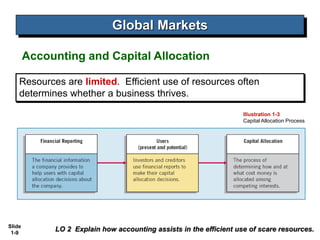
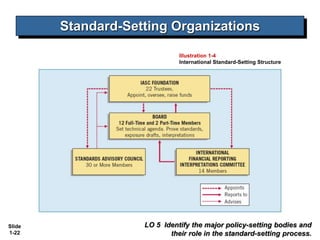
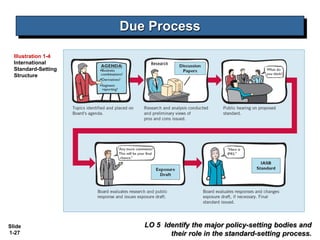
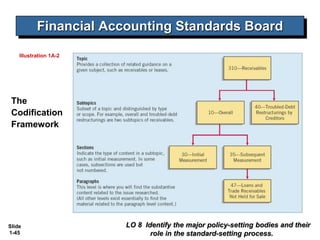
This document covers Chapter 1 of an intermediate accounting textbook. It introduces financial reporting and accounting standards. The chapter objectives are to identify major financial statements, explain how accounting assists resource allocation, explain the need for high-quality standards, identify financial reporting objectives, identify standard-setting bodies, explain IFRS, and describe challenges facing financial reporting. It discusses major financial statements, capital allocation, objectives of providing decision-useful information to capital providers, and roles of the IASB, FASB, and IOSCO in setting international standards. It also summarizes challenges like political influences, the expectations gap, and issues in international convergence.