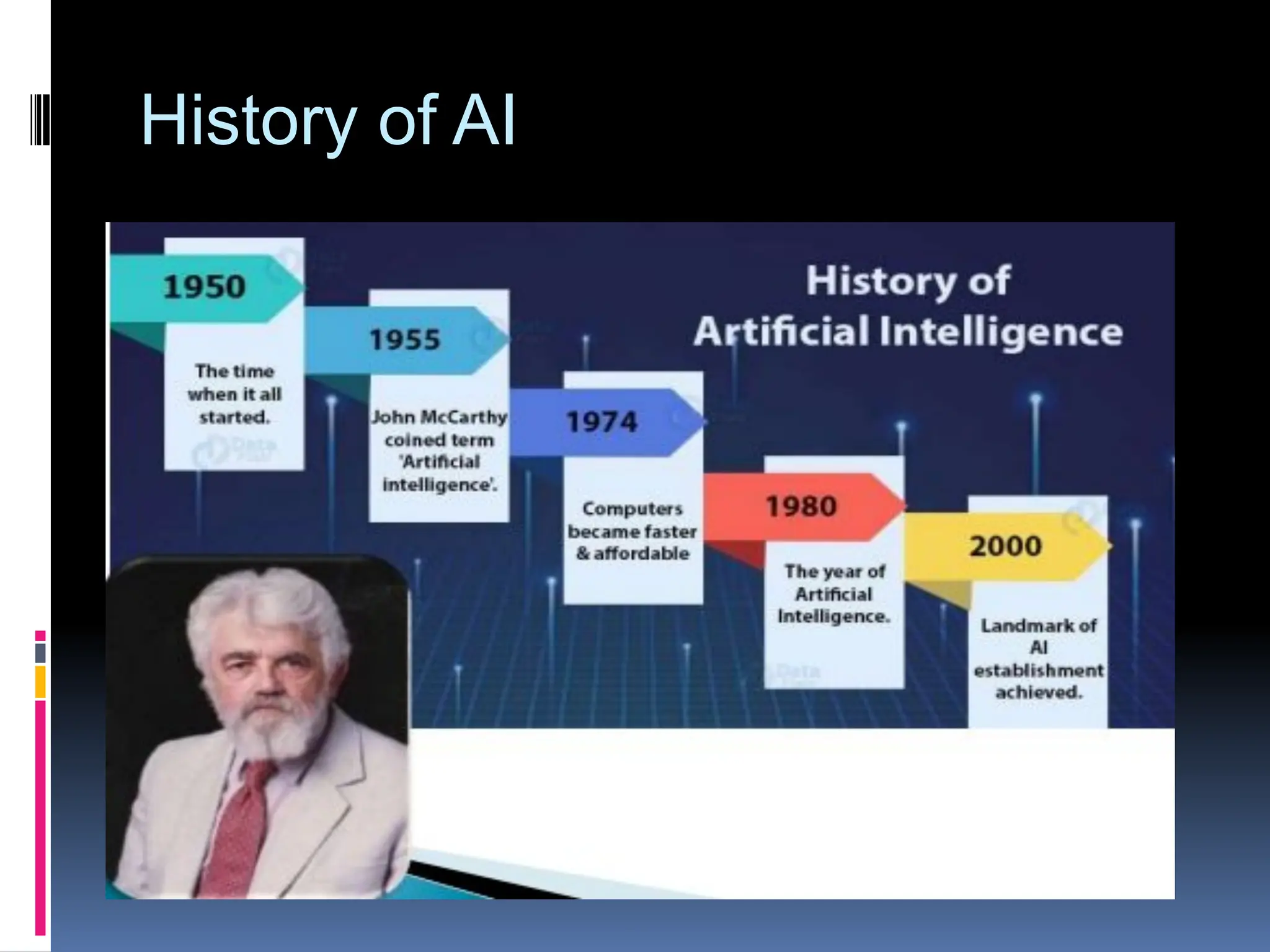
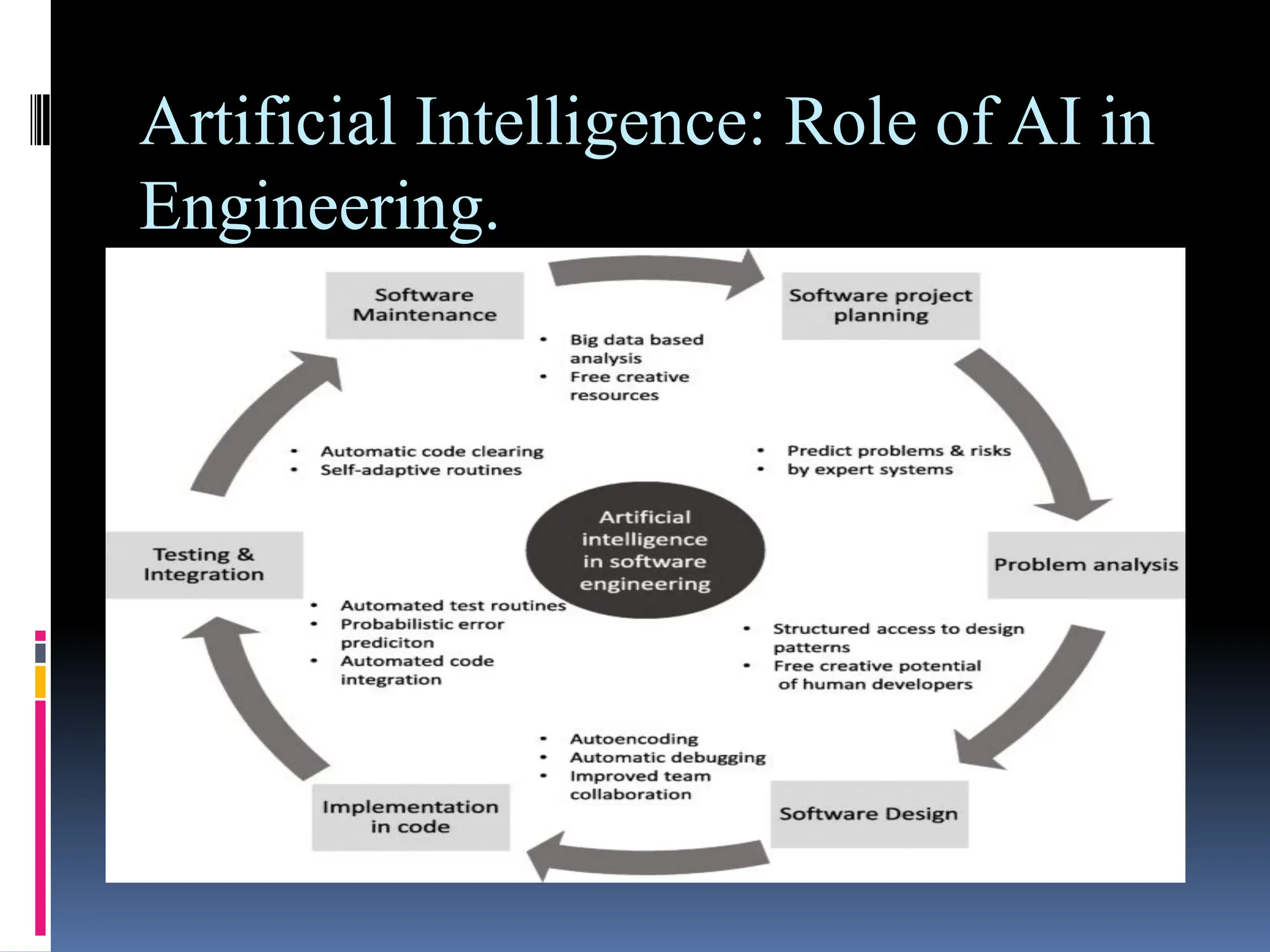
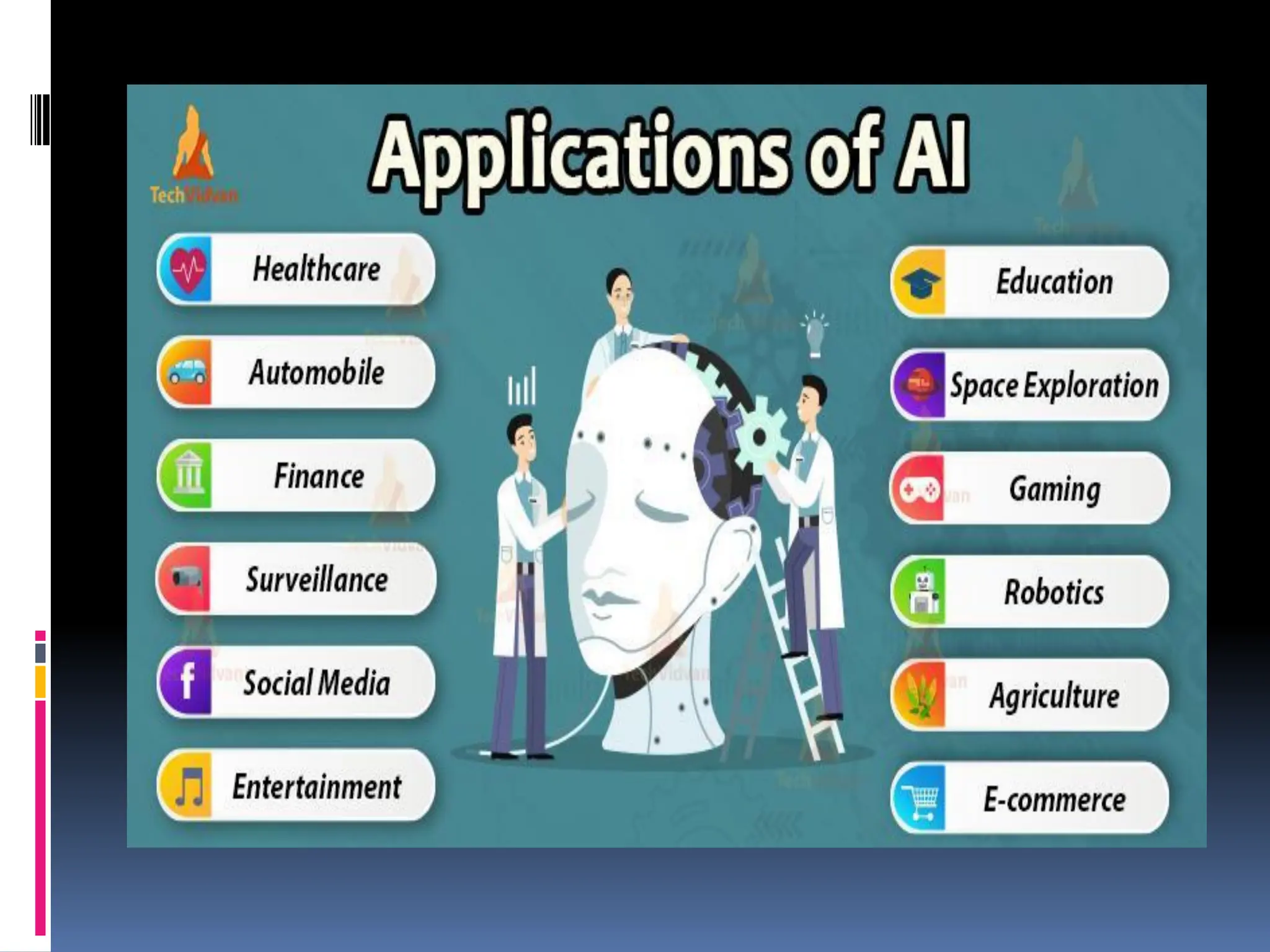
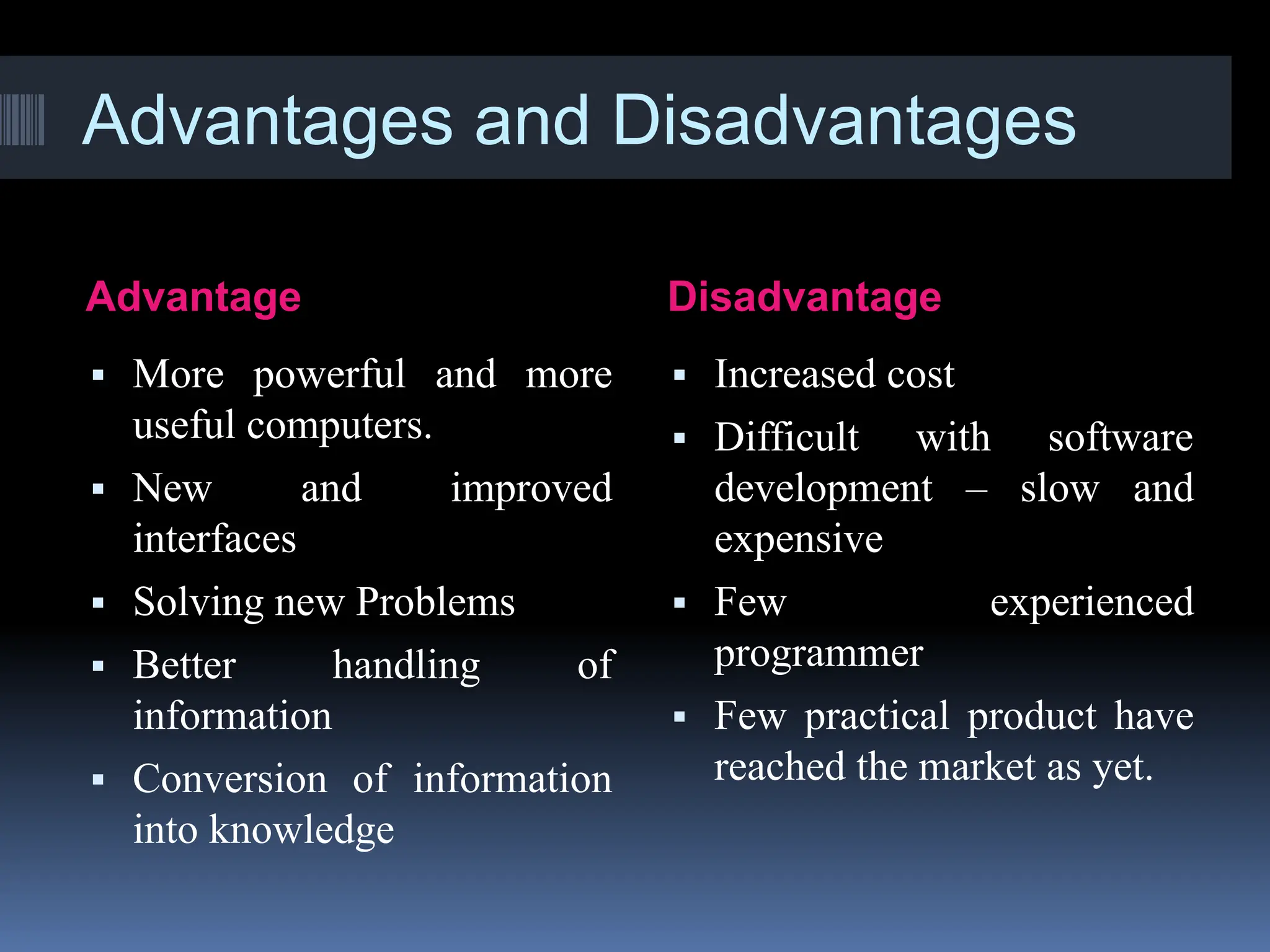
The document serves as an introduction to artificial intelligence (AI), outlining its definition, historical context, and applications in various fields like engineering and daily life. It discusses the concepts of intelligent agents, their types, and the rules governing their operation, including simple reflex agents, model-based agents, goal-based agents, utility-based agents, and learning agents. Additionally, it highlights the limitations of AI, such as high costs, lack of creativity, and dependency on machines.