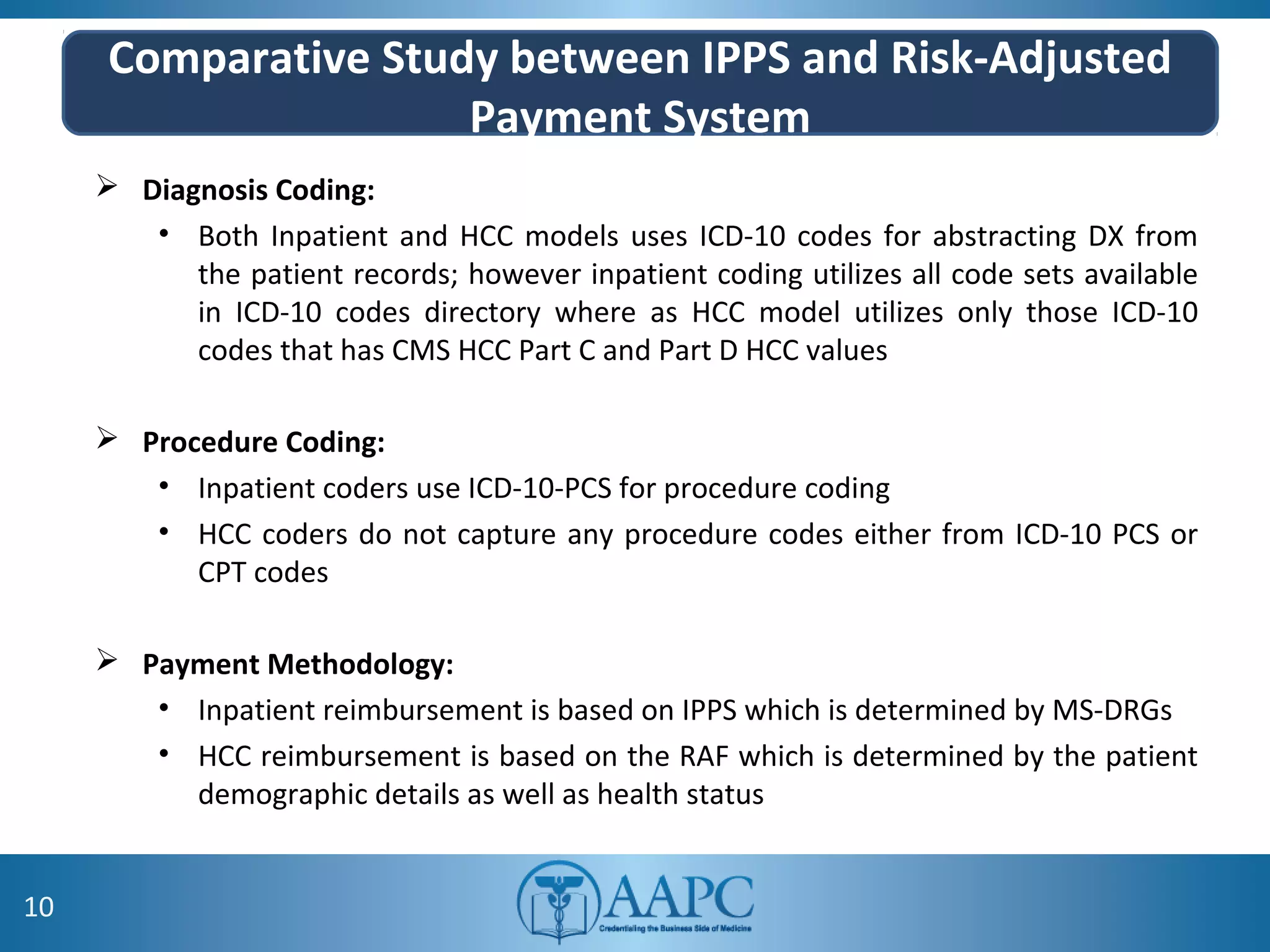
