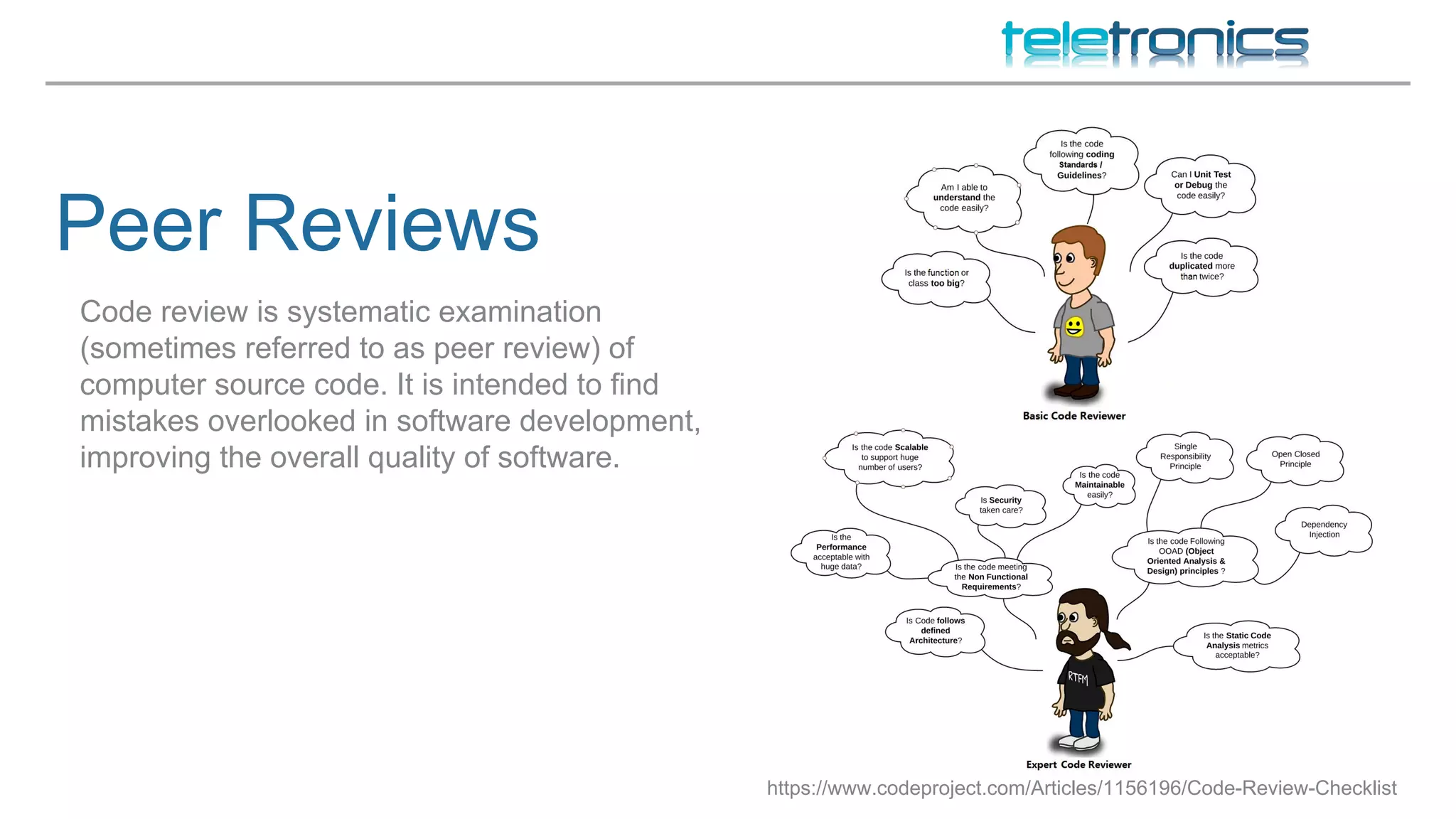
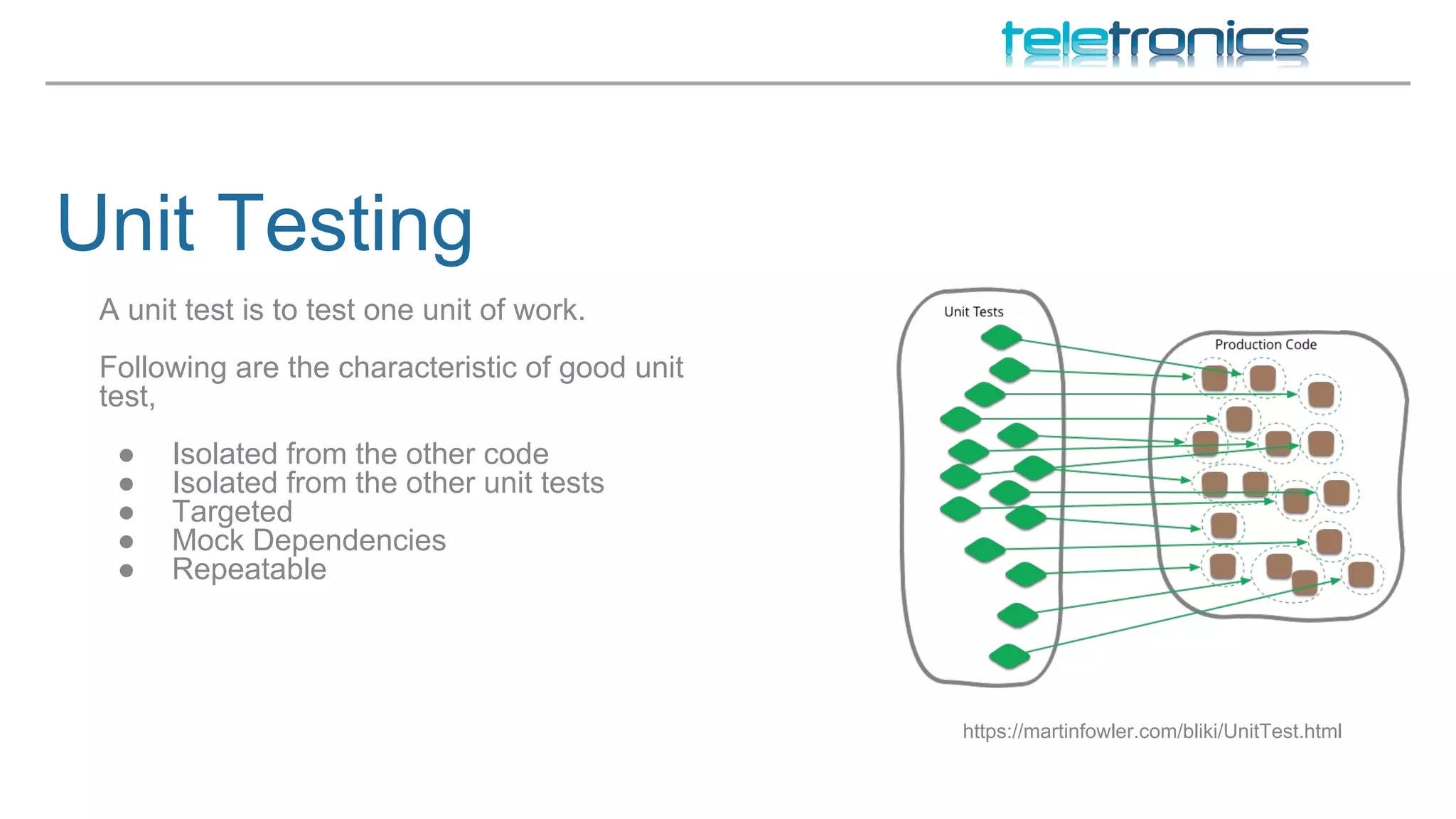
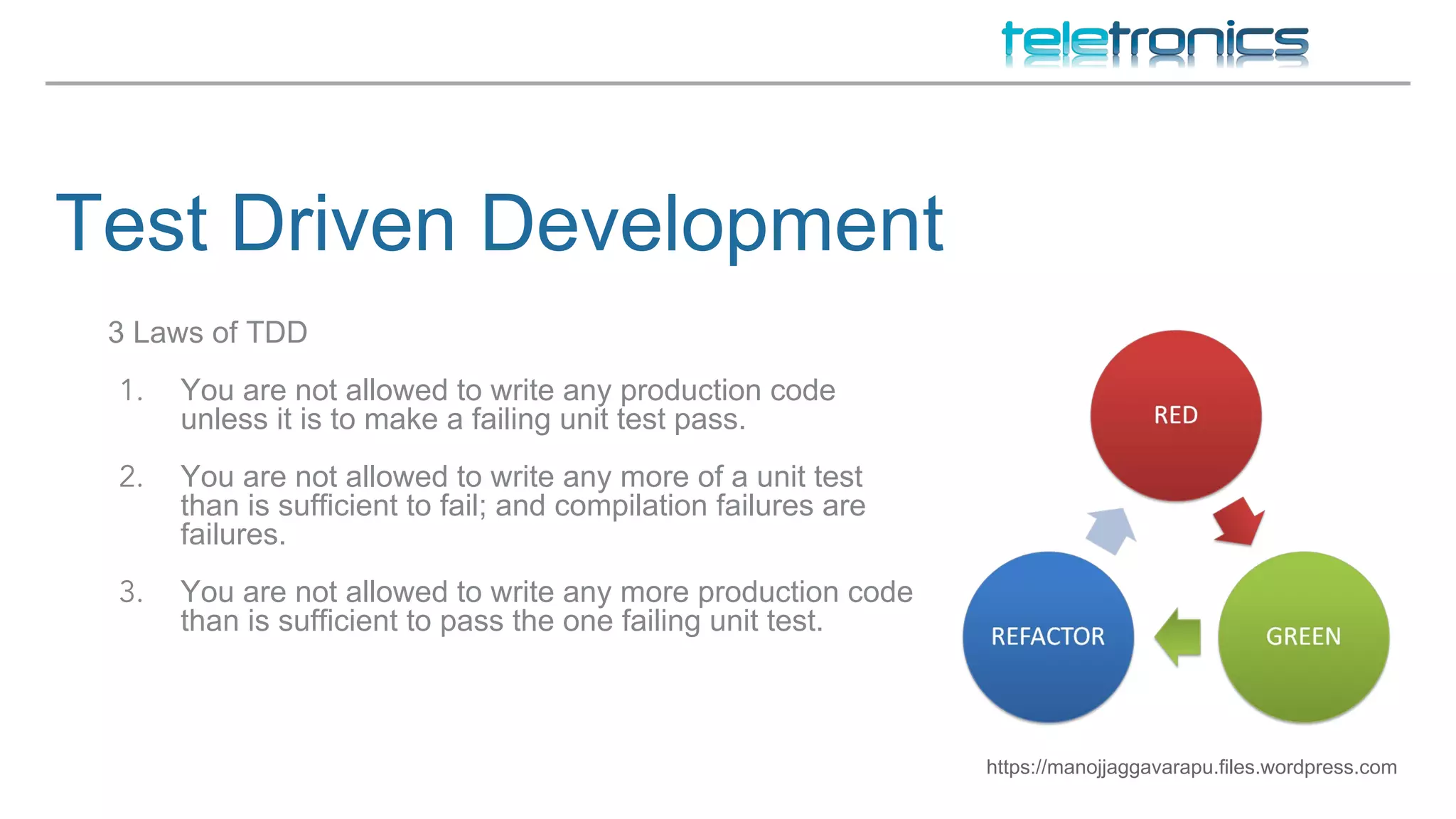
