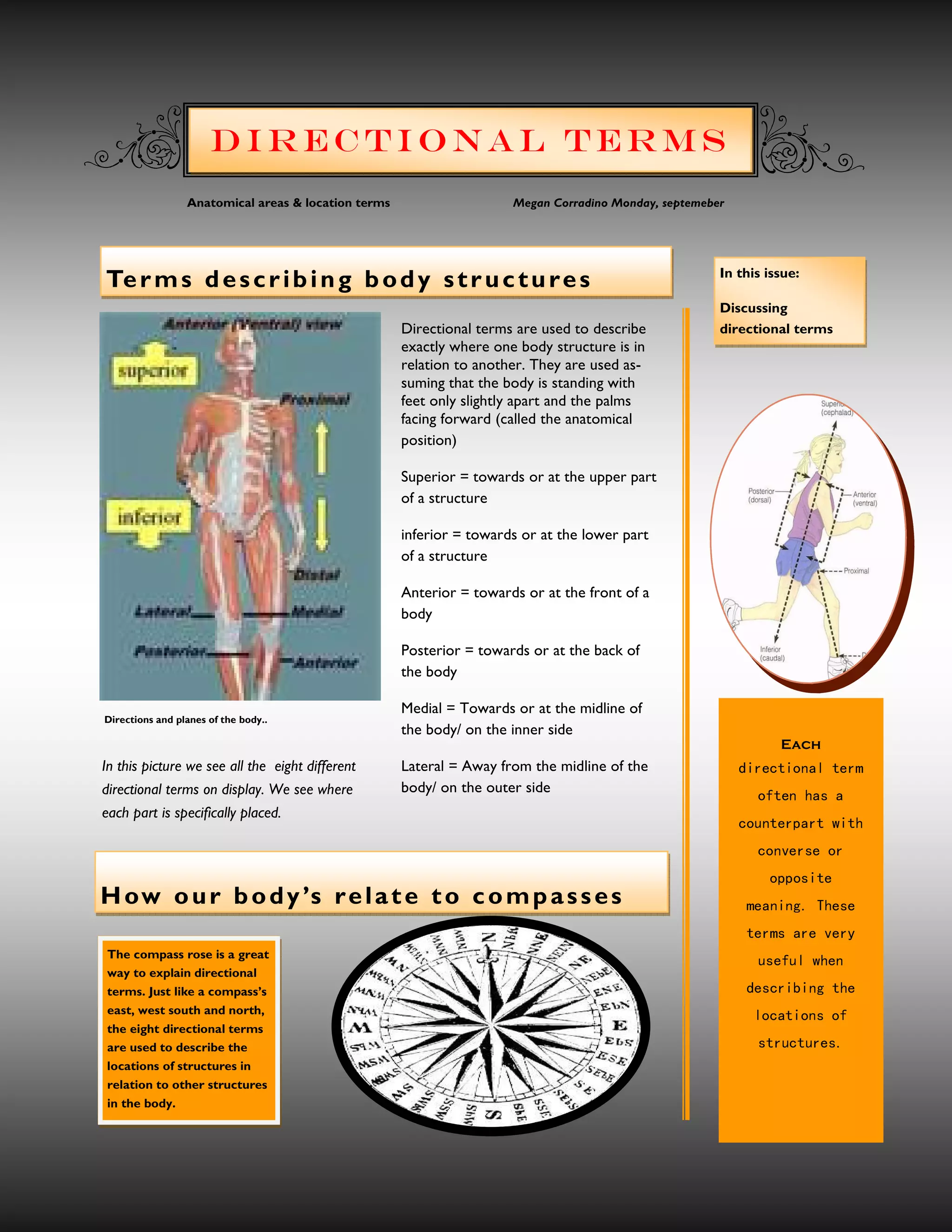
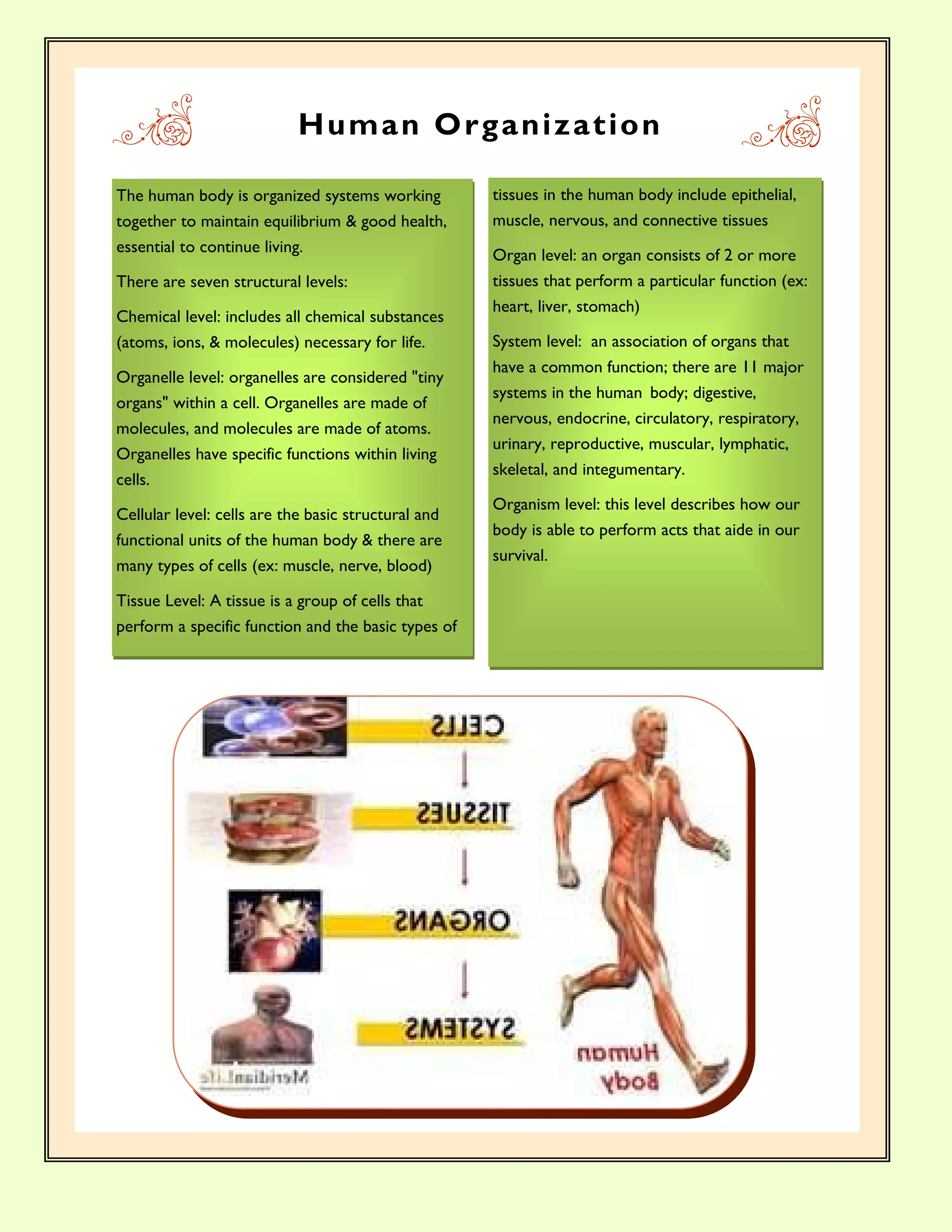
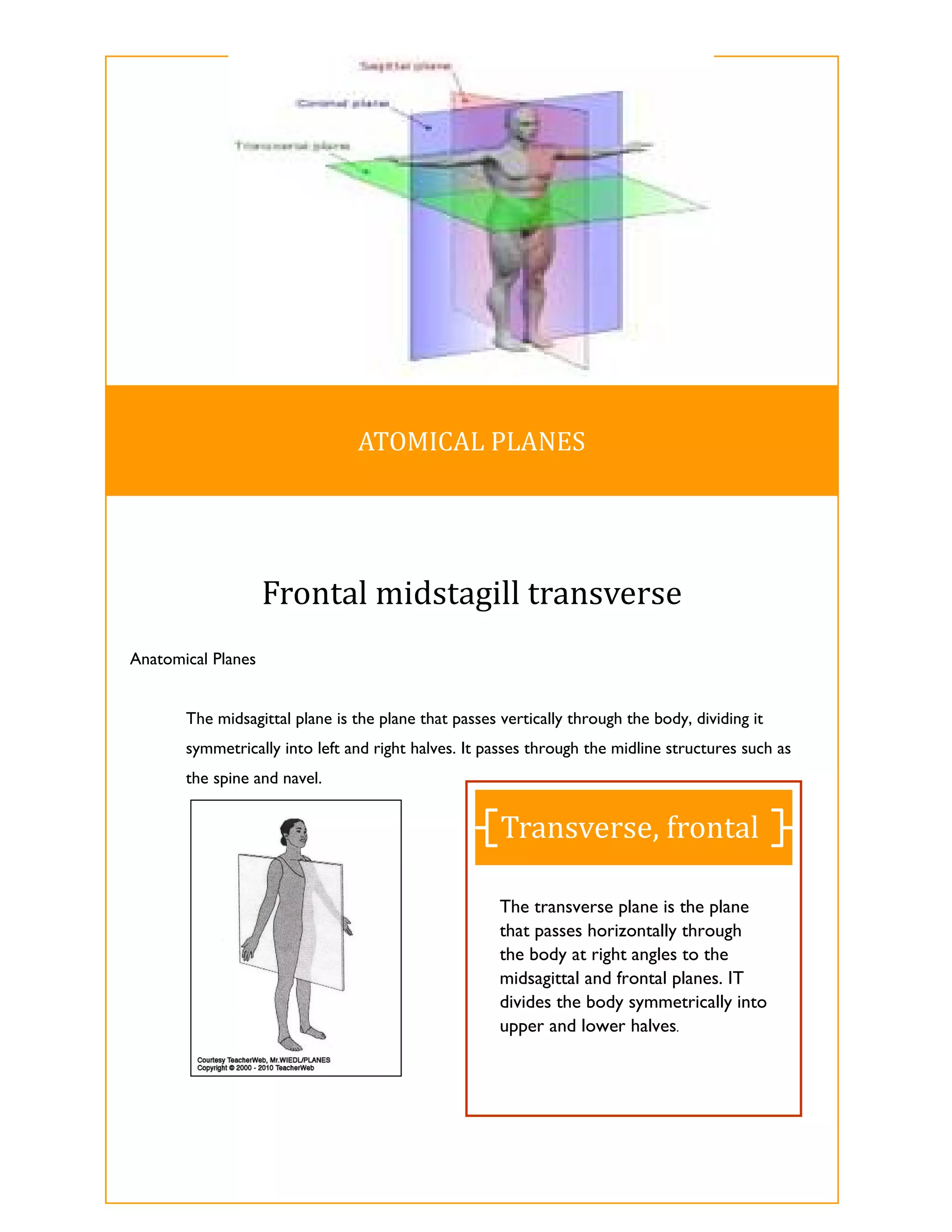
The document discusses directional terms used to describe locations in the body. It states that directional terms describe one body structure's position relative to another, assuming the anatomical position. Superior means towards the upper part, inferior means towards the lower part, anterior means towards the front, posterior means towards the back, medial means towards the midline, and lateral means away from the midline. It provides an image showing examples of the different terms.