This document summarizes the administration and scoring of the Qualitative Reading Inventory (QRI), including:
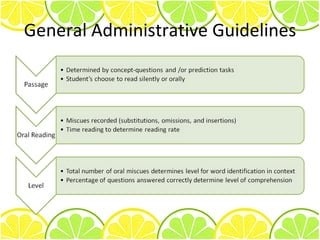
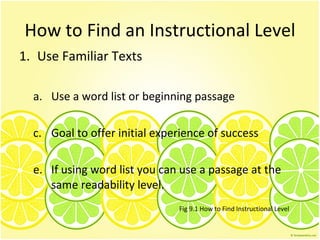
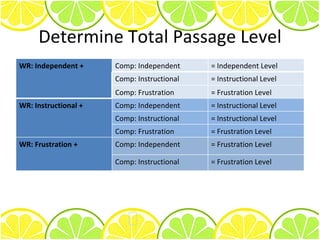
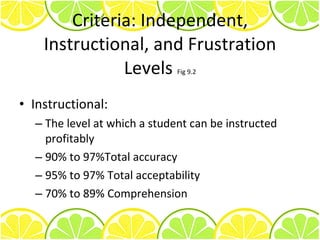
1) The main purposes of administering passages are to determine a student's independent, instructional, and frustration levels for word identification and comprehension.
2) Assessment options include evaluating prior knowledge, oral reading miscue analysis, comprehension through recall and look-backs, and think-alouds.
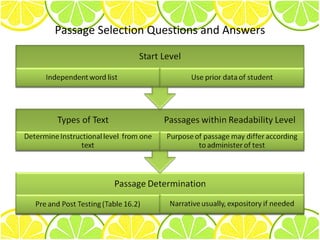
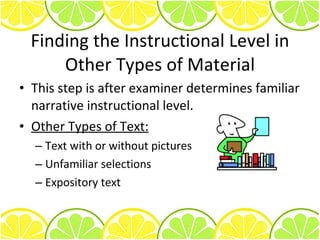
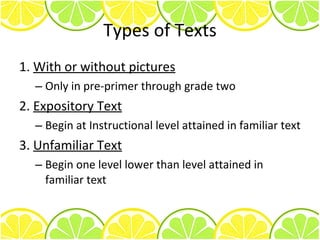
3) General guidelines are provided for administering passages, including instructions to students and selecting appropriate passages.