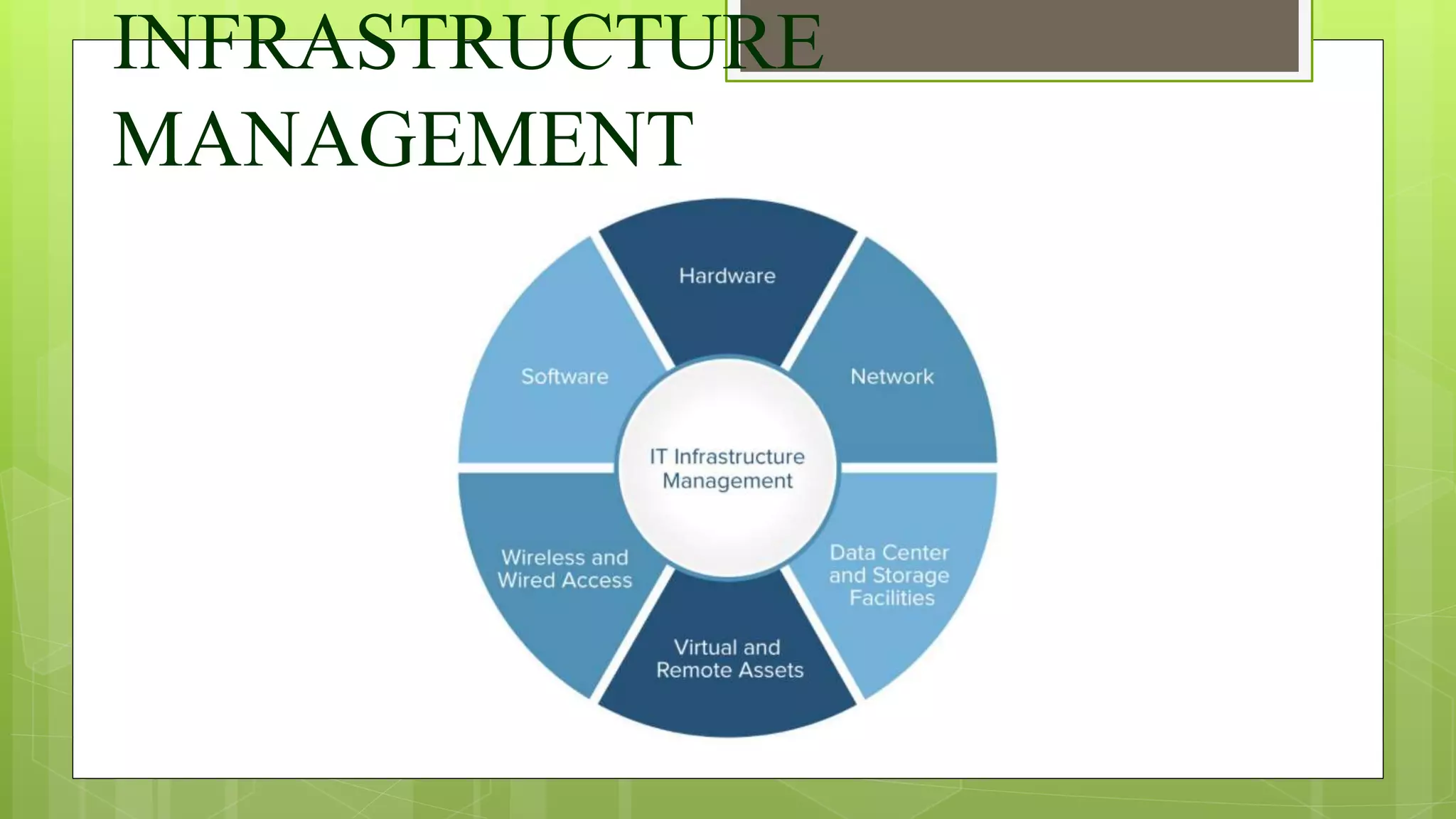
The document discusses various components of administrative support systems and educational institutions. It explains the importance of effective school administration by allowing teachers to focus on teaching, promoting accountability, and informing decisions. It then discusses personnel management, defining it and outlining the roles and responsibilities of personnel managers. It also discusses infrastructure management, defining it and outlining essential IT elements. Finally, it discusses financial management, outlining its scope, objectives, and functions in educational institutions.