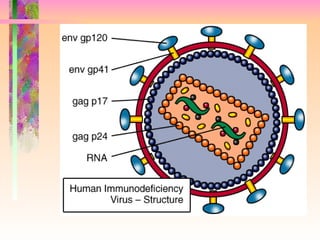
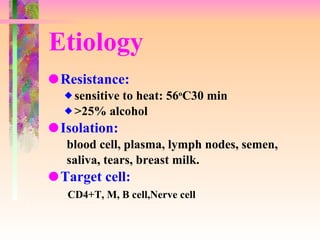
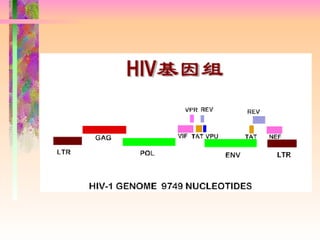
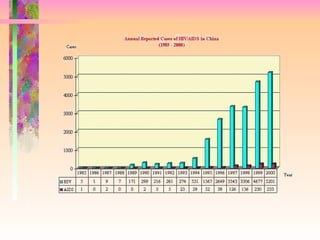
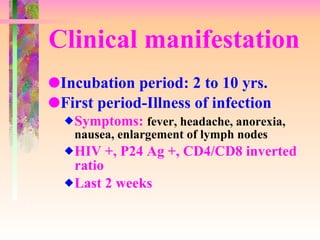
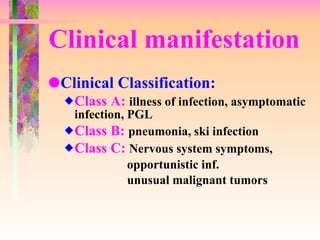
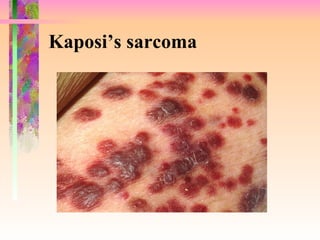
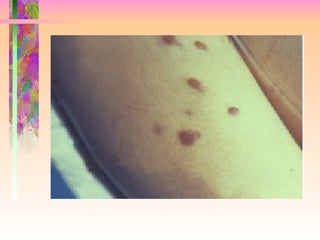
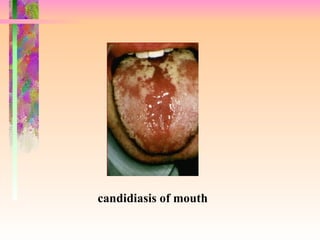
The document discusses AIDS/HIV, including its definition, etiology, epidemiology, pathogenesis, clinical manifestations, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention. It describes HIV's target cells (CD4+ T lymphocytes), its various stages from initial infection to AIDS, common opportunistic infections associated with AIDS like Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia treated with pentamidine, and combination antiretroviral therapy.