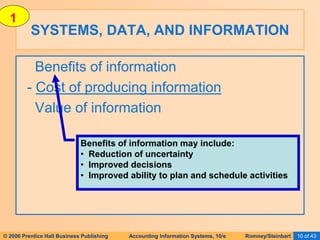
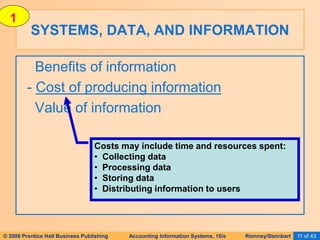
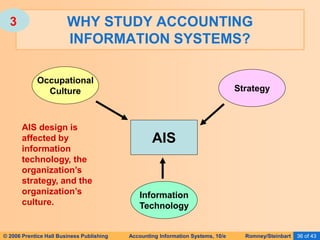
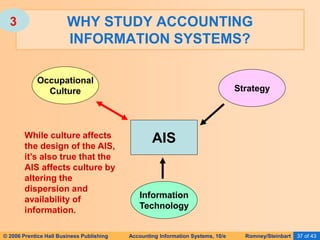
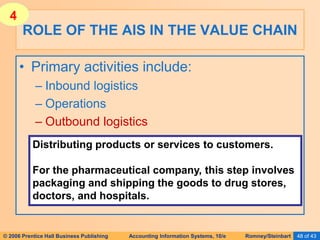
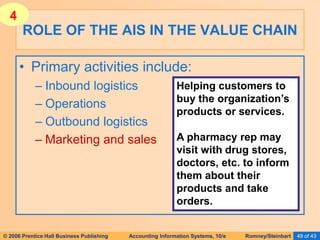
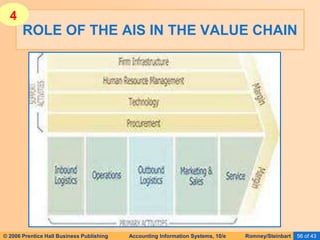
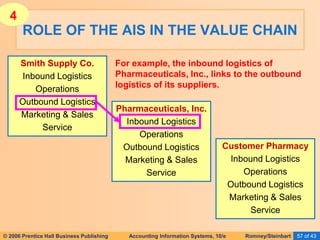
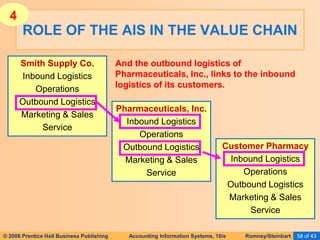
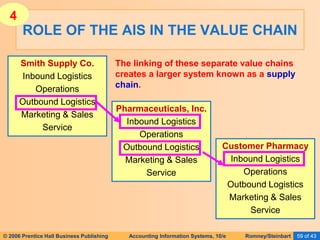
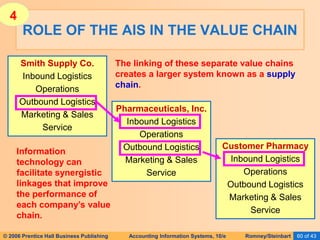
The document provides an overview of accounting information systems (AIS), defining key concepts such as systems, data, and information, and discussing their roles in organizations. It emphasizes the importance of AIS in decision-making, value creation, and its critical role in enhancing customer service through an organized structure of input, operations, and logistics. The document also highlights the skills needed to evaluate and implement AIS effectively, which are integral to career success in accounting.