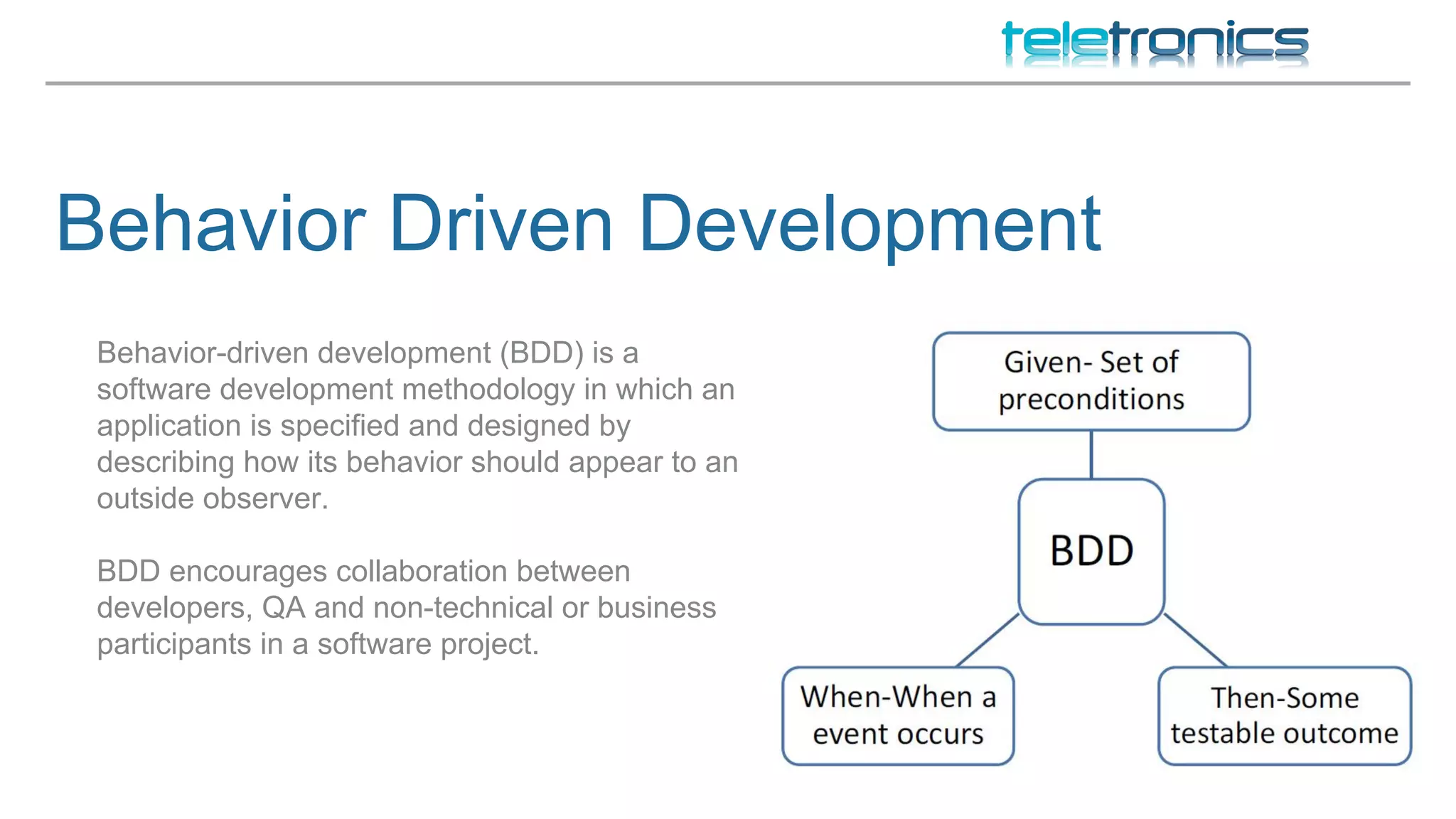
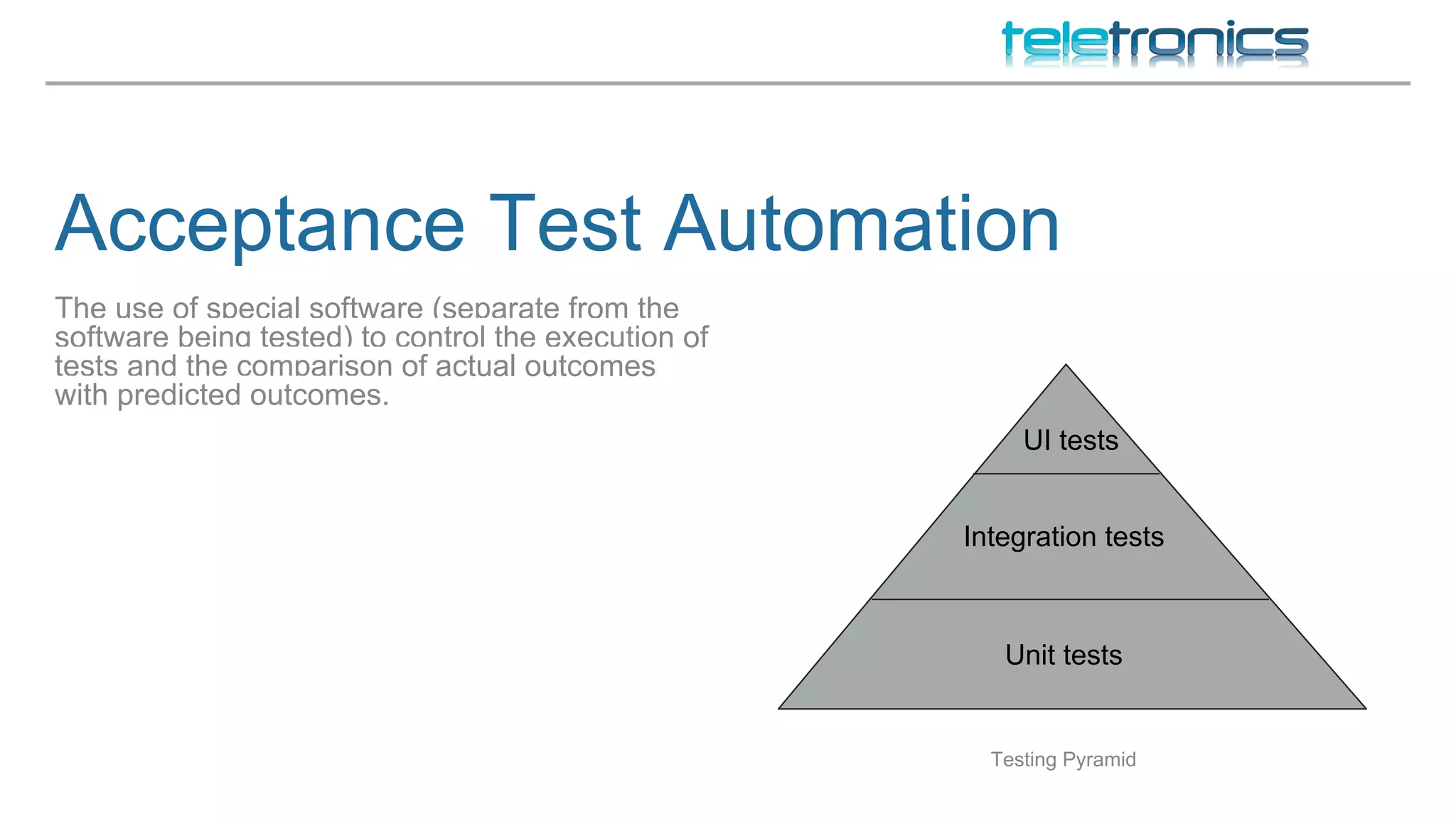
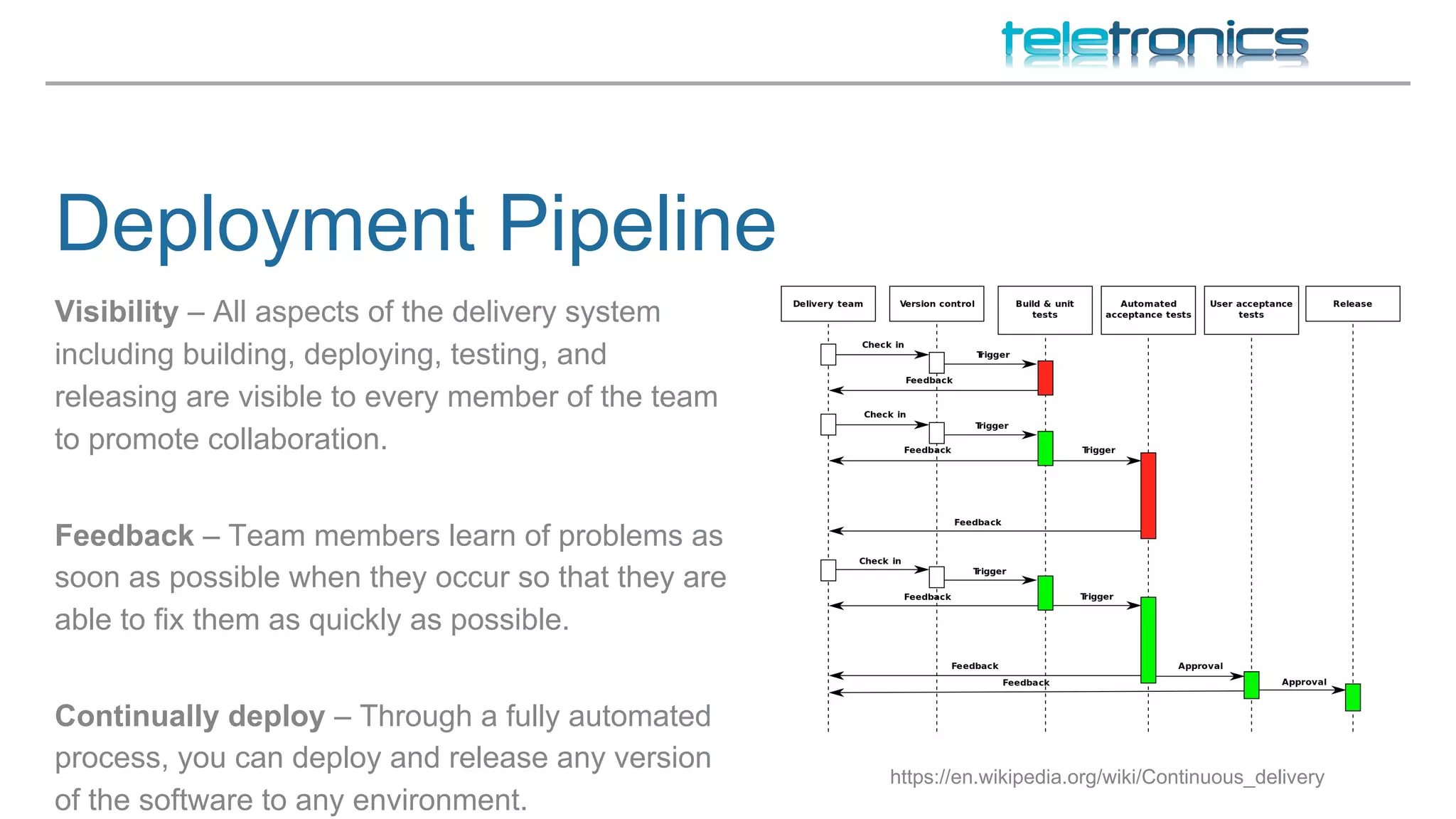
