The document outlines several models and processes for group dynamics, change management, and personal development.
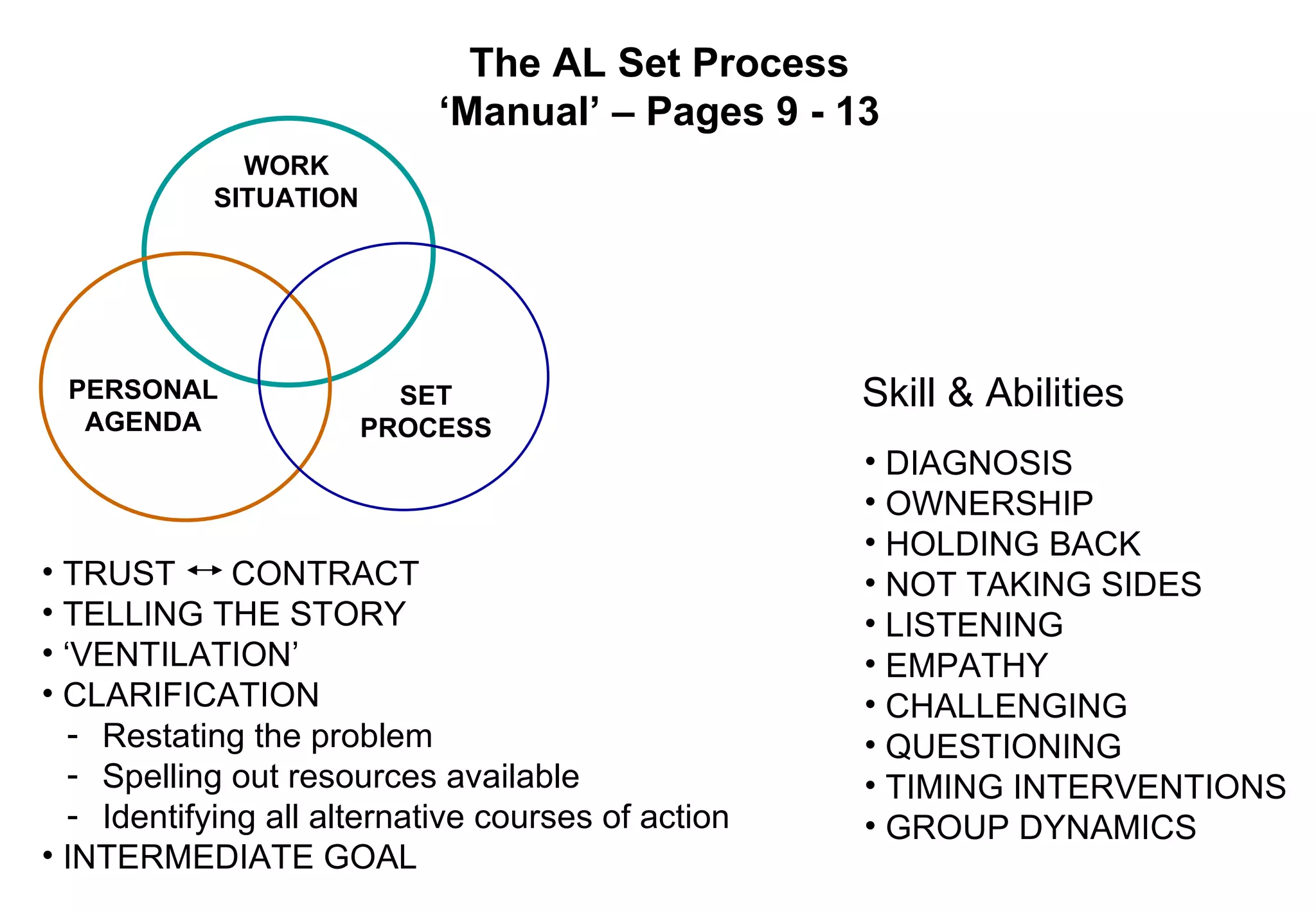
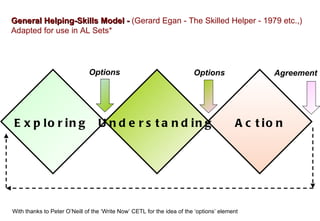
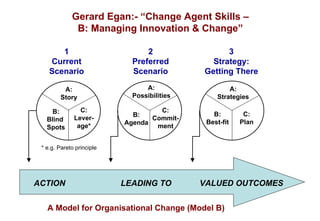
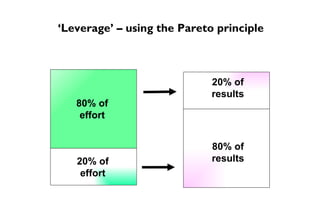
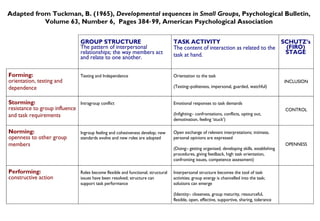
It includes models such as [1] the AL Set process for helping individuals work through problems, [2] Egan's helping skills model adapted for AL Sets, [3] Tuckman's model of group development that outlines the forming, storming, norming, and performing stages, and [4] a model for organizational change that outlines leveraging opportunities and developing strategies to create valued outcomes.
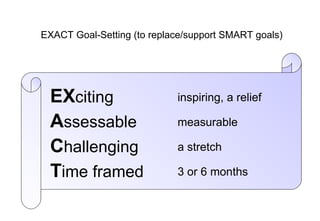
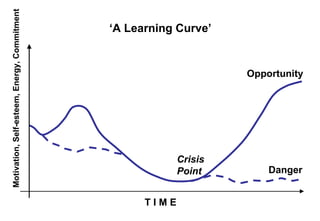
The document also discusses concepts like Schutz's stages of inclusion, control, and openness; Gerard Egan's model of identifying current/preferred scenarios and strategies for change; and representing motivation, self-