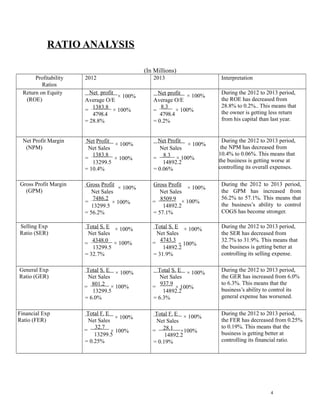
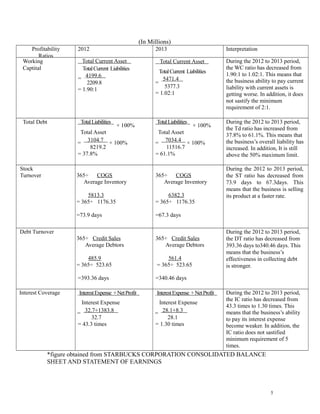
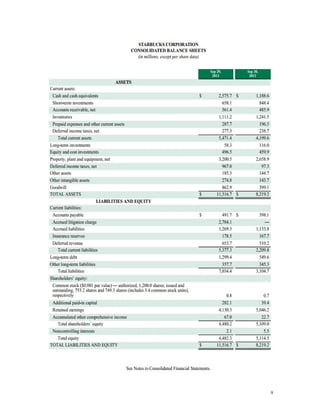
This document analyzes the financial ratios of Starbucks Corporation from 2012-2013. It finds that the company's profitability declined over this period as return on equity and net profit margin decreased. However, the gross profit margin increased, indicating better control of costs of goods sold. Liquidity also weakened as the current ratio fell below the minimum requirement of 2:1. The document recommends against investing in Starbucks due to low profitability, stability, and an expensive share price with a high P/E ratio of 28.6.