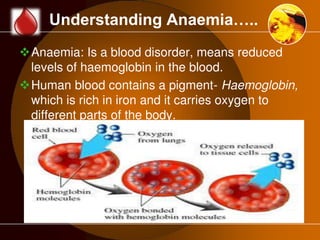
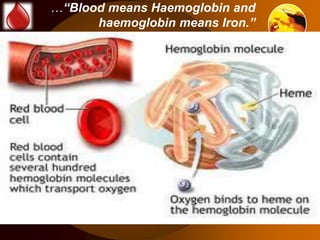
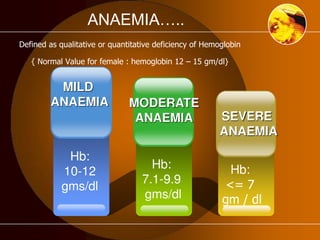
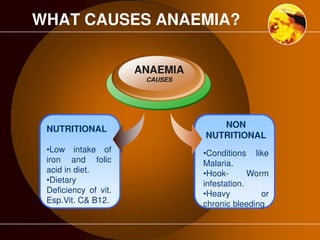
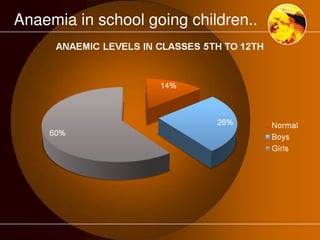
The document discusses anaemia, a public health issue in India characterized by low hemoglobin levels due to iron deficiency and poor nutrition. It highlights the importance of iron in maintaining health, particularly for adolescents, and emphasizes prevention strategies such as dietary improvements and iron supplementation. The role of teachers in monitoring and promoting health practices among adolescents is also outlined, alongside the need for early identification and referral to health facilities for affected individuals.