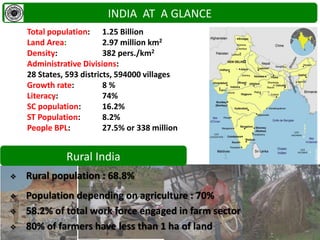
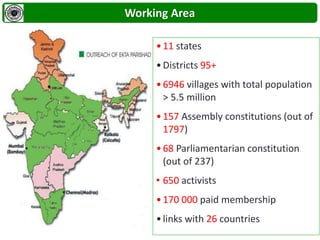
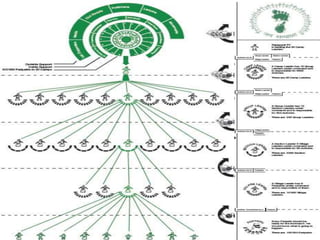
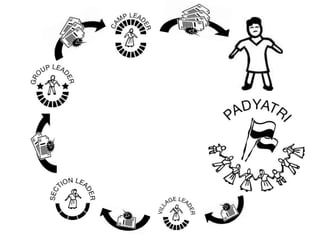
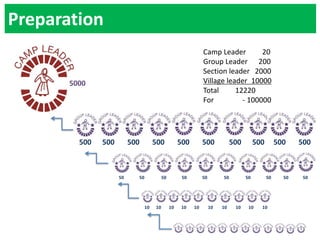
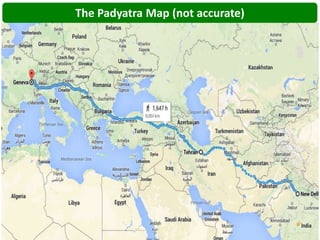
Ekta Parishad is a Gandhian organization dedicated to nonviolent action to help poor and marginalized people access natural resources like land, forests and water. It aims to mobilize 1 million people for a global march in 2020 to advocate for equitable and sustainable development, expand ethics in business and governance, and deepen social justice. Ekta Parishad conducts nonviolent training, foot marches, and advocacy campaigns to raise awareness of land rights issues, especially those facing rural farmers, women and tribal communities in India.