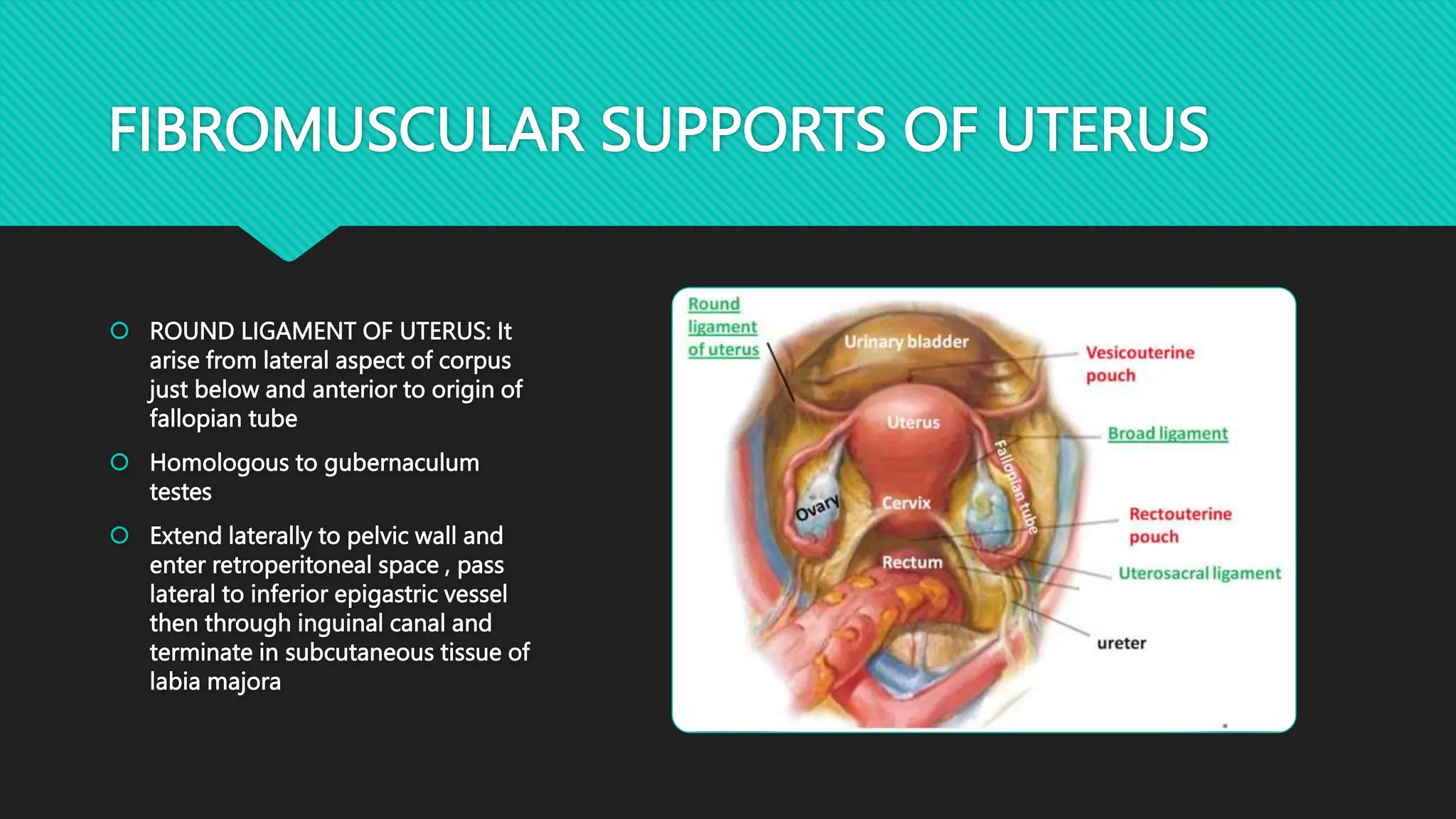
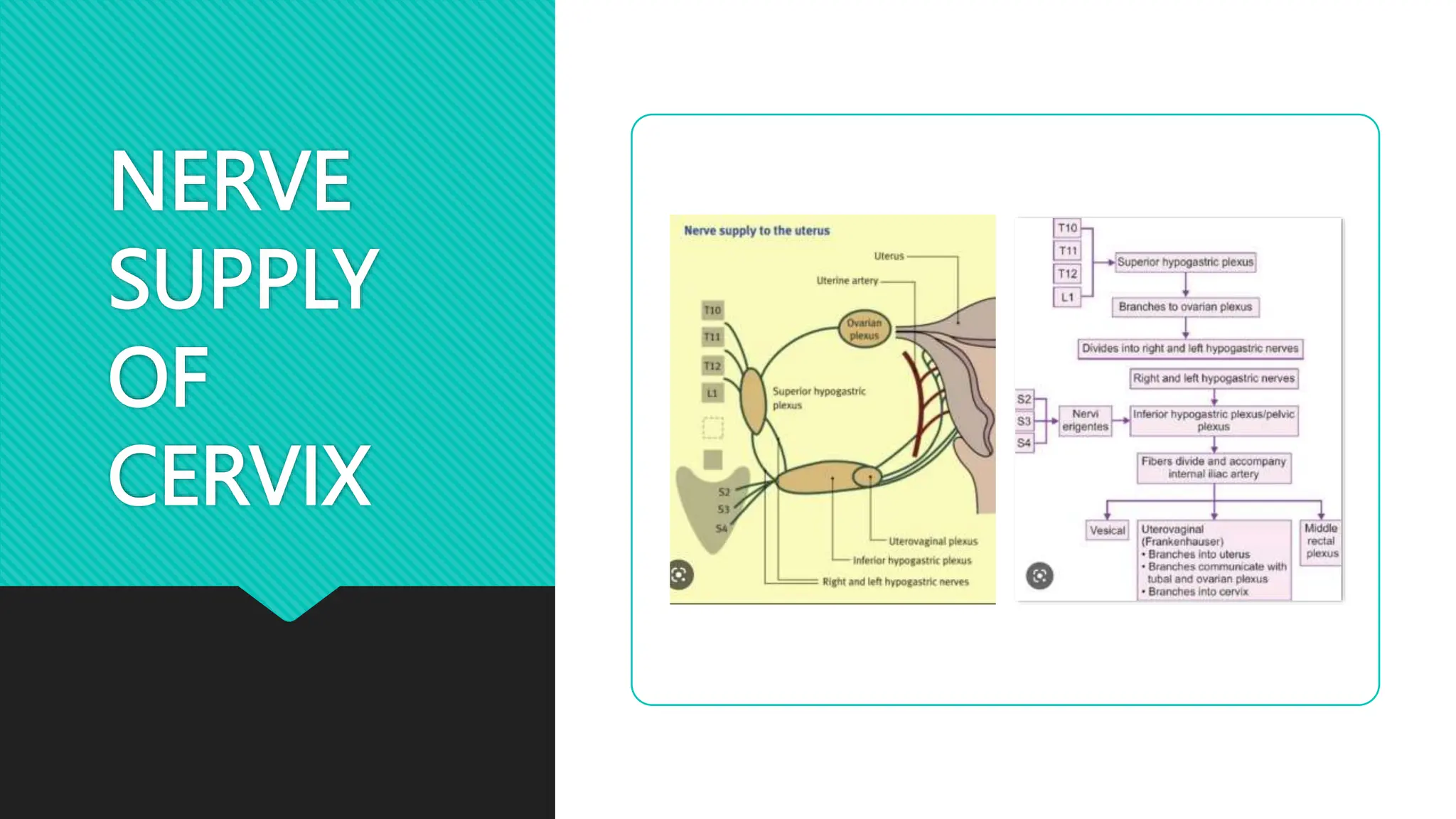
The document describes the anatomy of the cervix. It discusses that the cervix is the inferior part of the uterus that connects to the vagina. It has several parts including the internal os, external os, endocervical canal, and ectocervix. The squamocolumnar junction marks the transition between the endocervix lined with columnar epithelium and the ectocervix lined with squamous epithelium. The cervix has muscular, fibromuscular, and secondary supports that help support the uterus. It discusses the blood supply, nerve supply, and lymphatic drainage of the cervix.