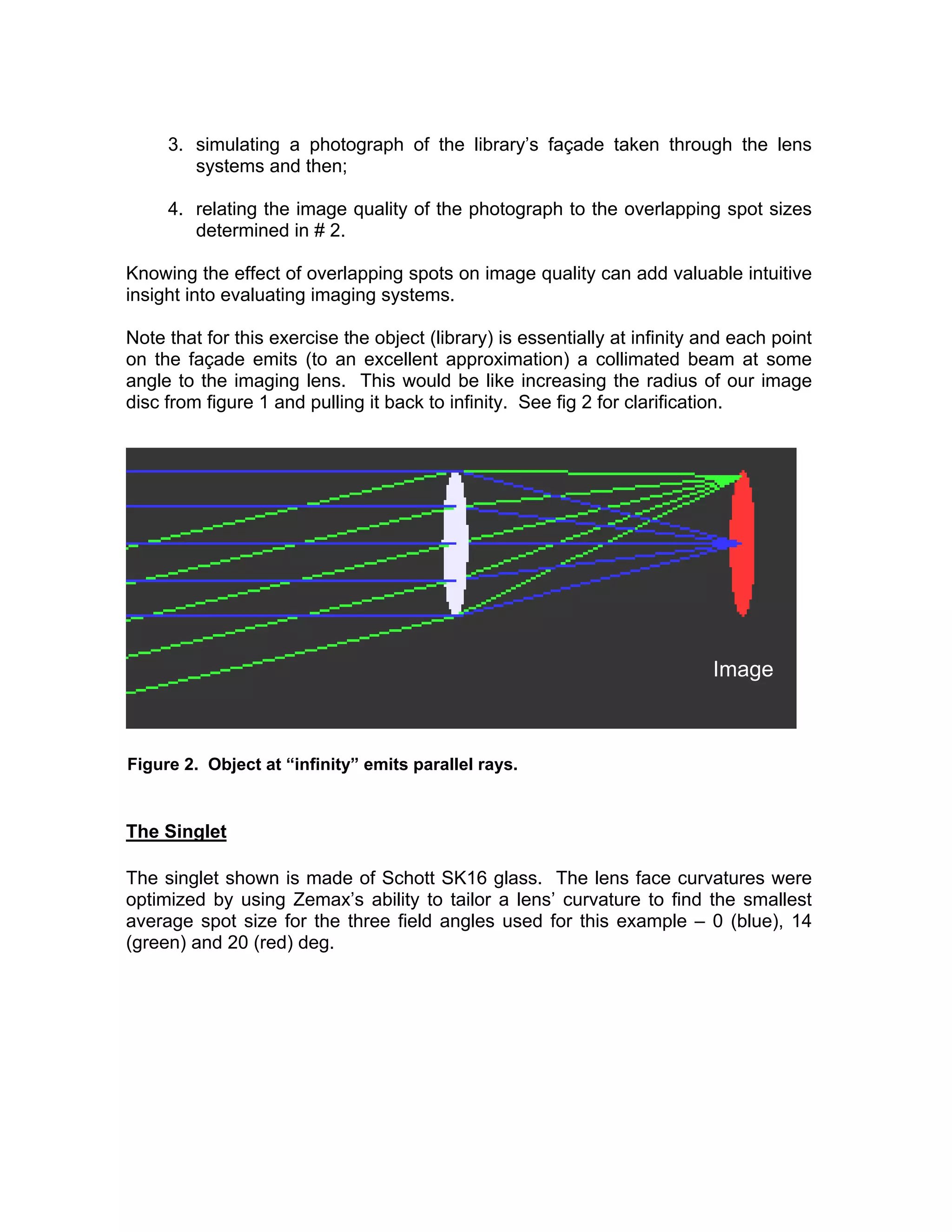
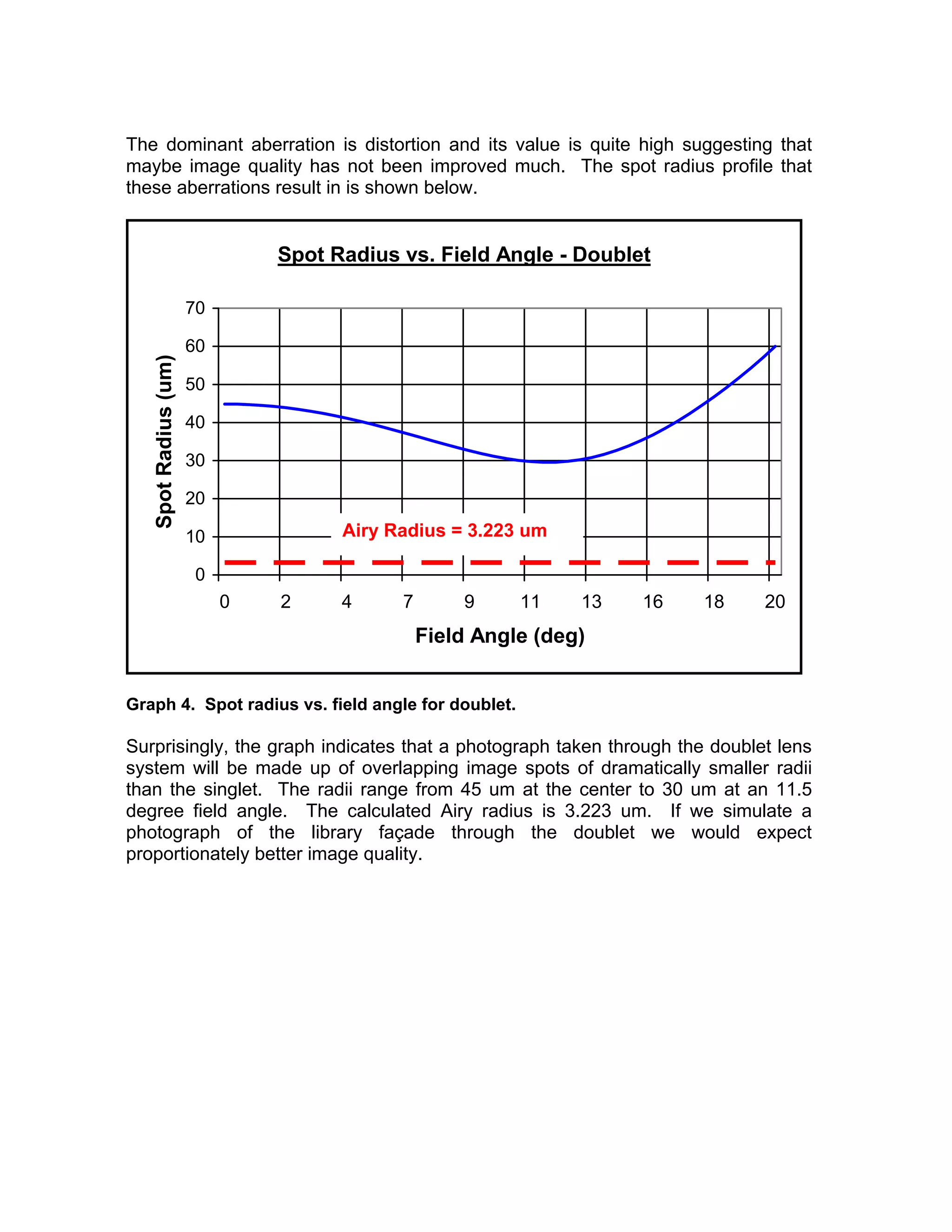
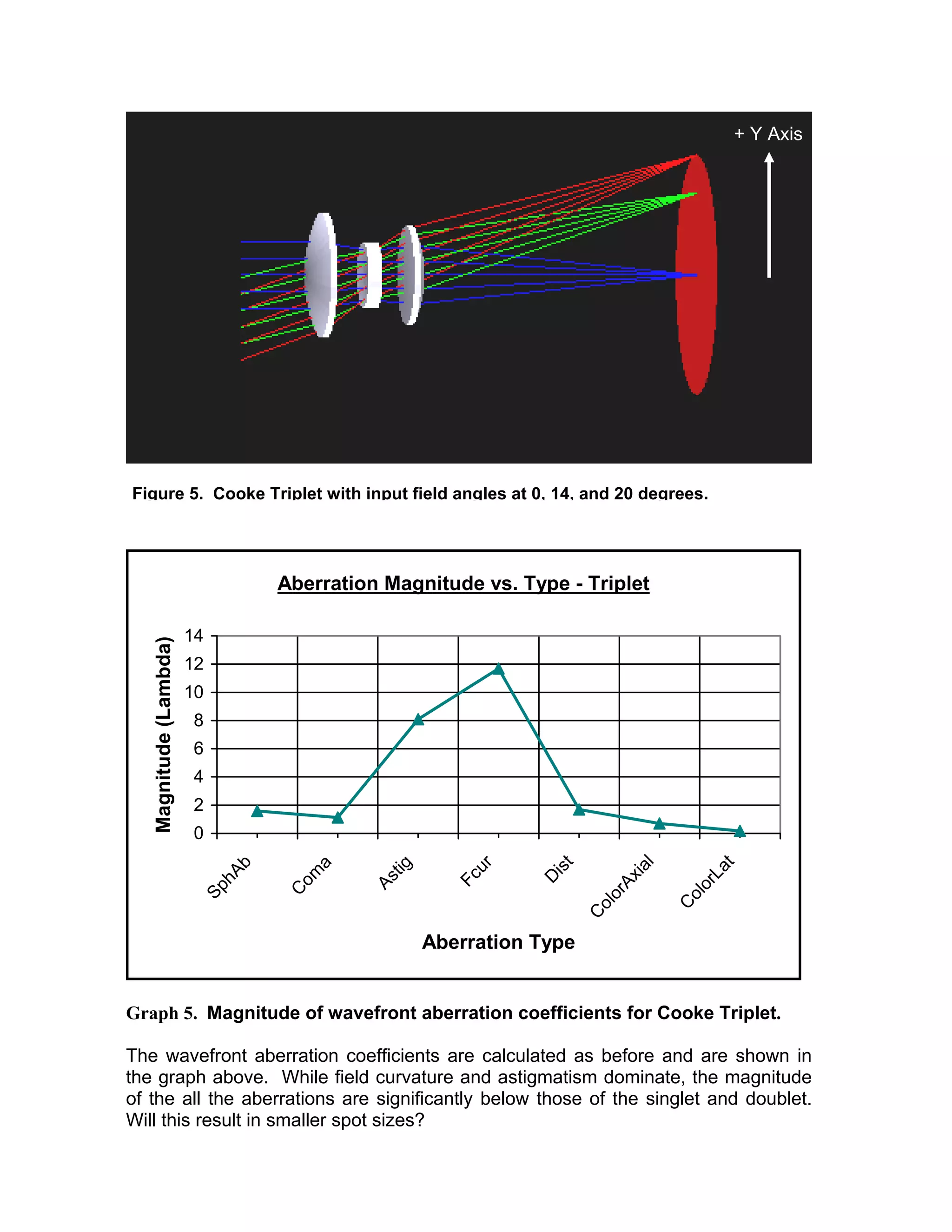
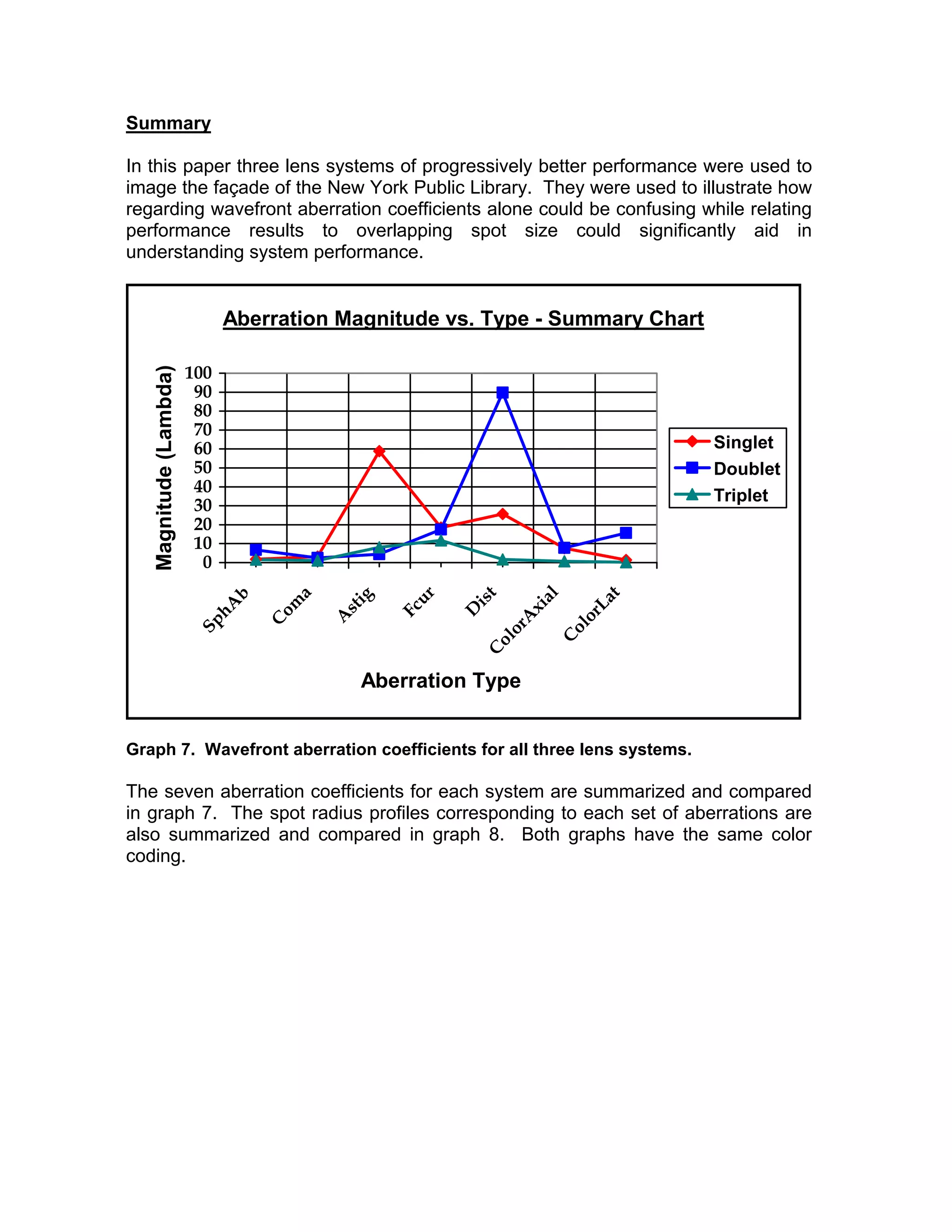
This document describes a technique for relating aberration errors in lens systems to final image quality by analyzing image spot size. It uses three example lens systems - a singlet, doublet, and triplet - to image the facade of the New York Public Library. The triplet produces the smallest image spots closest to the diffraction limit, resulting in the highest quality photograph. Analyzing aberrations in terms of overlapping image spot size provides intuitive insight into how aberrations affect image quality that is easier for non-specialists to understand than technical reports on aberration coefficients alone.