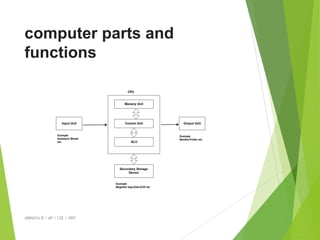
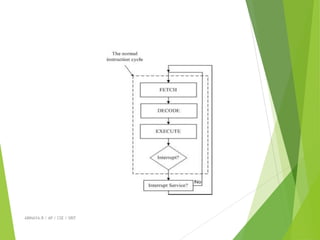
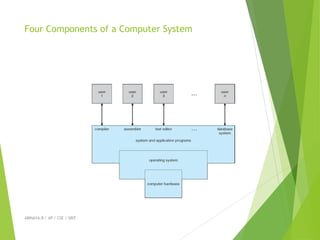
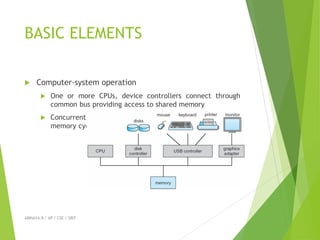
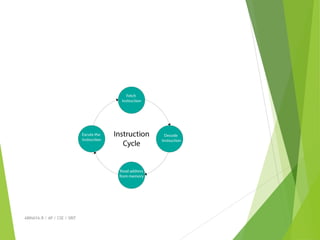
The document provides an overview of operating systems, detailing their functions, components, and the underlying principles of computer systems. It explains the role of operating systems as intermediaries between users and hardware, highlighting elements such as input/output devices, memory, and processing units. Additionally, it covers system structures, instruction execution, and the necessity of operating systems for efficient computer operation.