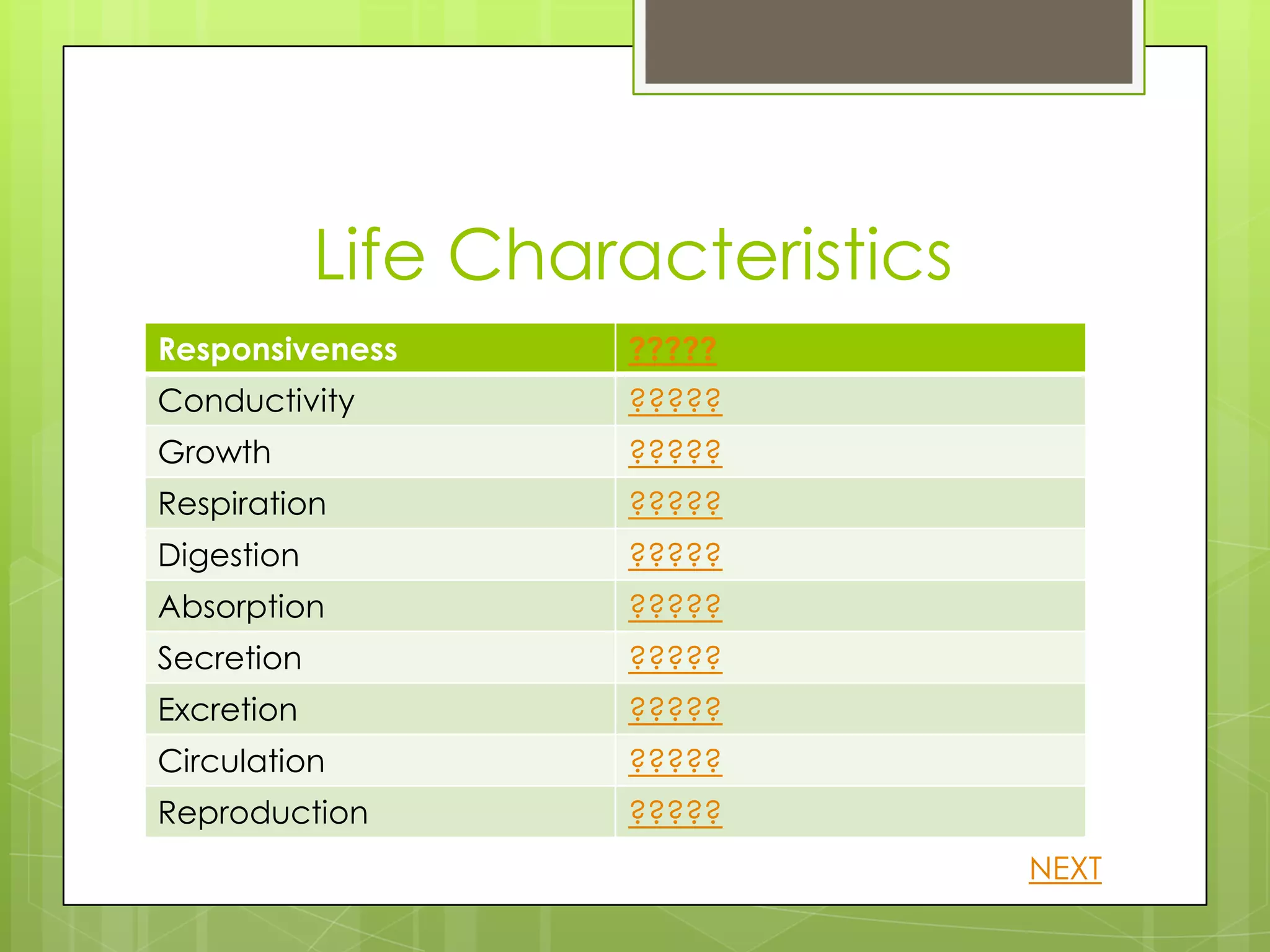
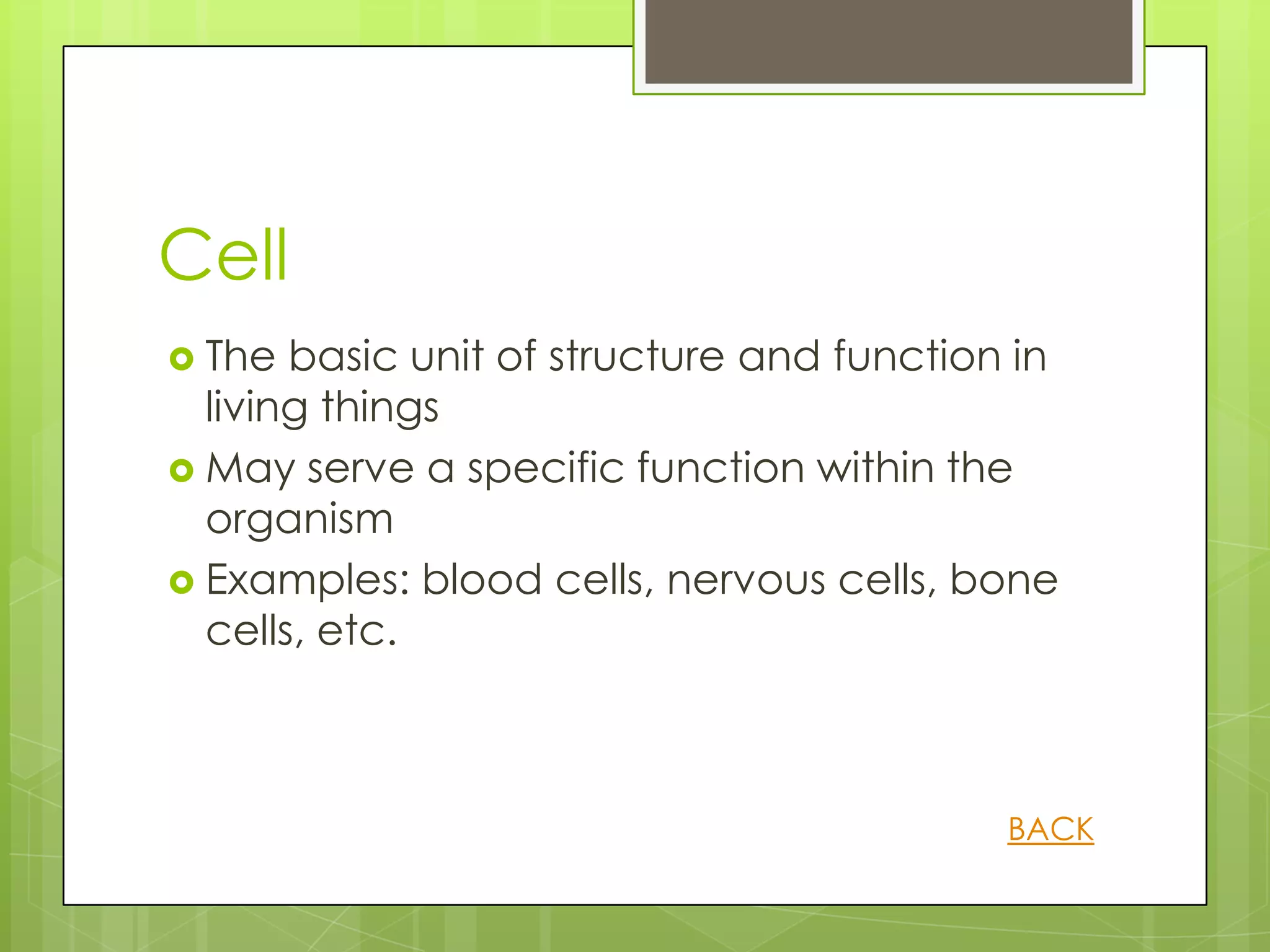
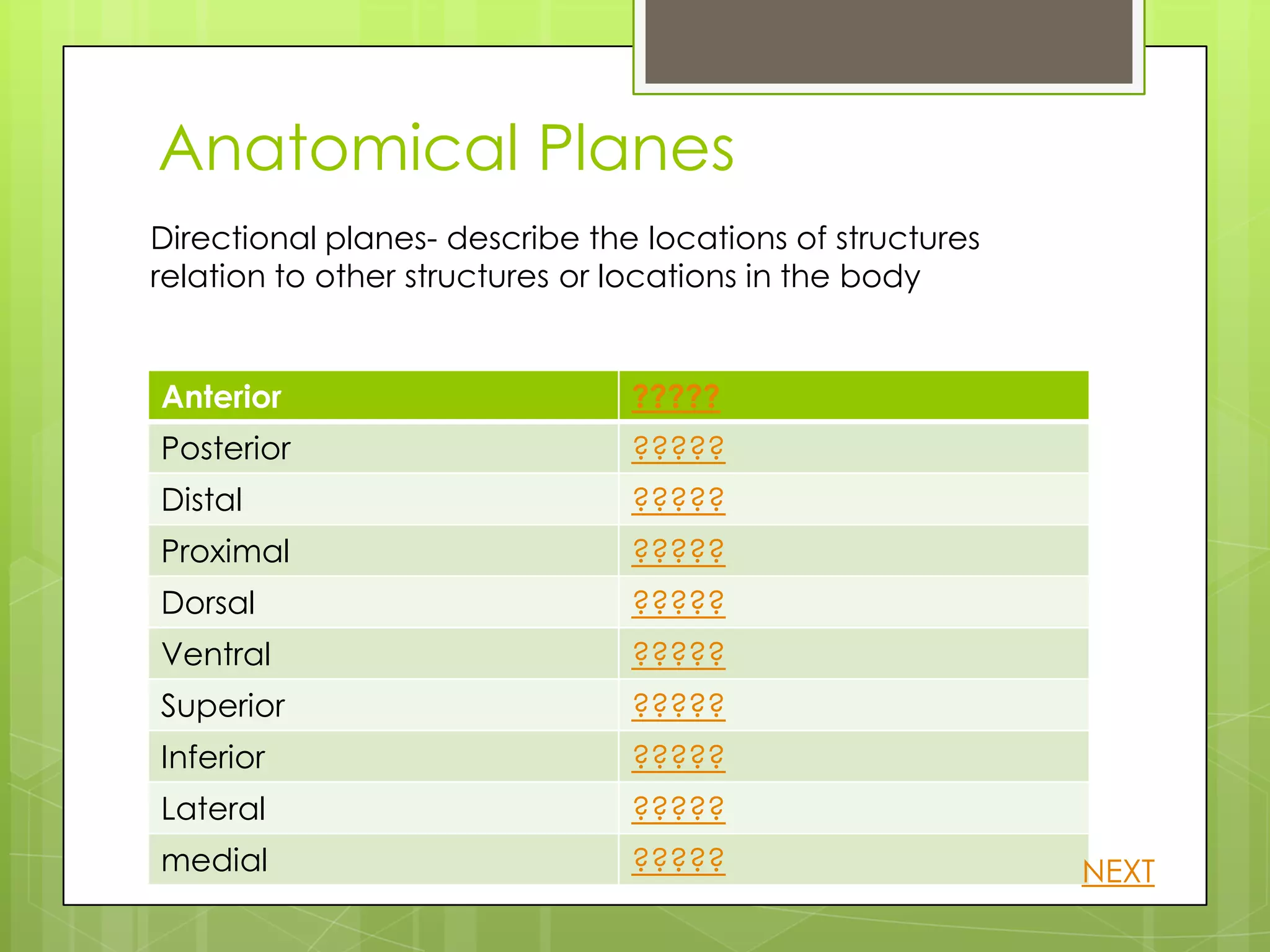
