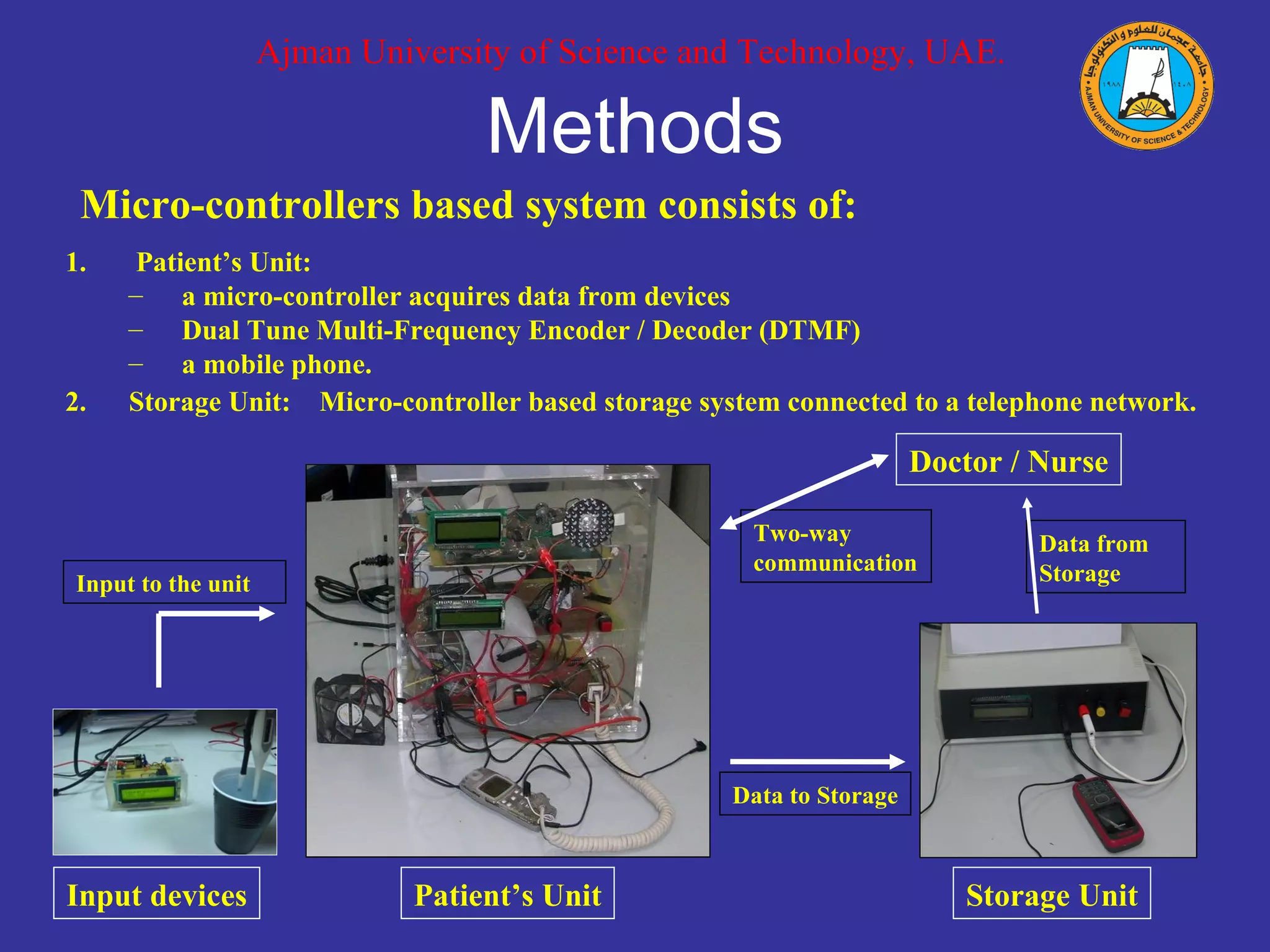
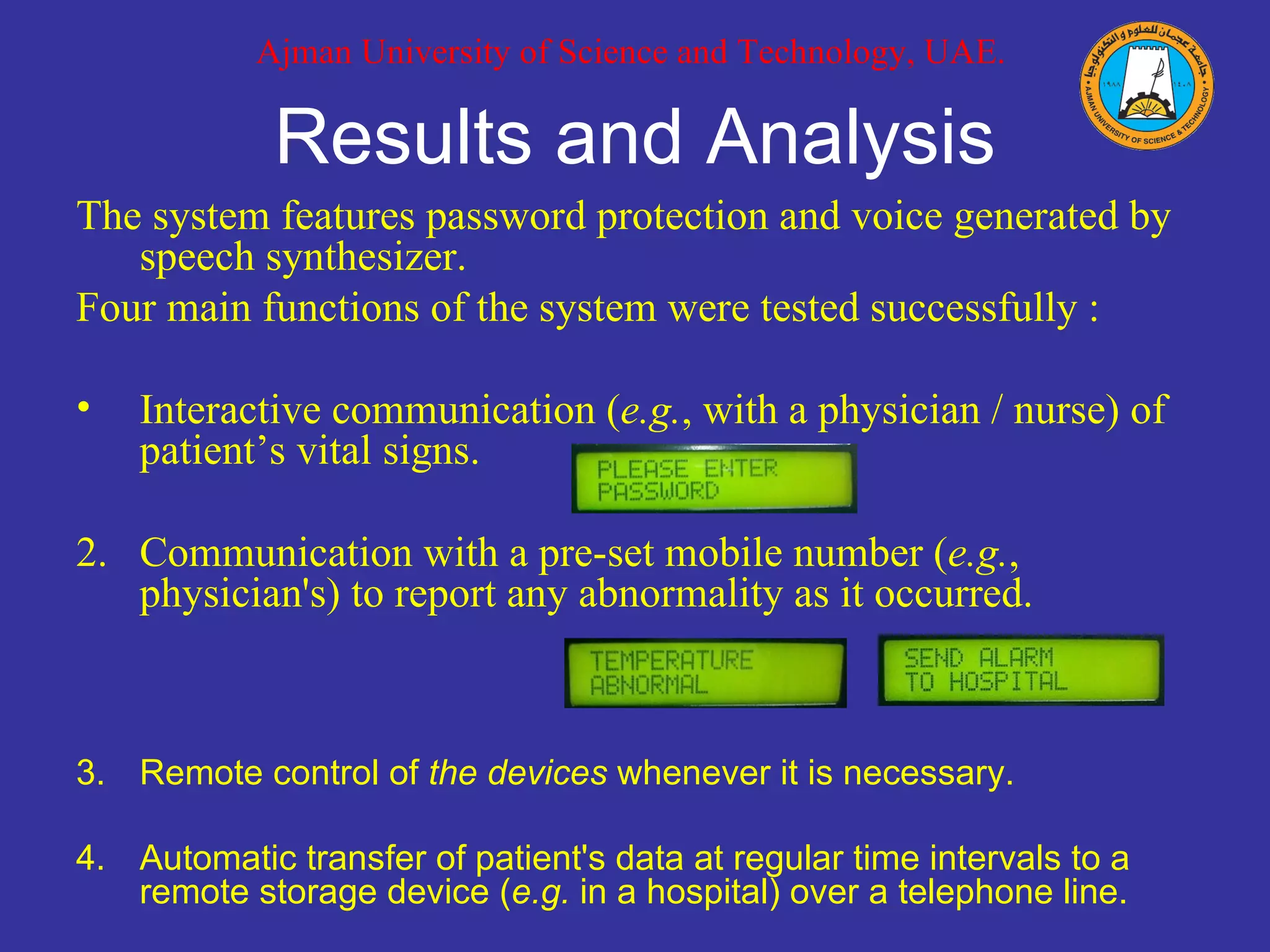
The document describes a mobile phone-based remote monitoring and control system for individualized healthcare presented at the AMA-IEEE Medical Technology Conference on Individualized Healthcare in 2010. The system uses microcontrollers and mobile phones to acquire patient vital sign data, store it, and allow two-way communication between patients and doctors/nurses. The system was tested successfully for interactive communication of vital signs, alerting doctors of abnormalities, remote control of devices, and automatic transfer of patient data to remote storage.