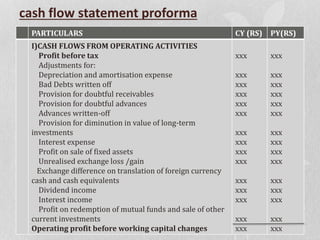
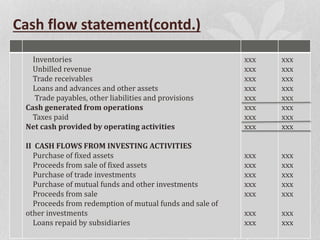
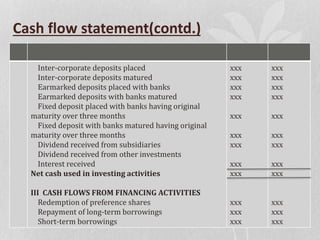
The document discusses the key components of an annual report for a company. It explains that an annual report provides shareholders and other stakeholders a comprehensive overview of the company's financial performance and activities over the preceding year. It then describes the typical sections included in an annual report such as the reports of directors and management, audited financial statements, notes on accounting policies, and segmented reporting. The document also includes examples of balance sheet, cash flow statement, and profit and loss proformas that are commonly included in annual reports.