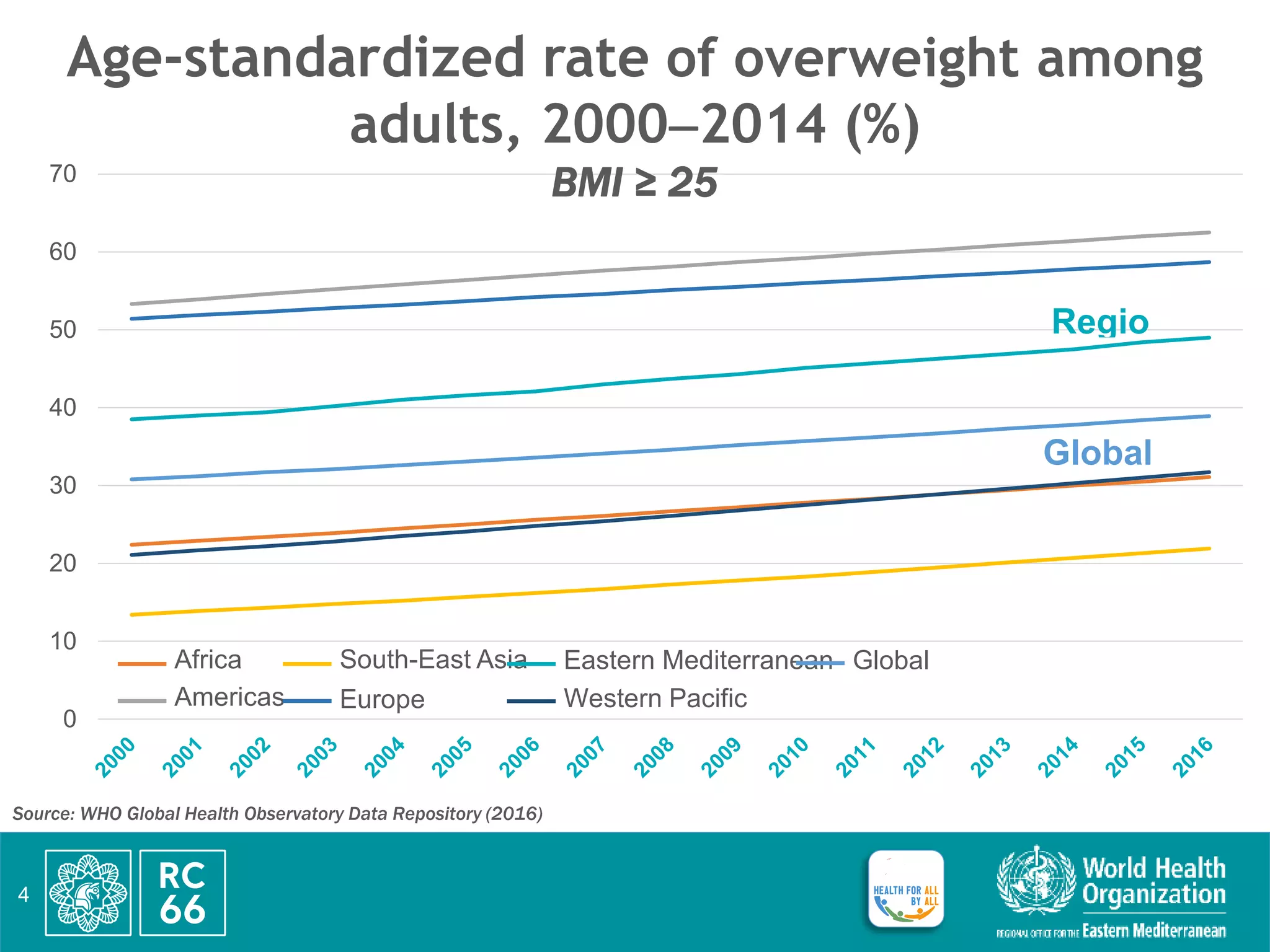
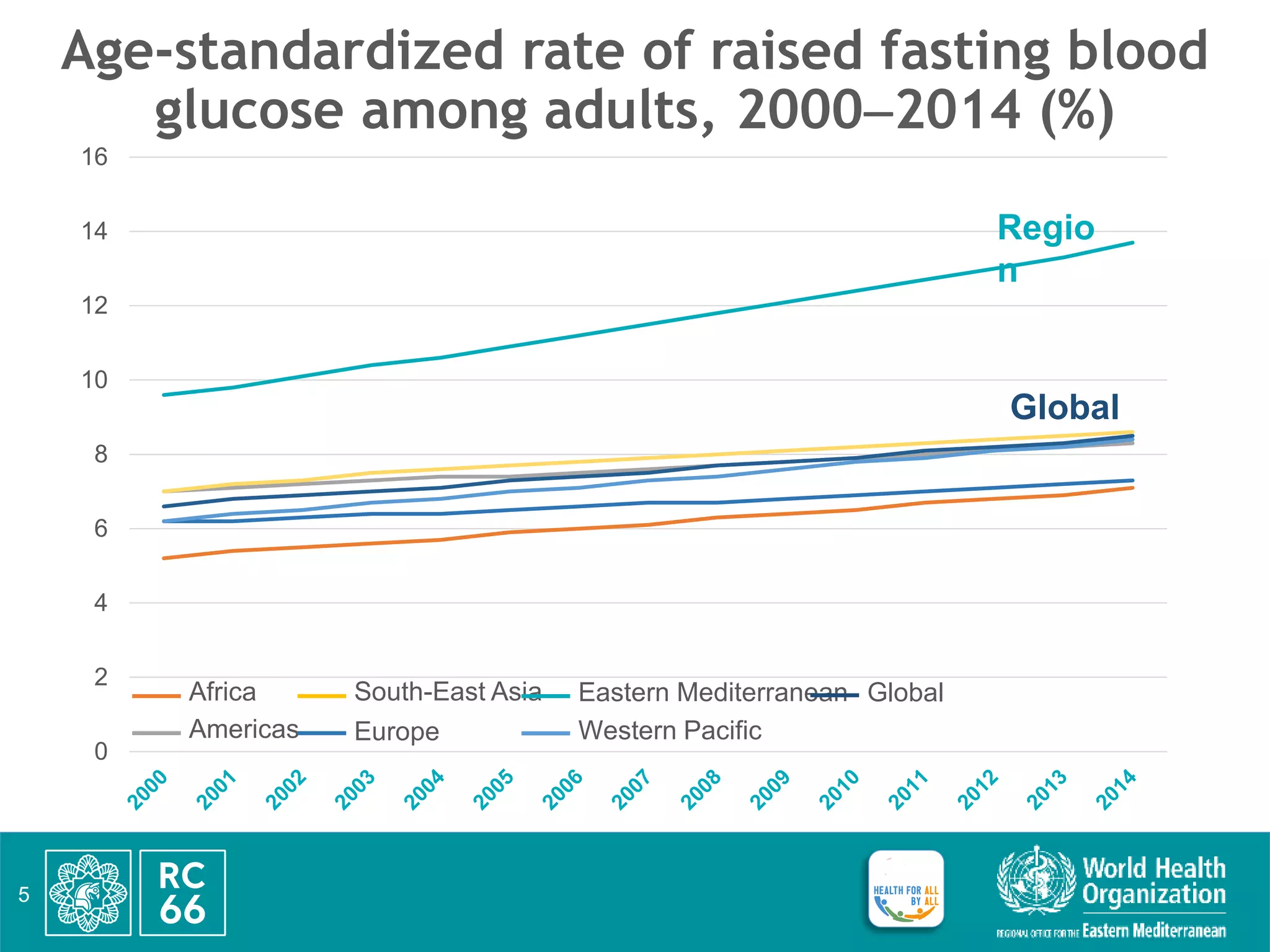
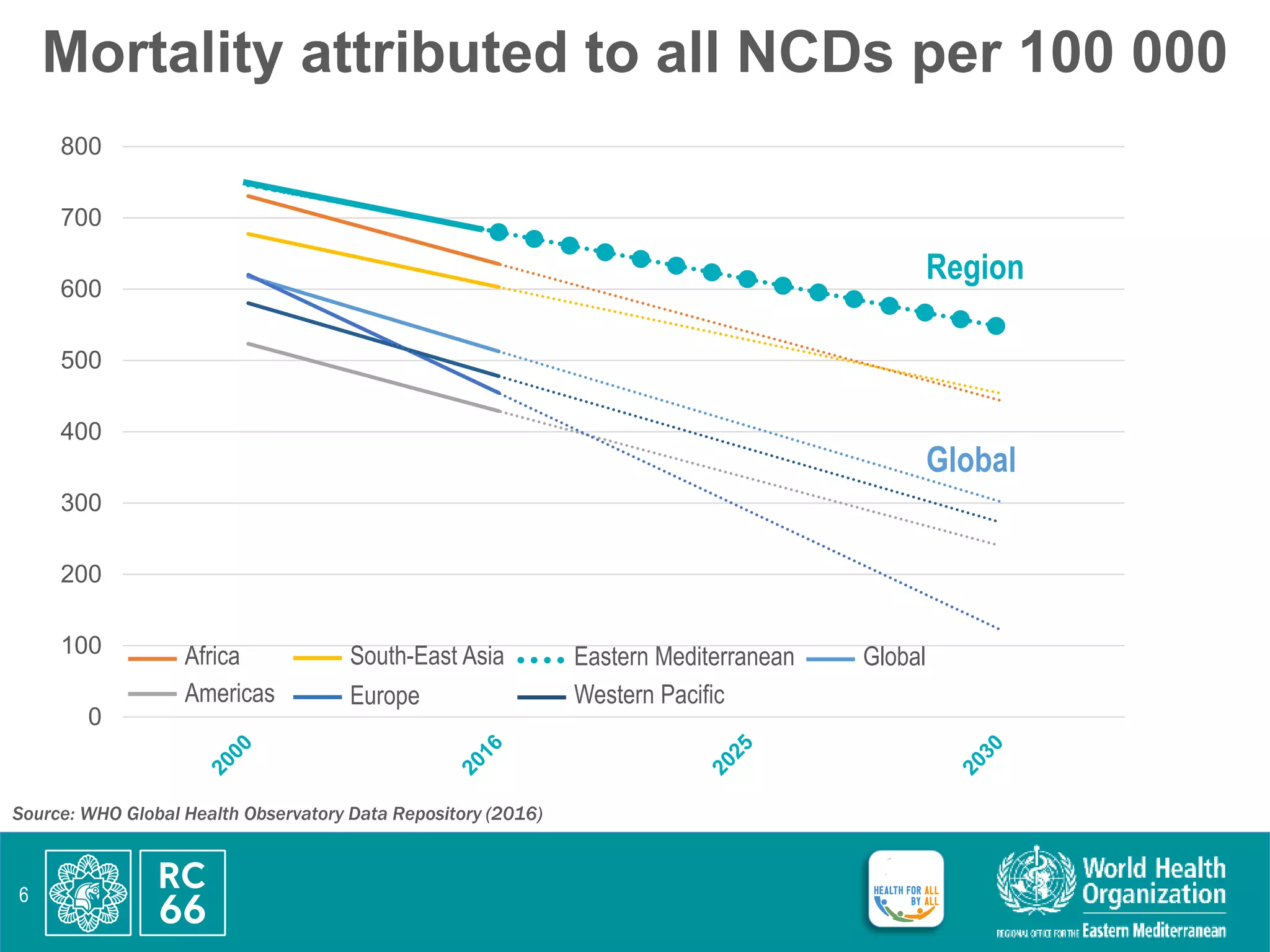
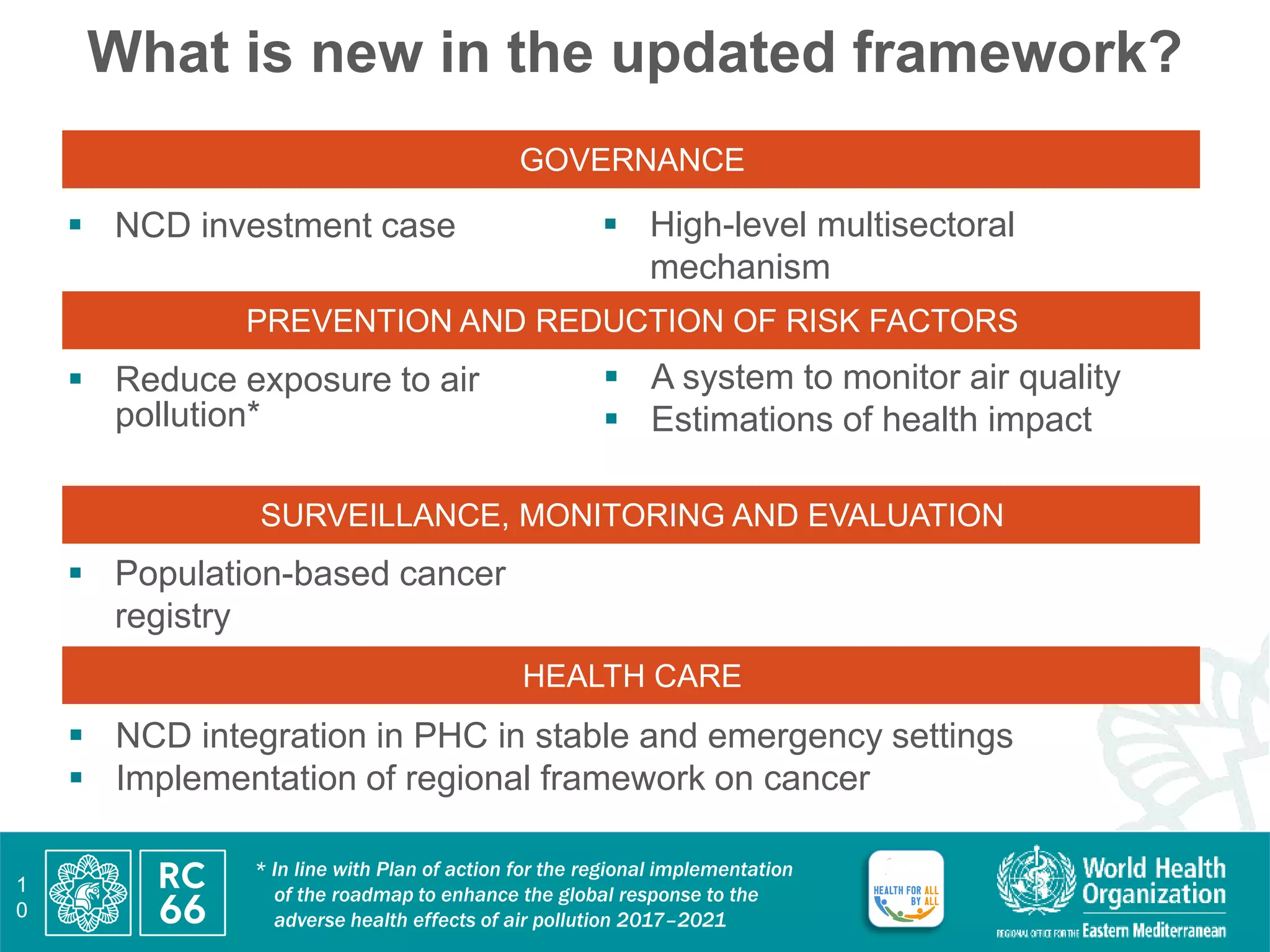
This document discusses accelerating regional implementation of the Political Declaration on noncommunicable diseases (NCDs) from 2018. It provides an overview of the burden of NCDs including obesity, diabetes, and mortality rates. It notes that while progress has been made since the RC59-RC66 resolutions, more action is needed in areas like high-level commitment, prevention, health systems, and surveillance. The updated regional framework strengthens governance, prevention of risk factors like air pollution, integration of NCD care into primary healthcare and emergencies, and cancer surveillance. Member states are urged to endorse the framework, ensure high-level leadership, prioritize cost-effective NCD interventions, strengthen data and accountability, and expand N