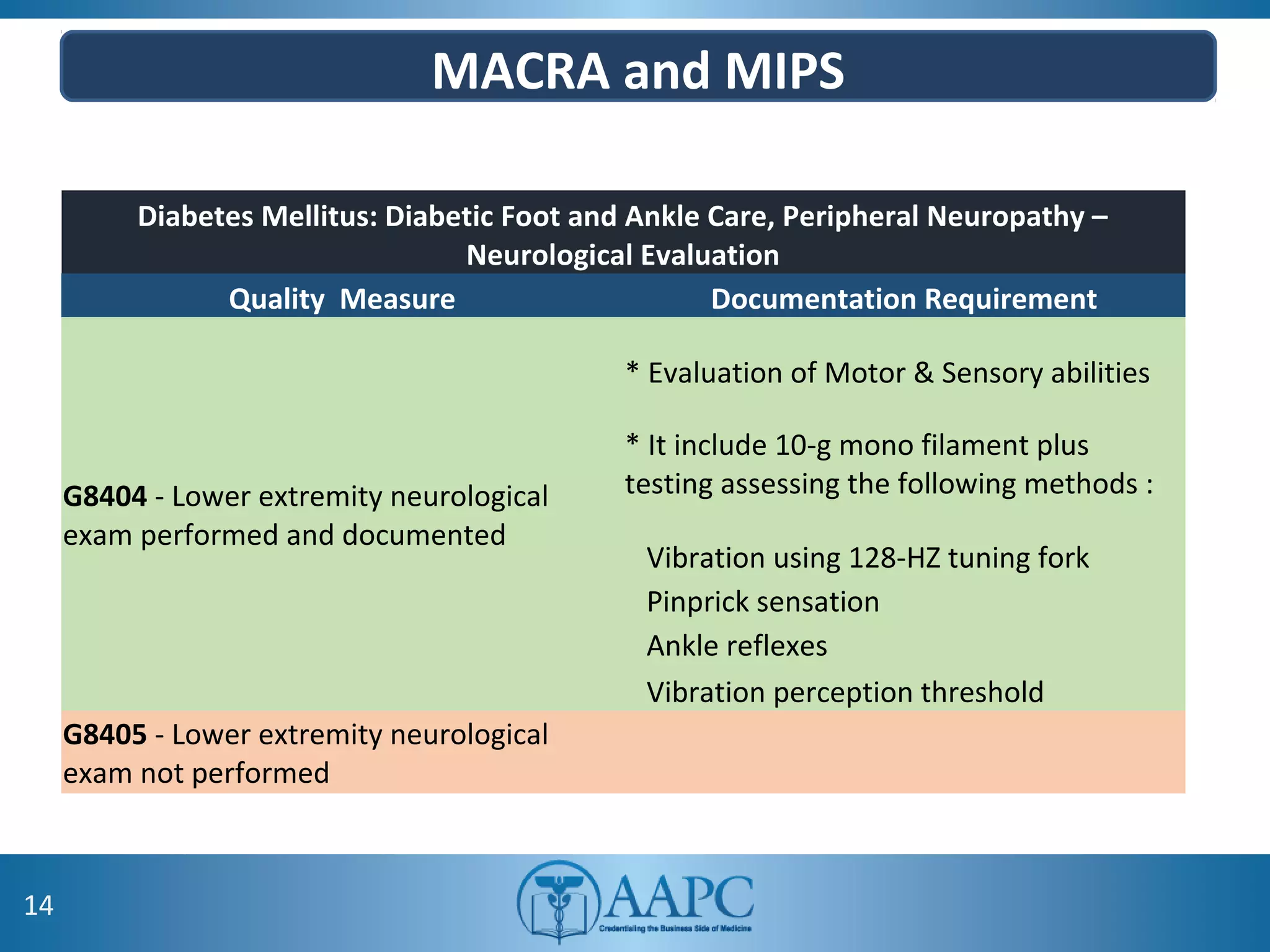
