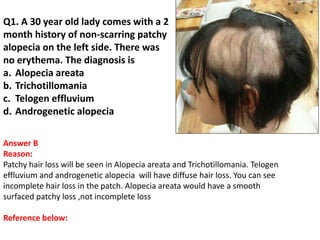
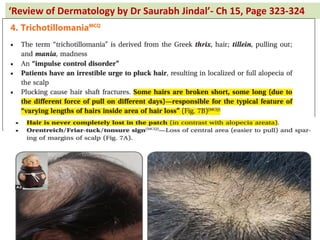
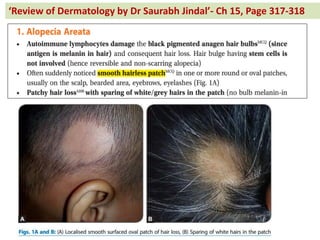
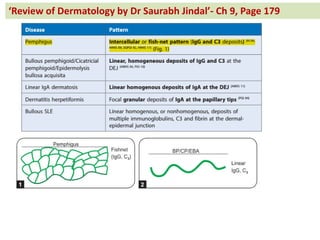
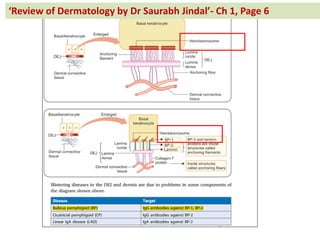
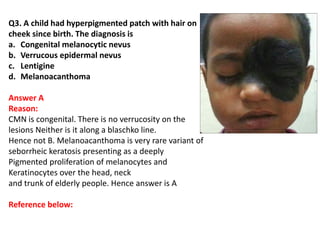
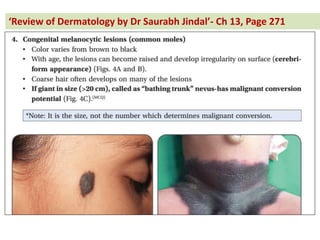
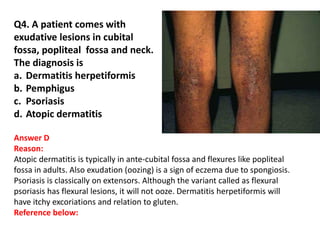
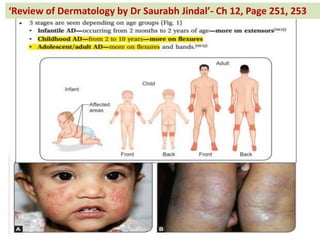
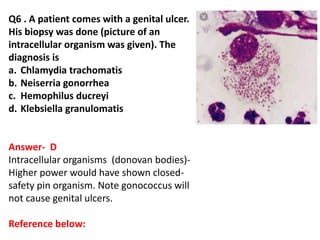
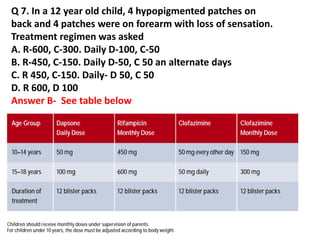
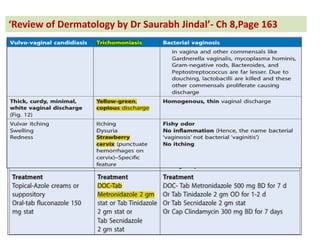
The document contains a series of dermatology multiple-choice questions (MCQs) with answers and explanations based on a reference book by Dr. Saurabh Jindal. These MCQs cover various skin conditions, diagnostic methods, and treatment regimens relevant to dermatology, as well as the underlying principles and reasoning for the provided answers. Each question highlights a specific clinical scenario, aiding in the understanding of dermatological diagnoses and management.