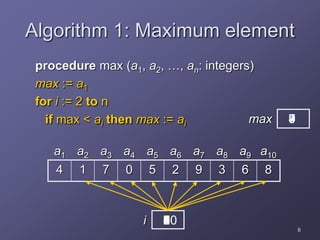
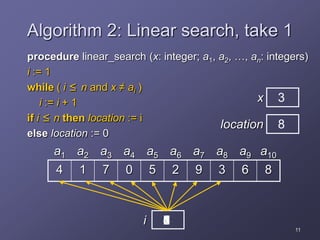
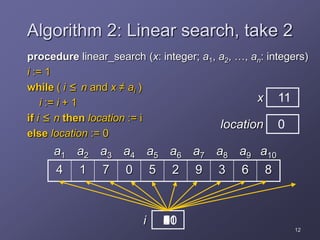
1. The document discusses several algorithms including those for finding the maximum element in a list, linear search, binary search, bubble sort, and insertion sort.
2. It provides pseudocode to describe each algorithm and analyzes their running times, finding that linear search takes n steps, binary search takes log2n steps, and bubble sort and insertion sort each take about n2 steps.
3. Faster sorting algorithms like heap sort, quick sort, and merge sort have running times of nlogn steps.