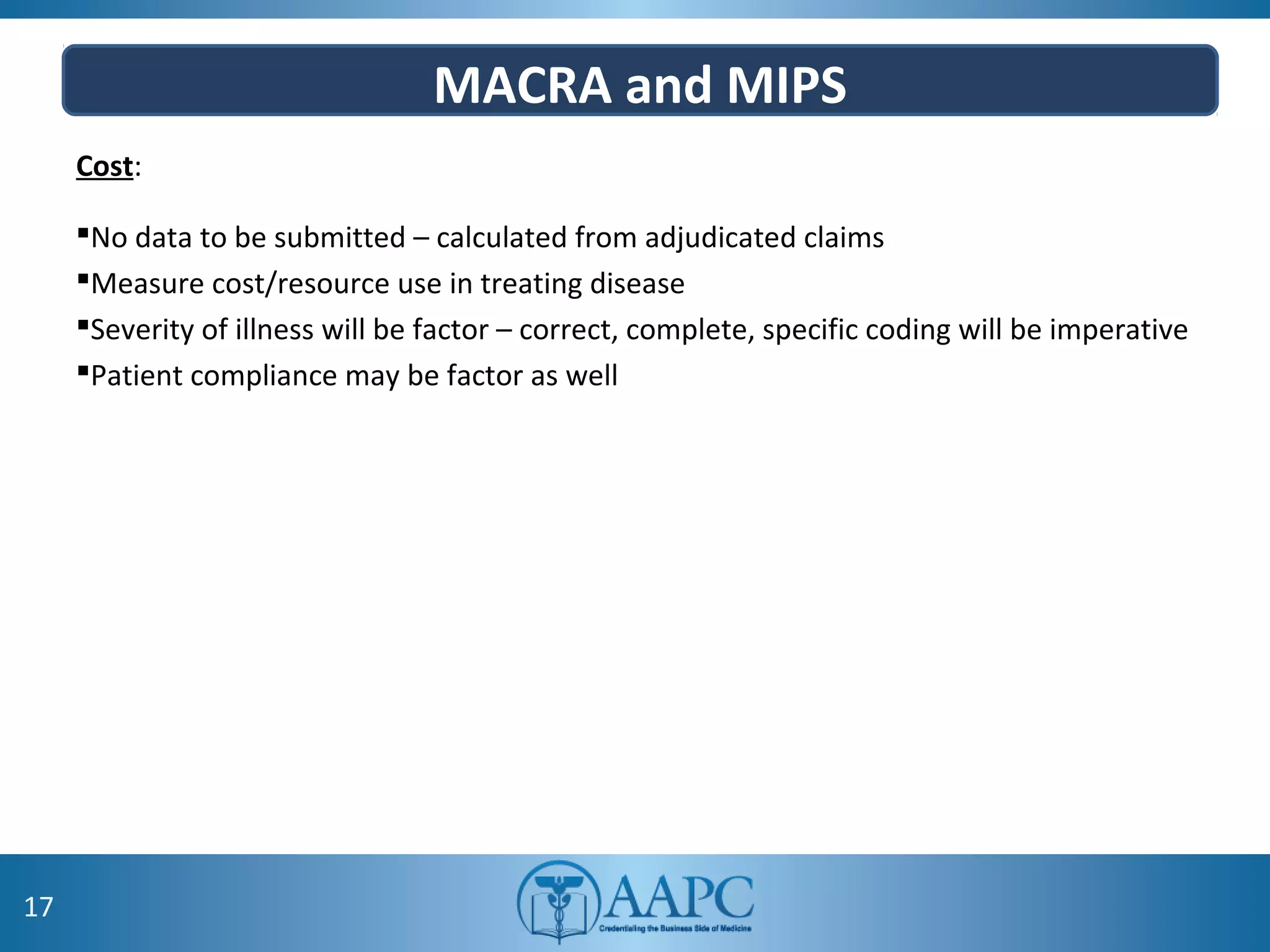
