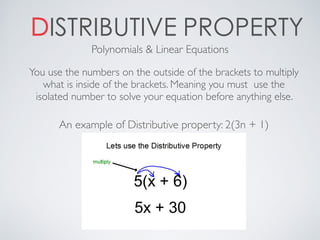
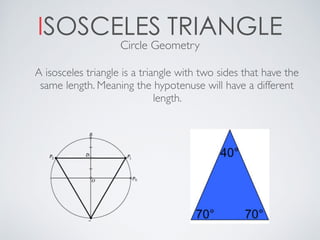
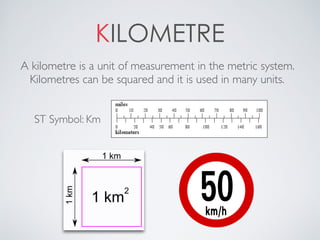
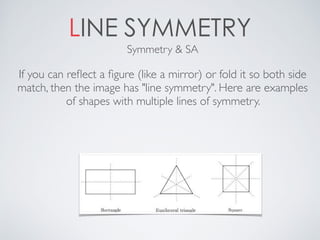
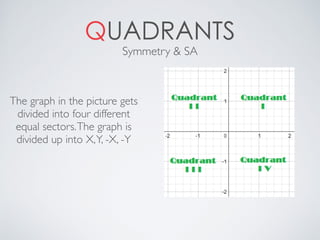
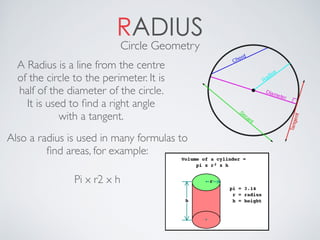
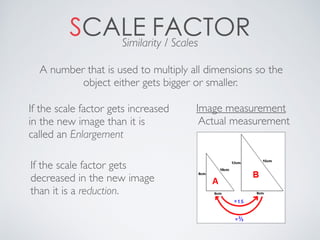
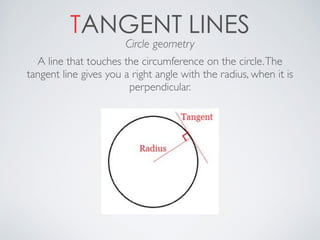
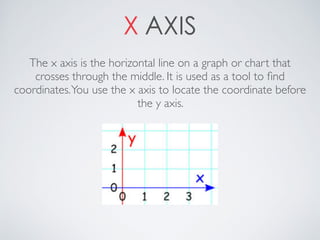
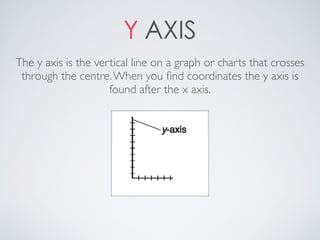
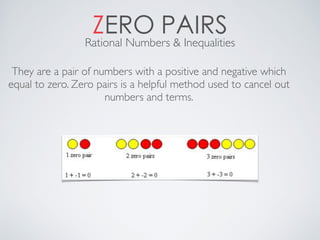
This document contains definitions and explanations of various math terms starting from A to Z. Some of the key terms defined include:
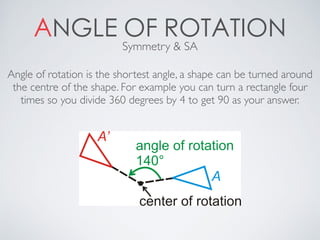
- Angle of rotation which is the shortest angle an object can be turned around its center.
- Bedmas which outlines the order of operations for solving equations.
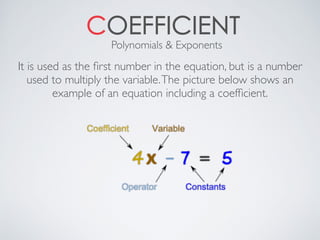
- Coefficients which are numbers used to multiply variables in an equation.
- Exponents which indicate how many times to multiply a base number by itself.
- Fractions which are numbers below 1 and can be converted to decimals.
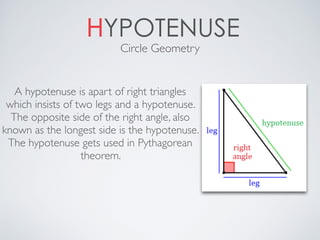
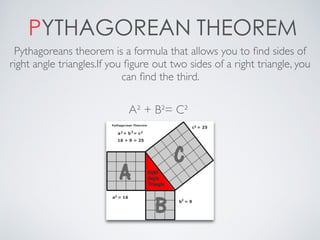
- Hypotenuse which is the longest side of a right triangle opposite the right angle.
- Pythagorean theorem which uses the formula a2 + b2 = c2 to