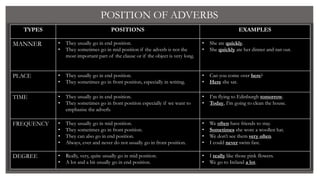
This document provides information about different types of adverbs in English grammar. It begins with defining adverbs as words that modify verbs, adjectives, and other adverbs by describing manner, place or time. It then lists the main kinds of adverbs as: manner, place, time, frequency, and degree. For each type, examples are given and the typical positions of each adverb in a sentence are discussed. The document concludes by emphasizing the importance of adverbs in literature.