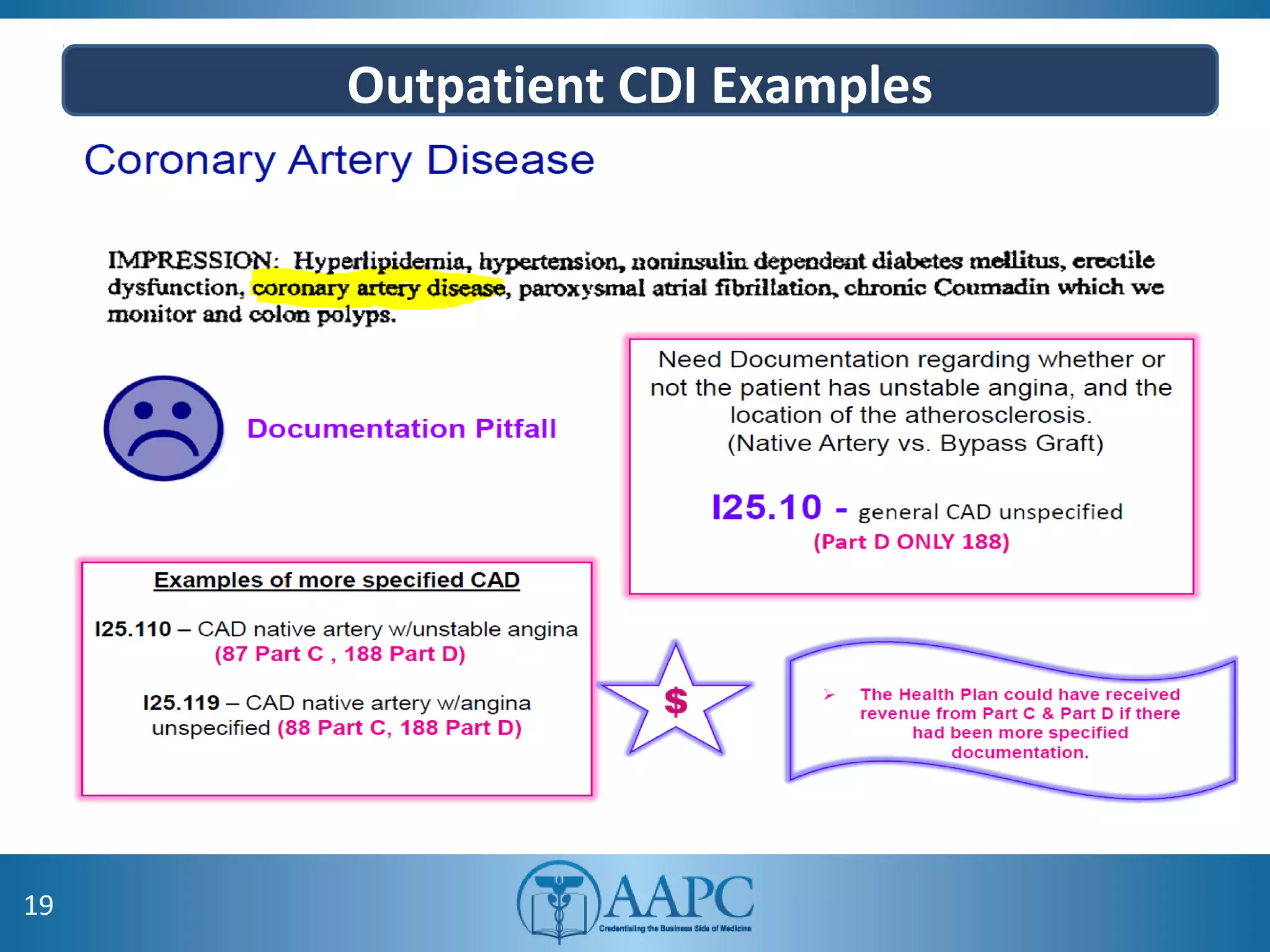