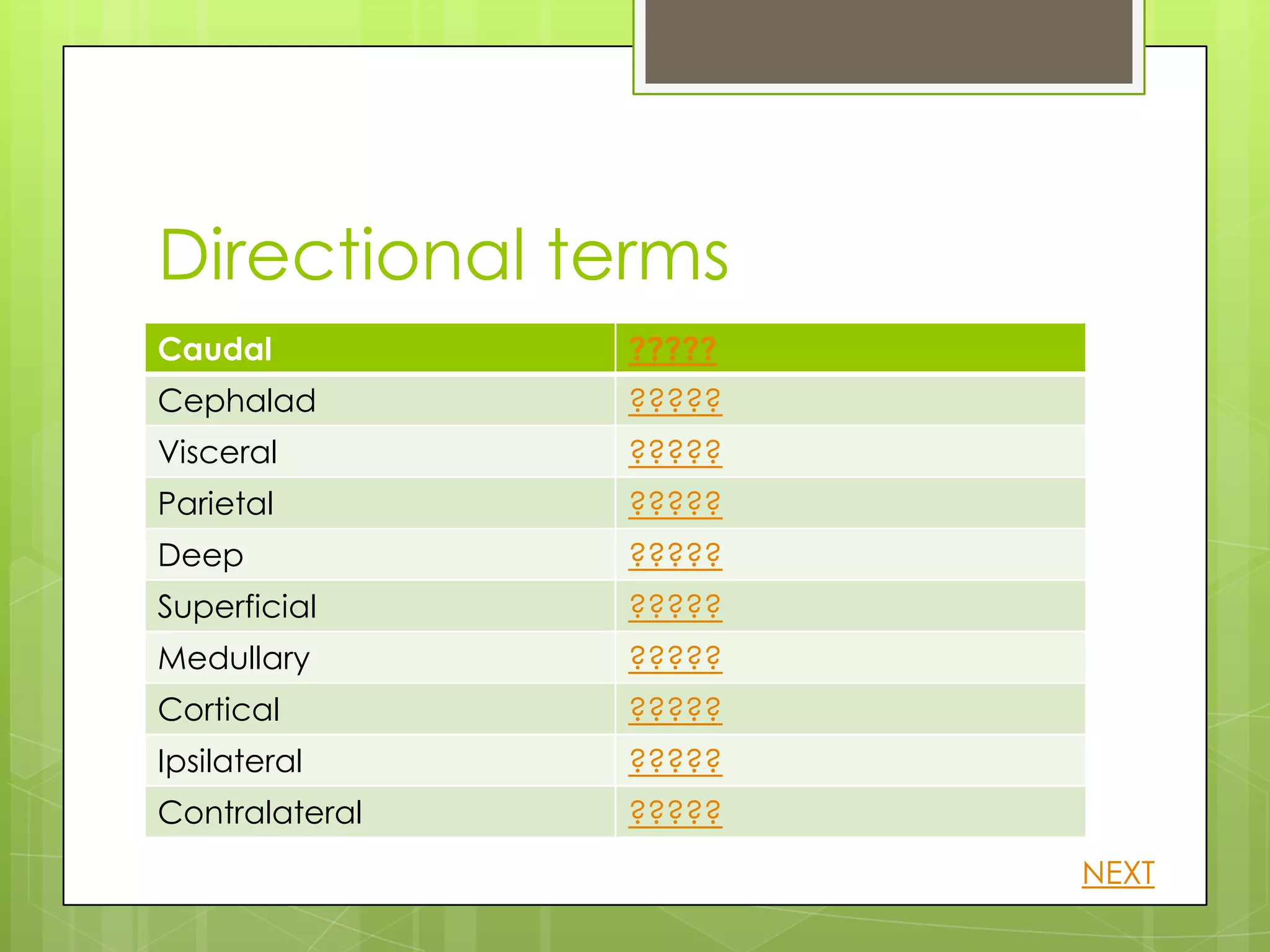
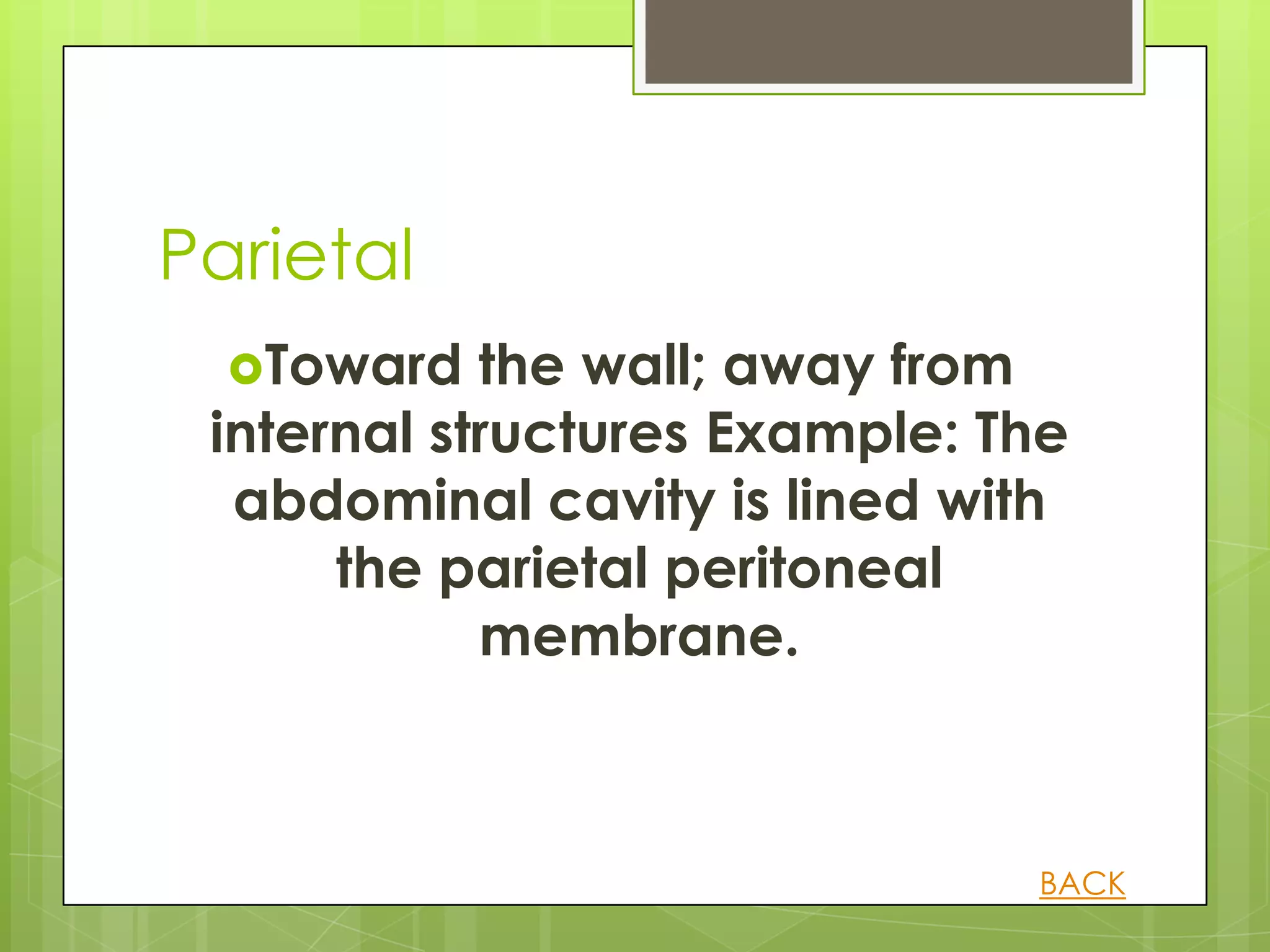
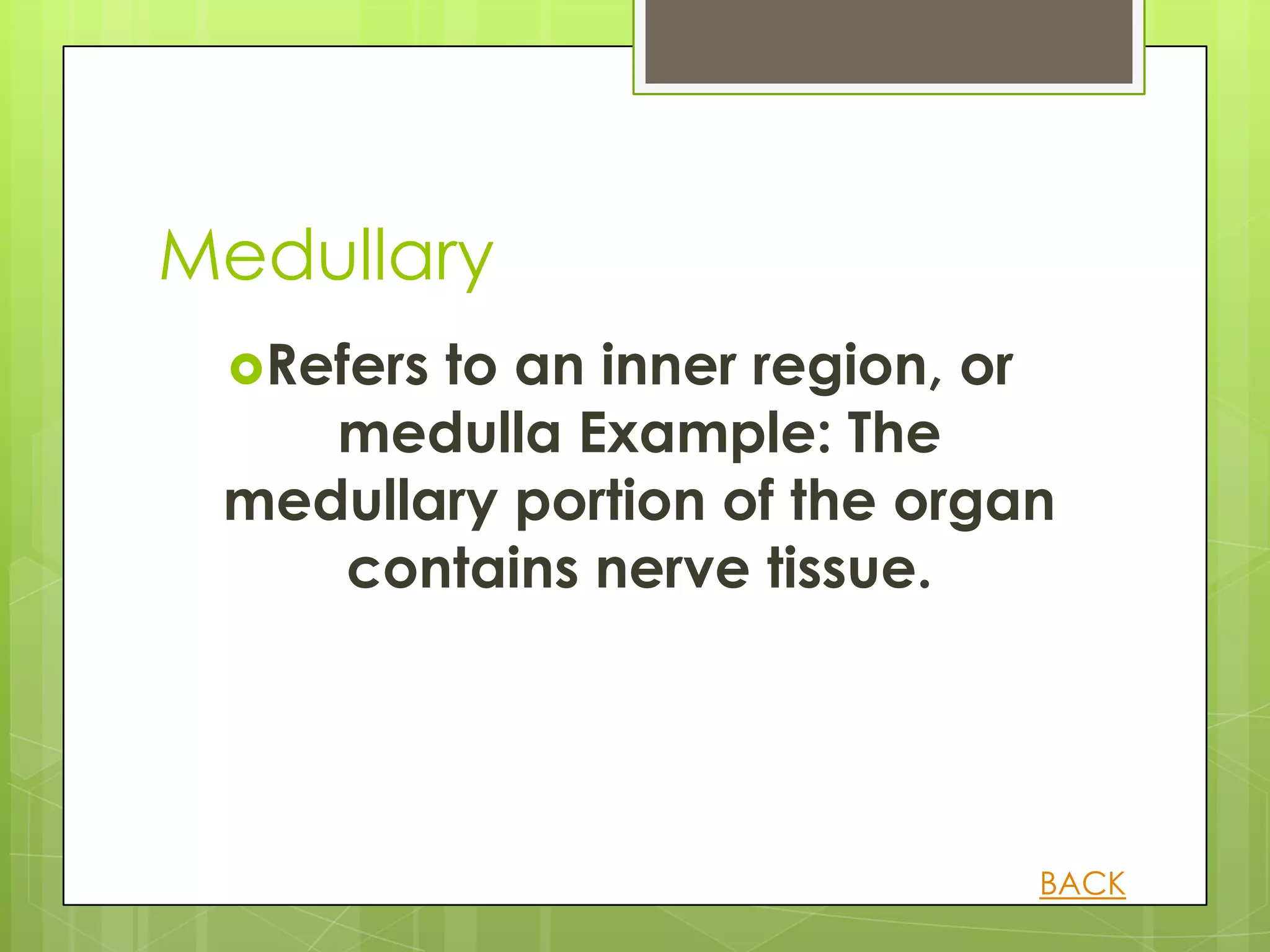
This document provides information about human anatomy and physiology organized into different sections and topics. It begins with an introduction and overview of the structure and function of key body systems like anatomy, physiology and characteristics of living things. It then covers organizational levels like cells, tissues, organs and organ systems. Other sections define anatomical planes and directions, key body structures, and homeostasis. The learner can click through topics that are revealed by question marks to learn definitions and examples in a self-paced manner.