The document presents a comparative analysis of security in Windows and Linux operating systems, highlighting vulnerabilities in both, especially in login processes and program execution. It discusses existing solutions and emphasizes the lack of comprehensive comparisons in prior research, offering a proposed framework that addresses various security aspects in both systems. Future work is suggested to focus on memory management and kernel security vulnerabilities.




![Existing recent solutions
Research has been done previously on different standalone
features but not as a comparison point of view.
Stacey Quandt has a great article on the same at linux.com but
lacks a depth comparison.
Topic covered include patch management, logging, authentication,
protocols used, acl etc.
A research paper “WINDOWS AND LINUX OPERATING
SYSTEMS
FROM A SECURITY PERSPECTIVE” [link] by Youssef Bassil is
also a great read.
http://tinyurl.com/security1o1 December 2017 5 / 17Analysis windows and Linux](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/project-180426110350/85/Analysis-and-Exploiting-Windows-and-Linux-Security-5-320.jpg)




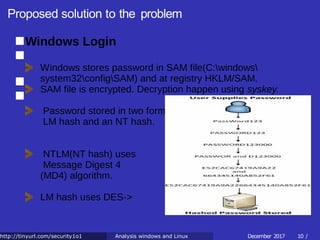



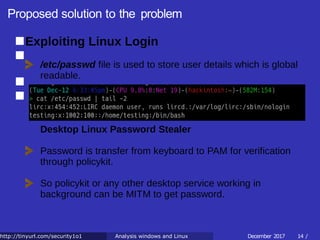
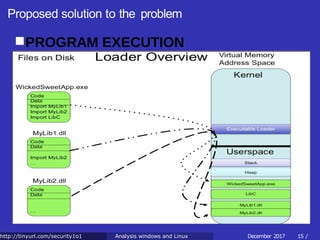

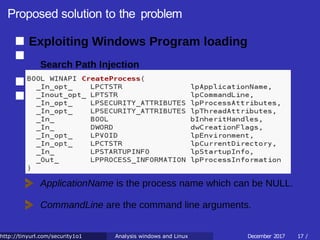

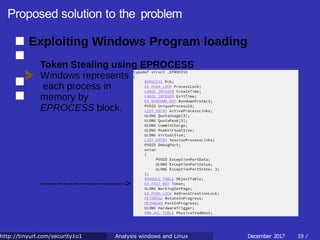
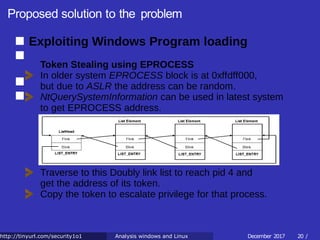


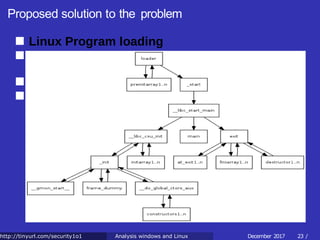

![Proposed solution to the problem
http://tinyurl.com/security1o1 December 2017 25 /Analysis windows and Linux
Exploiting Linux Program loading
Buffer overflow using environment variable
Program can be exploited by overflowing buffer[10]
and replacing return address with shellcode address.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/project-180426110350/85/Analysis-and-Exploiting-Windows-and-Linux-Security-25-320.jpg)