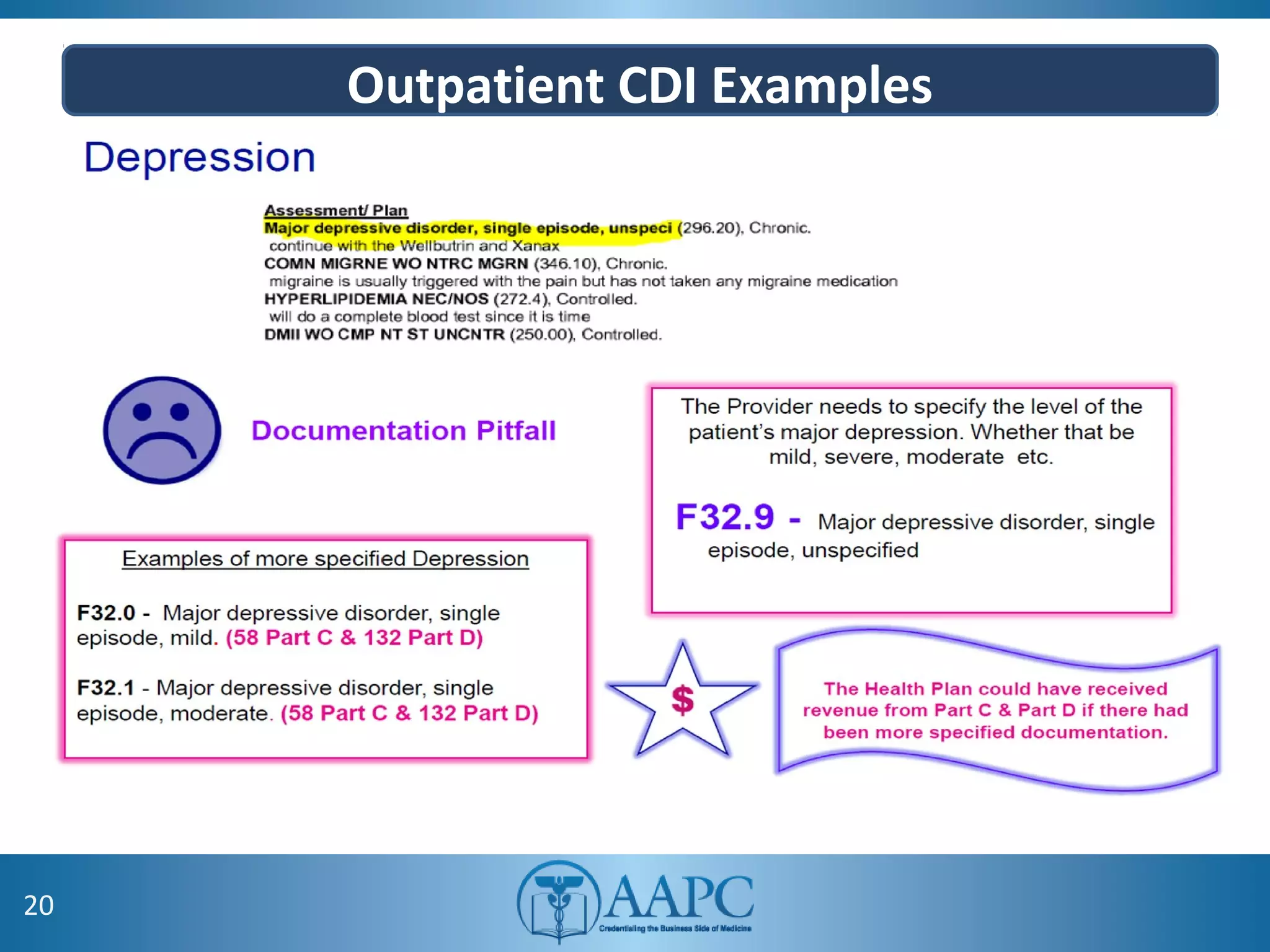
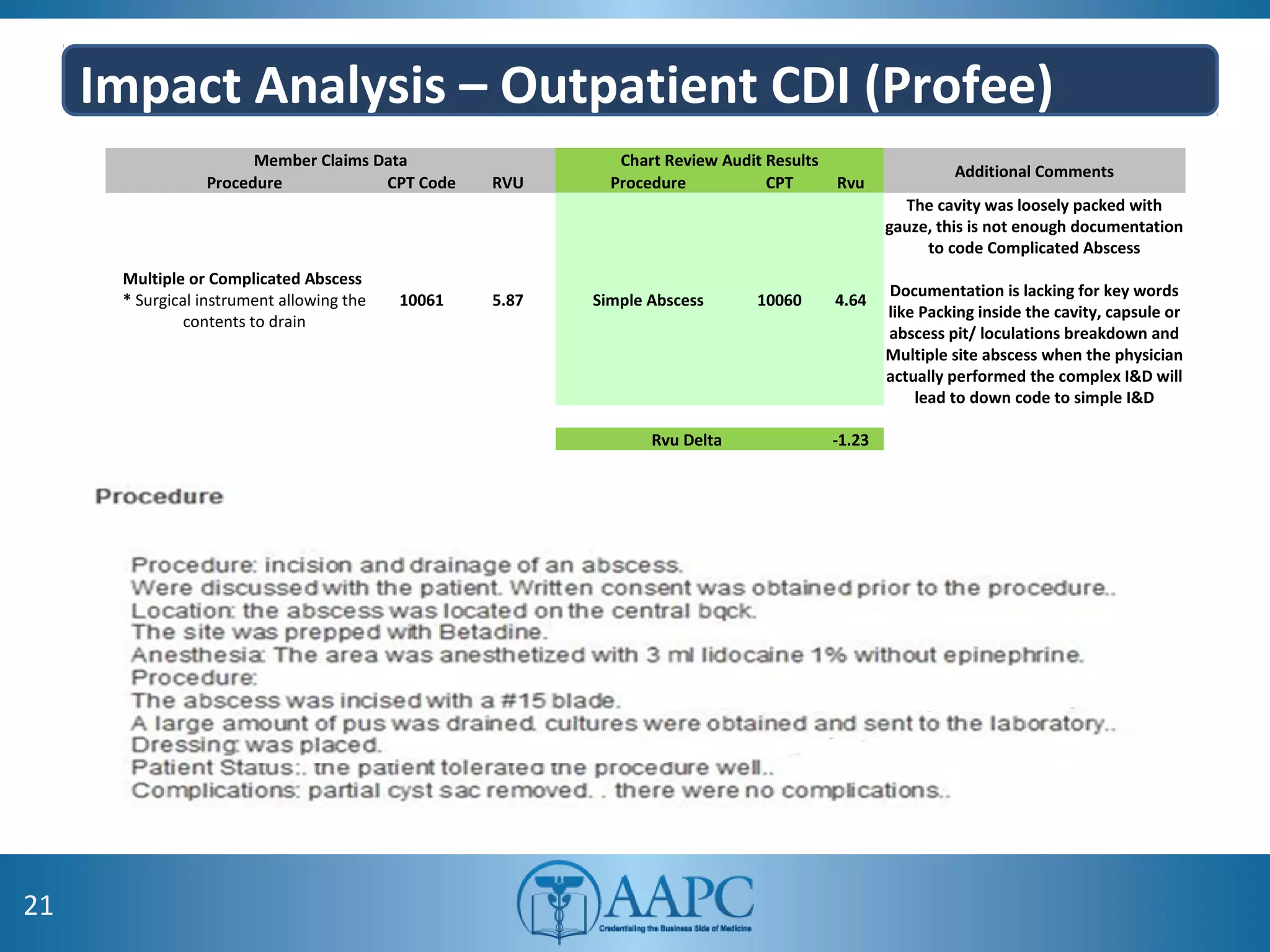
