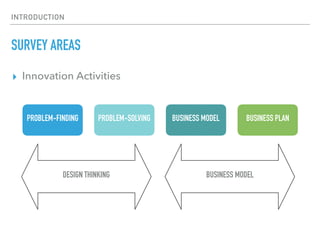
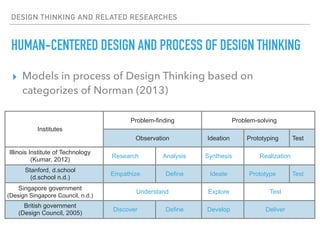
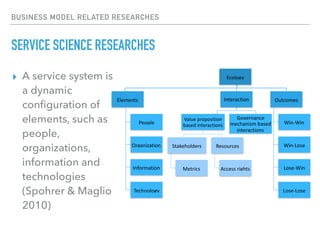
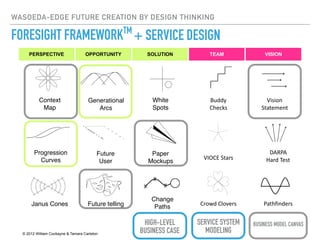
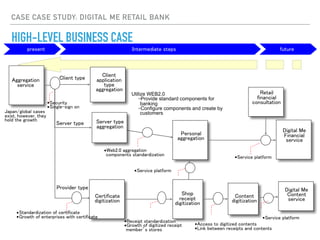
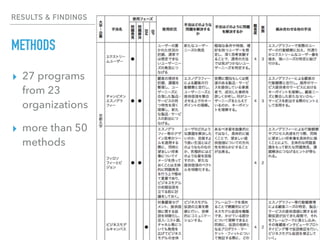
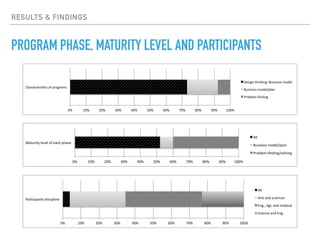
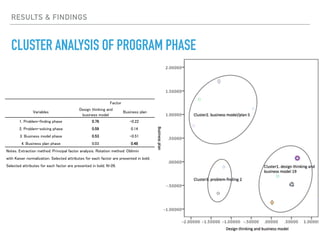
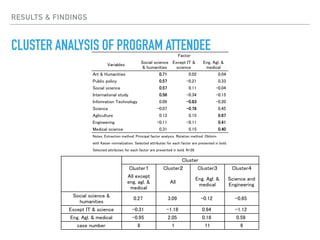
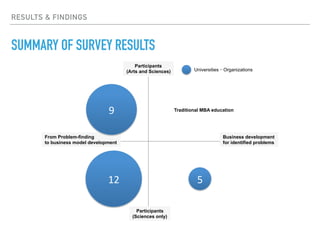
This document summarizes a survey of innovation creation methodologies used in various university programs in Japan. The survey found that most programs focused on design thinking and business modeling and included students from a variety of disciplines. Analysis of the programs identified three clusters: those focused on business development after problem identification; those taking problems through to business models; and some resembling traditional MBA programs. The results provide insight into common approaches and how programs are addressing different phases of the innovation process.