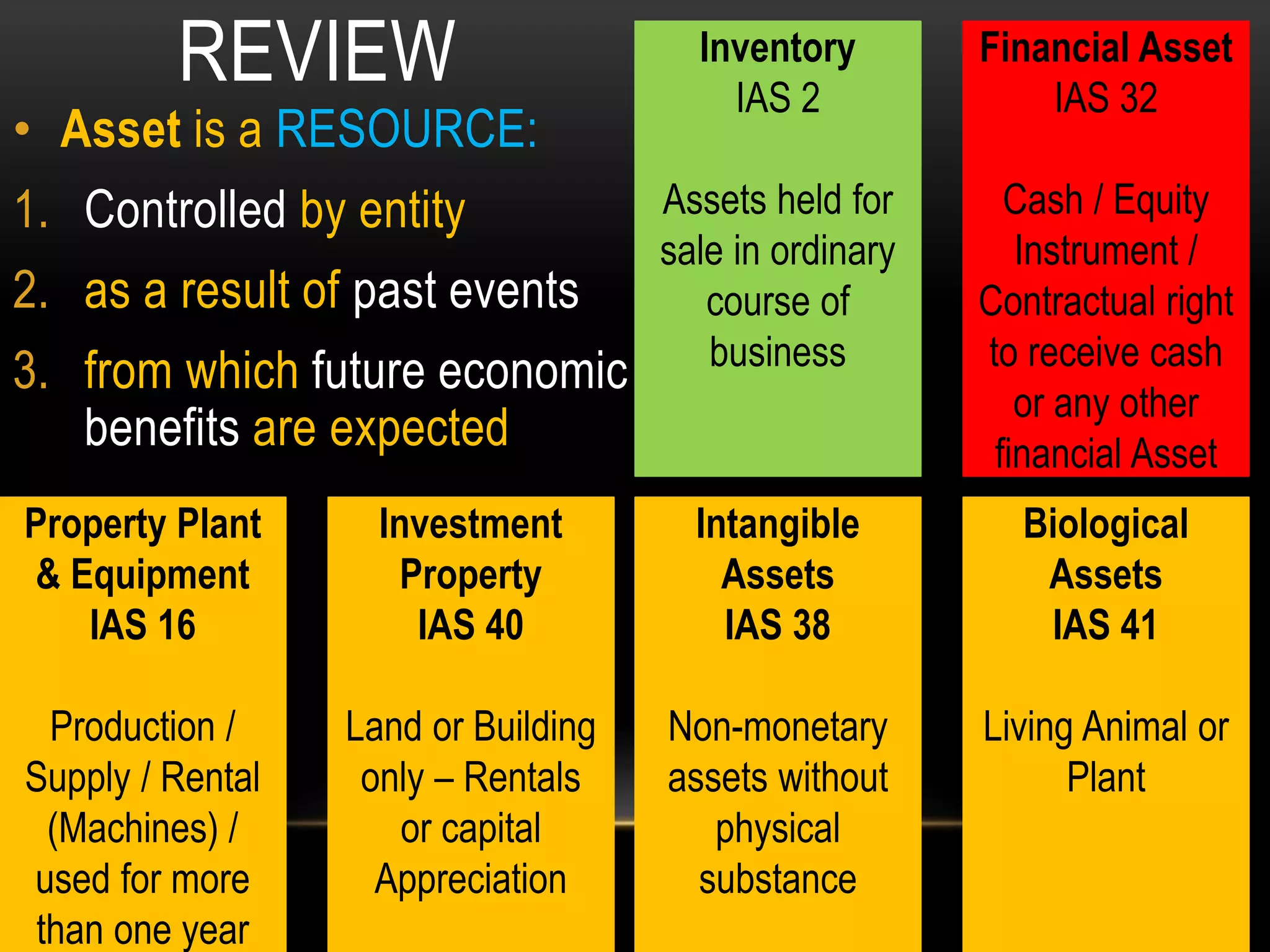
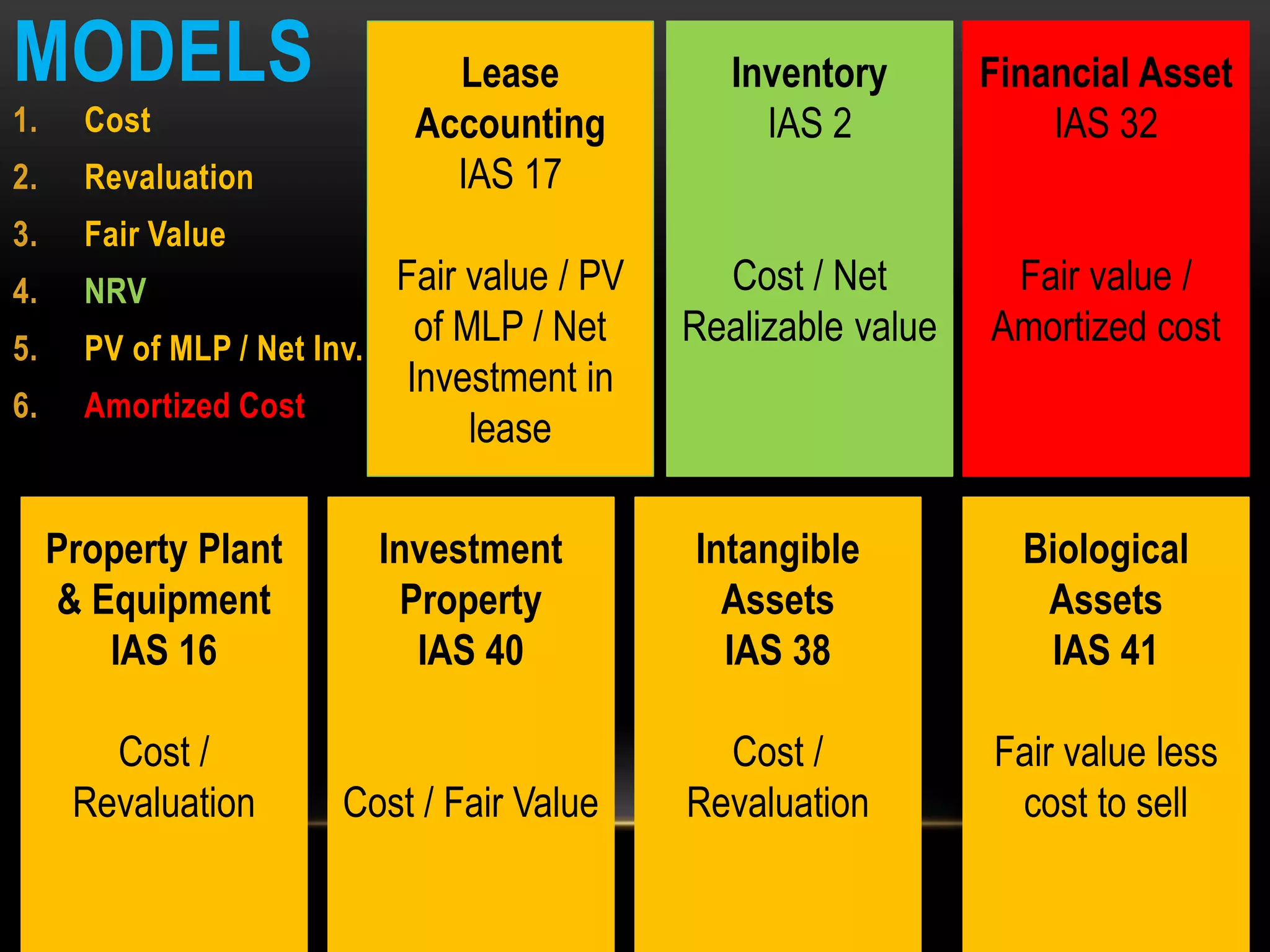
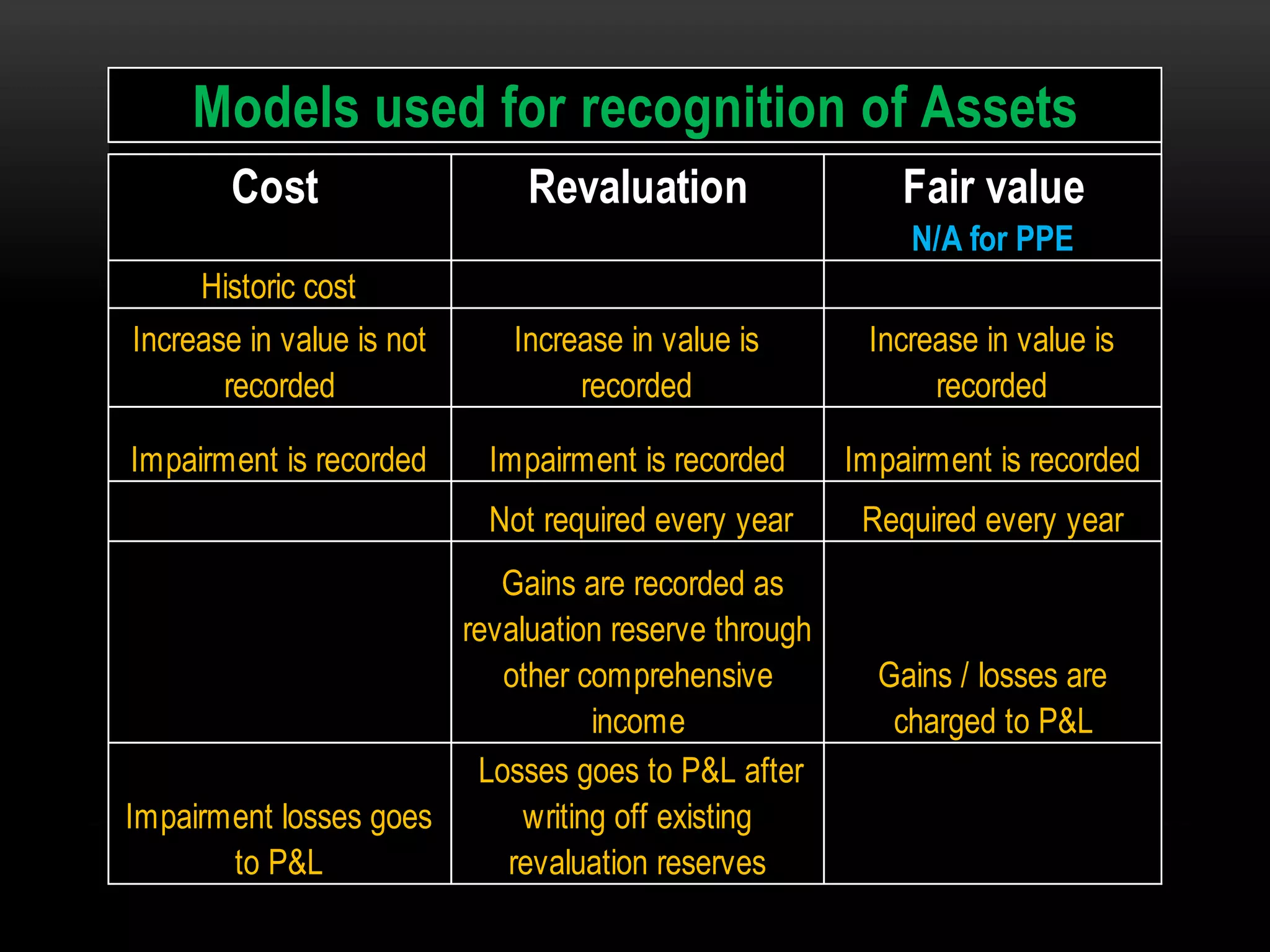
This document provides an overview of an advanced financial reporting course. It discusses topics that will be covered, including property, plant, and equipment, intangible assets, investment property, biological assets, and more. It also outlines new topics like provisions, contingent liabilities, revenue recognition, and cash flows. The document describes the components of annual financial statements and provides information on accounting standards, reporting frameworks, asset models, and cost versus revaluation versus fair value accounting.