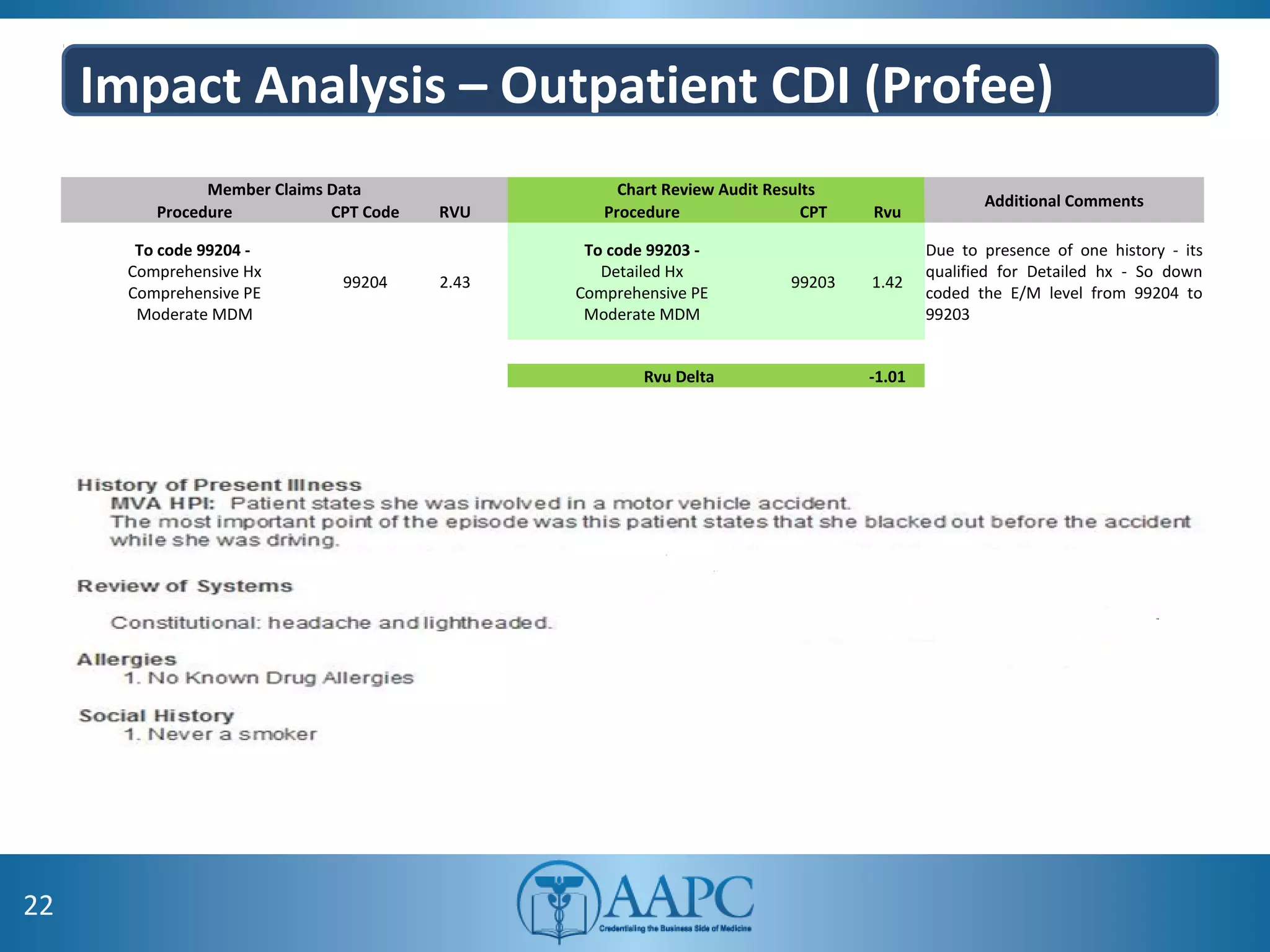
