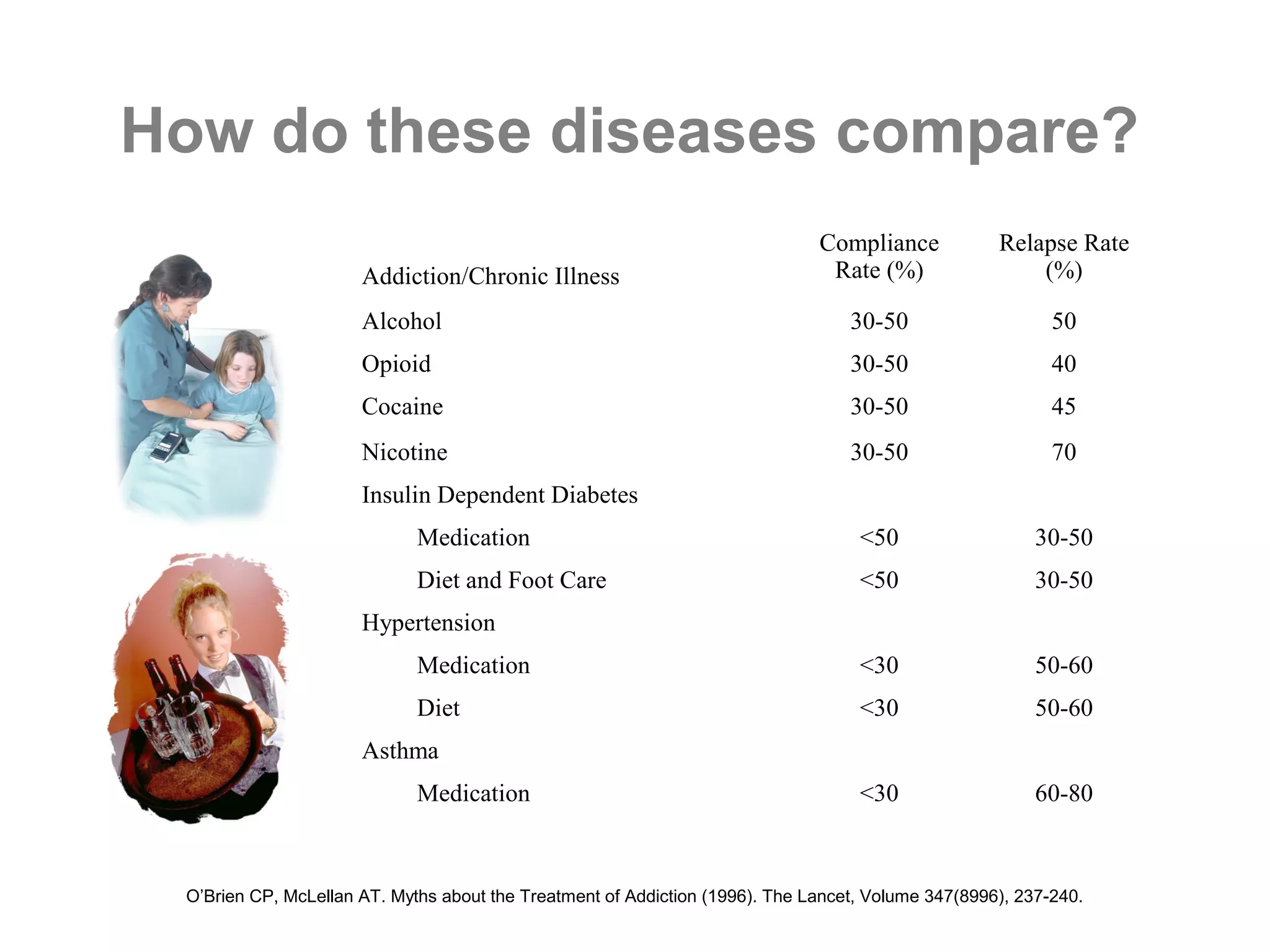
This document provides an overview of addiction as a disease. It defines addiction and alcoholism, and examines addiction through the framework of the causal disease model. Addiction is characterized by craving, loss of control, tolerance, withdrawal, and compulsion. Compliance and relapse rates for various addictions are similar to chronic illnesses like diabetes and hypertension. The development of alcoholism involves priming, early experimentation, and learning how to drink. Untreated addiction stems from mental obsession, fear, and loneliness. AA offers a counterintuitive model for intervention based on attending meetings, finding a sponsor, and helping other addicts.