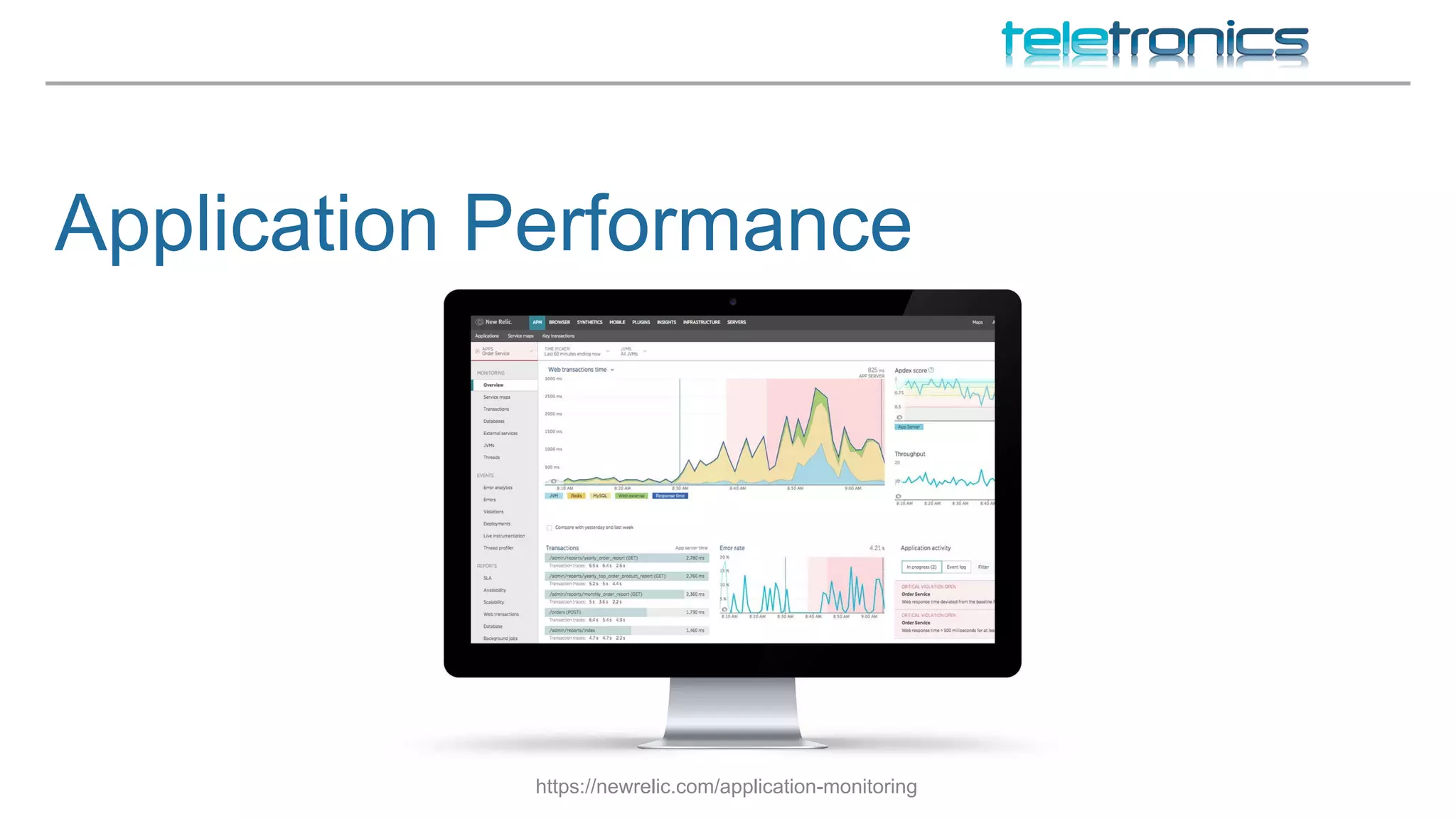
This document discusses DevOps practices for improving software development processes through feedback loops, collaboration, visibility, and shared responsibility. It covers version control, peer reviews, pair programming, unit testing, test-driven development, behavior-driven development, testing strategies, continuous integration, continuous delivery, deployment pipelines, infrastructure considerations, monitoring, analytics, performance, and security. The overall aim is to build, test, and release software faster and more reliably through automation, visibility, and collaboration between teams.