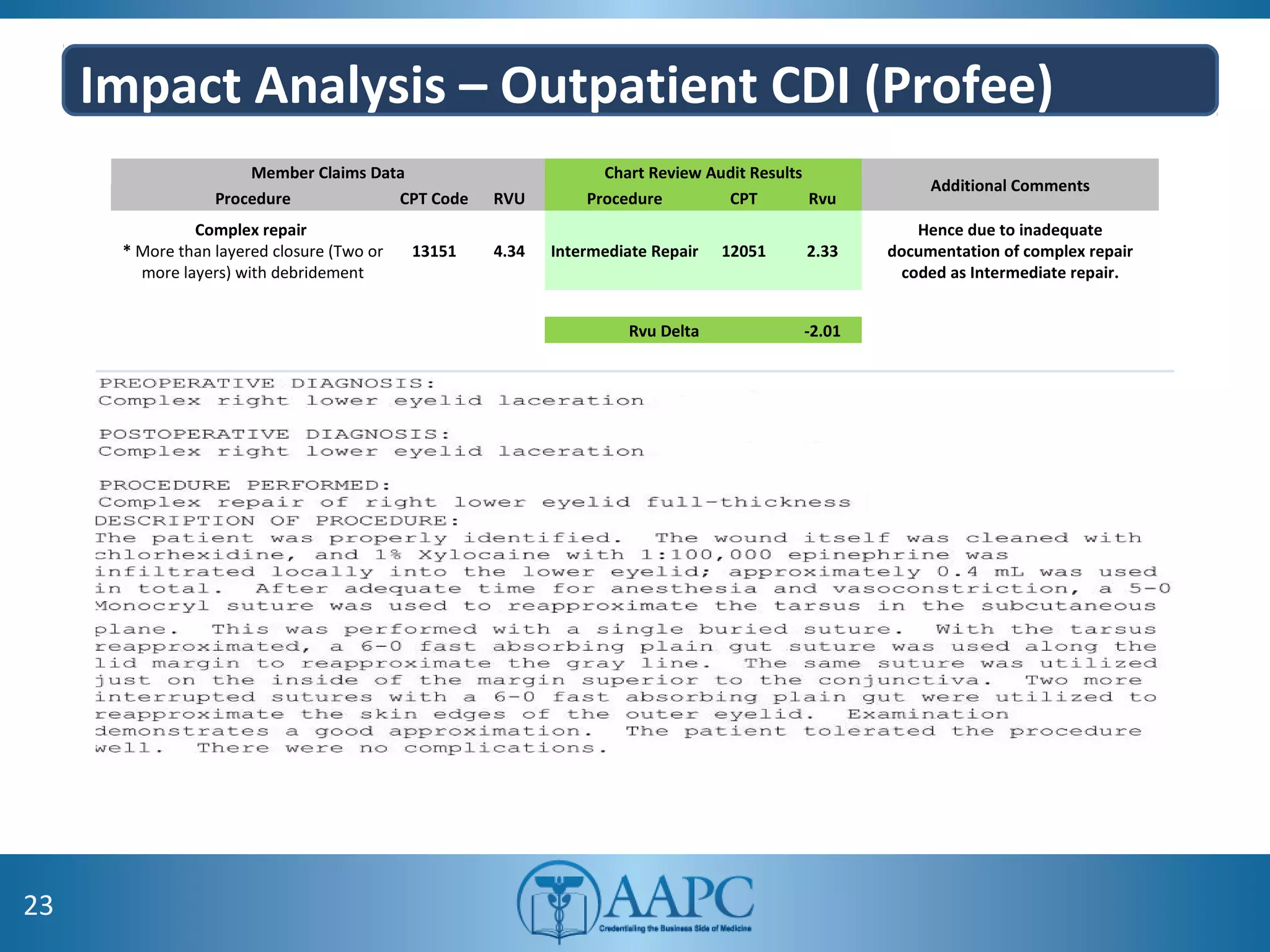
