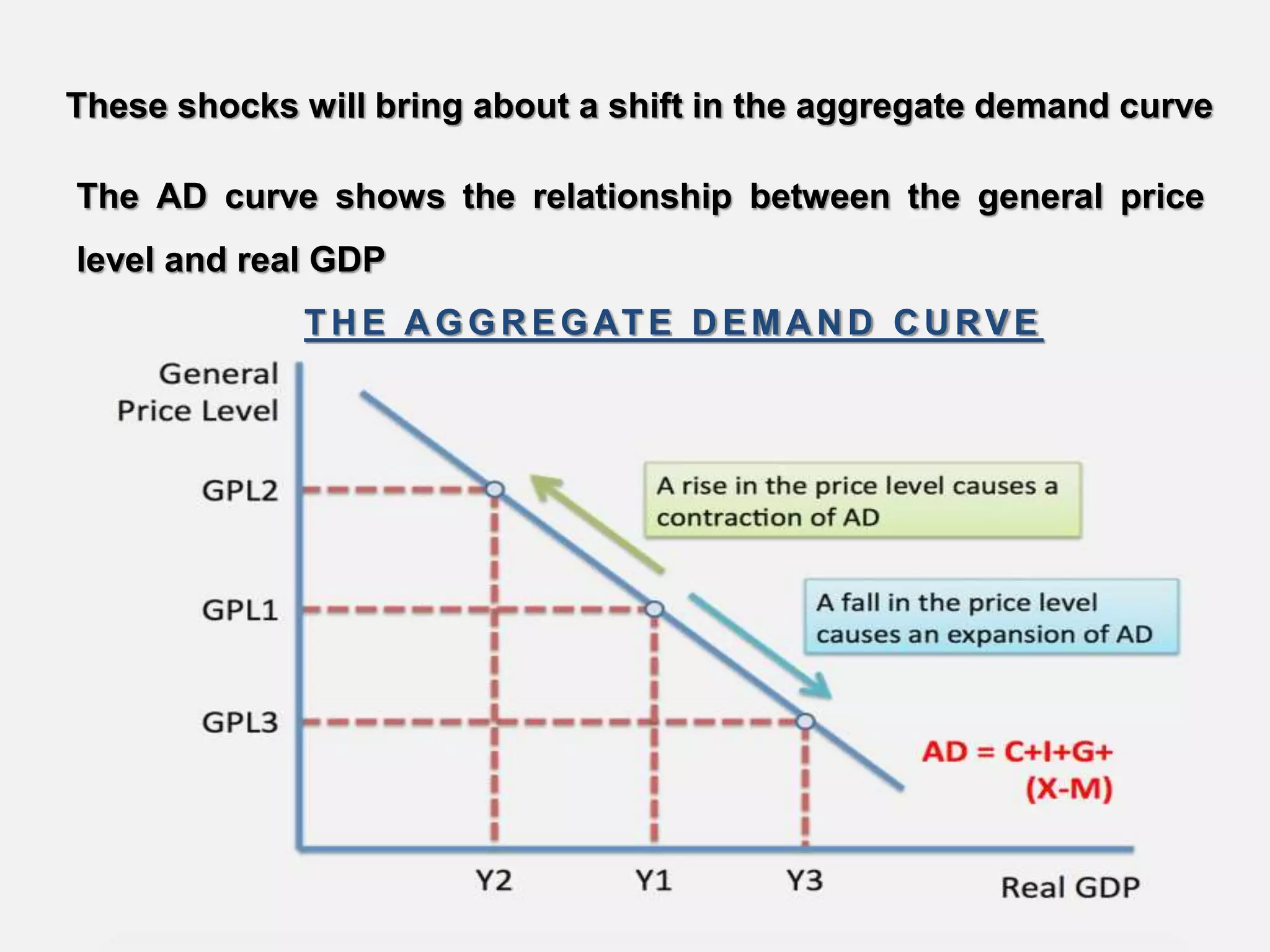
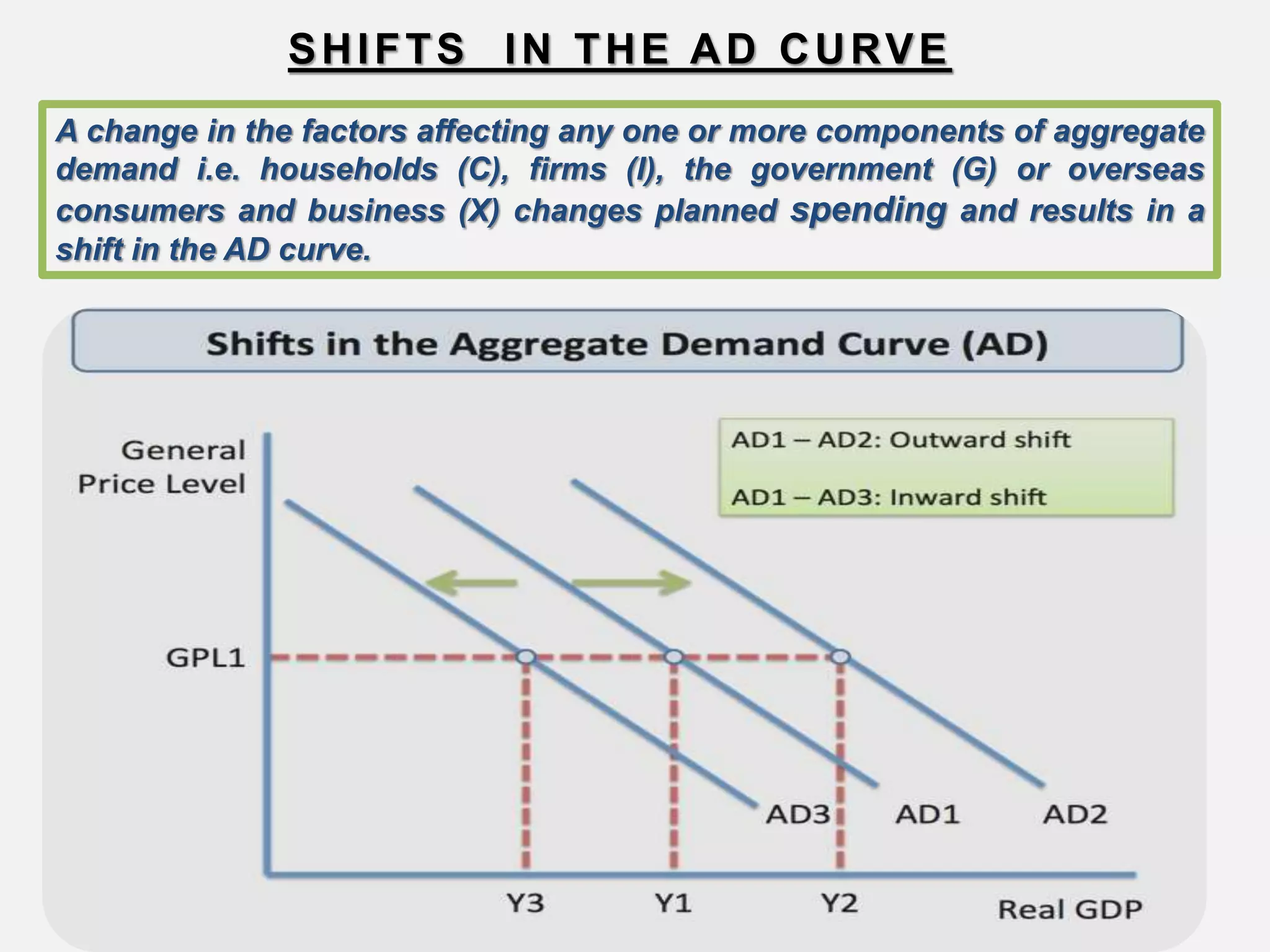
Aggregate demand is the total spending on goods and services in an economy. It is calculated as the sum of consumption (C), investment (I), government spending (G), and net exports (X-M). Shocks to aggregate demand can occur due to events like a housing market slump, credit crunch, or unexpected changes in interest rates or fiscal policy. These shocks cause the aggregate demand curve to shift, showing a new relationship between the price level and real GDP. Factors that can cause the aggregate demand curve to shift include changes in expectations, monetary policy, fiscal policy, economic conditions abroad, household wealth, and the availability of credit.