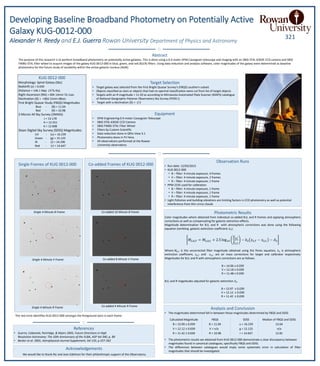
1) The document describes broadband photometry performed on the potentially active galaxy KUG 0012-000 using a 0.4 meter telescope and CCD camera to obtain images in blue, green, and red filters.
2) Color magnitudes were determined for the galaxy and reported as B = 13.97, V = 12.12, and R = 11.42 to establish baseline photometry for future study of variability in the galaxy's active galactic nucleus.
3) The magnitudes determined in this study fall between those reported in previous studies from the First Bright Quasar Survey and Sloan Digital Sky Survey, suggesting systematic errors in those catalogs' magnitude calculations.