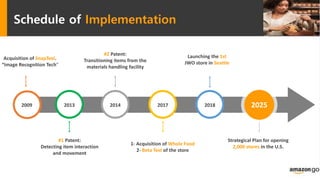
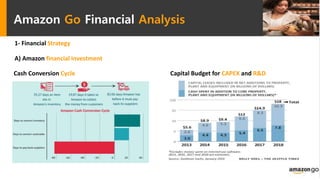
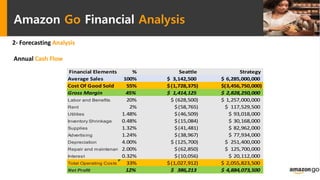
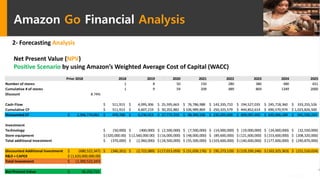
Amazon Go is a new concept store from Amazon that uses sensor fusion, computer vision, and deep learning algorithms to allow customers to shop and walk out without stopping to pay. The technology aims to reduce operating costs for retailers. A feasibility study found that while the technology provides benefits like increased profit margins and customer data collection, there are also risks like high implementation costs, regulatory issues from job losses, and competitive responses. The study recommends Amazon pursue both developing its own store network while also licensing the technology to non-competing retailers to generate additional revenue and reduce financial risks from the new store concept.