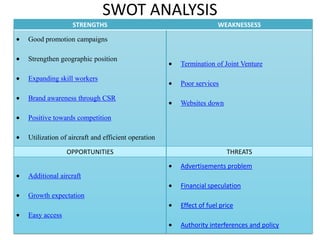
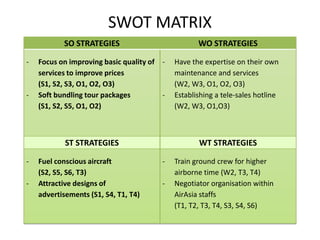
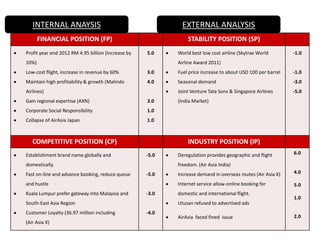
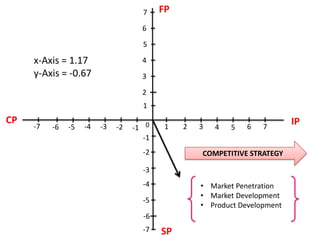
The document provides information on Air Asia's mission, vision, history, and analyses. Air Asia's mission is to be the best company to work for and create an ASEAN brand while attaining the lowest costs. Its vision is to be the largest low-cost airline in Asia. Air Asia was established in 1994 and faced debt issues in 2001. Analyses include PEST on political, economic, social and technological factors, SWOT on strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats, and SPACE on internal and external positioning. Recommendations focus on improving responsiveness, advertisements, passenger convenience and business expansion.