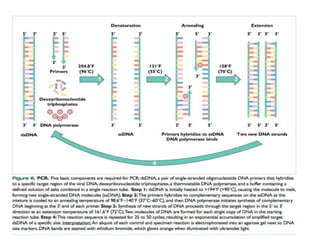
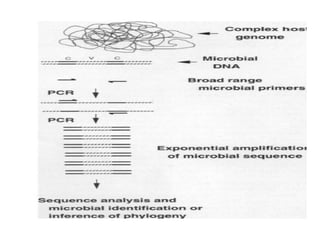
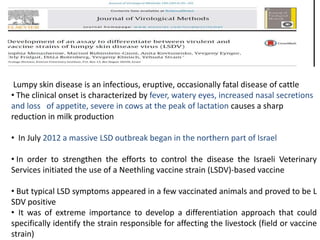
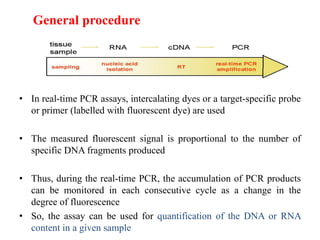
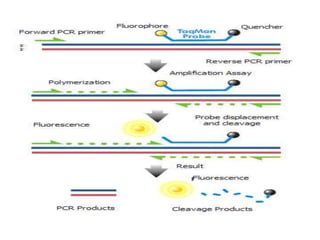
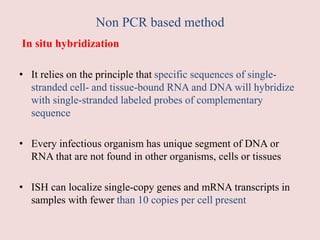
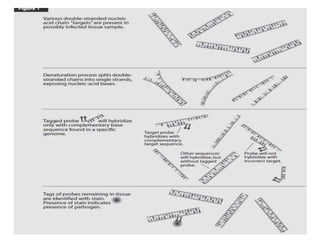
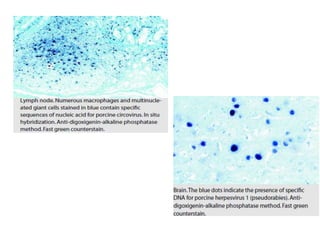
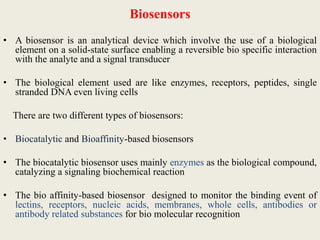
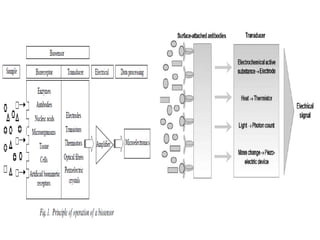
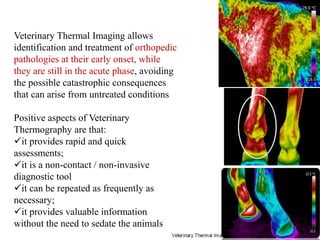
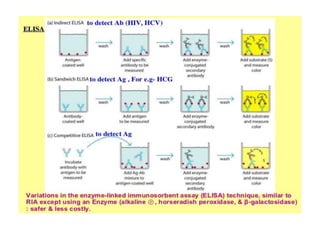
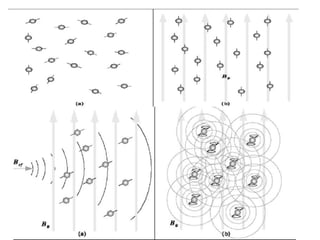
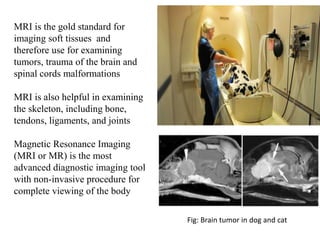
Advances in diagnostic technology allow for more sensitive, specific, rapid and cost-effective diagnosis of diseases. New methods like PCR, real-time PCR, in situ hybridization, biosensors, infrared thermography, and ELISA have improved on classical diagnostic approaches by being able to detect minute amounts of pathogens, identify pathogens rapidly, and differentiate between field strains and vaccine strains. These advanced diagnostic techniques are important for disease control, treatment, and surveillance.