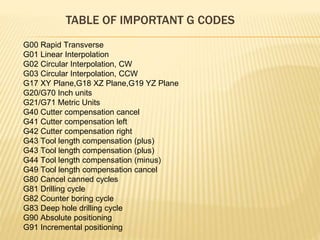
This document provides an overview of computer numerical control (CNC) machines. It discusses the history of NC machines dating back to the 1940s and the evolution of CNC machines with the development of computers in the 1980s. The key elements of a CNC machine are described, including the input device, machine control unit, machine tool, driving system, feedback devices, and display unit. The document explains how CNC machines work using G and M codes and provides examples of common G and M codes for different functions. Advantages of CNC machines are highlighted such as easier programming, storage of programs, changing programs, avoiding human errors, and safely producing complex geometries with close tolerances.