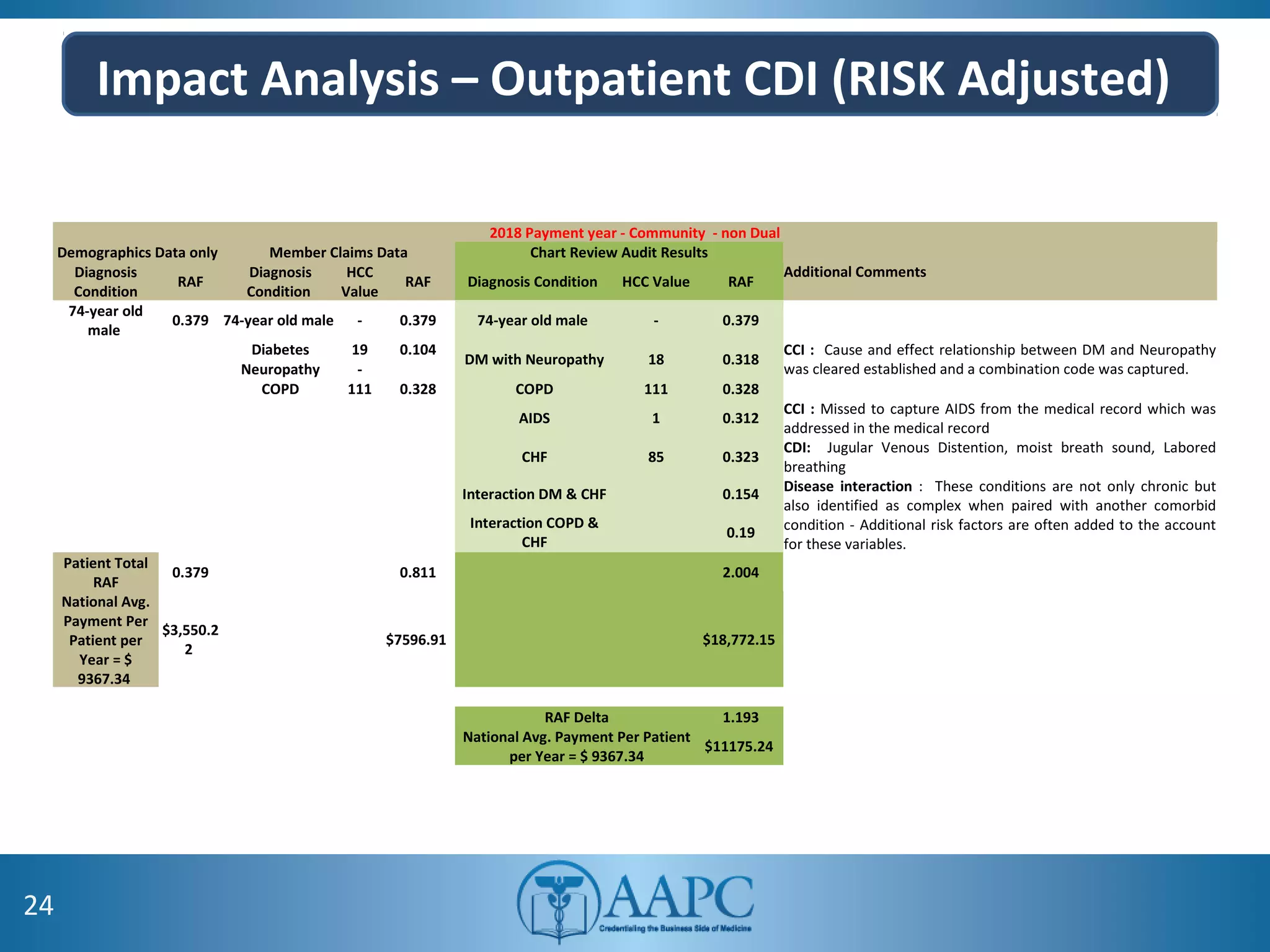
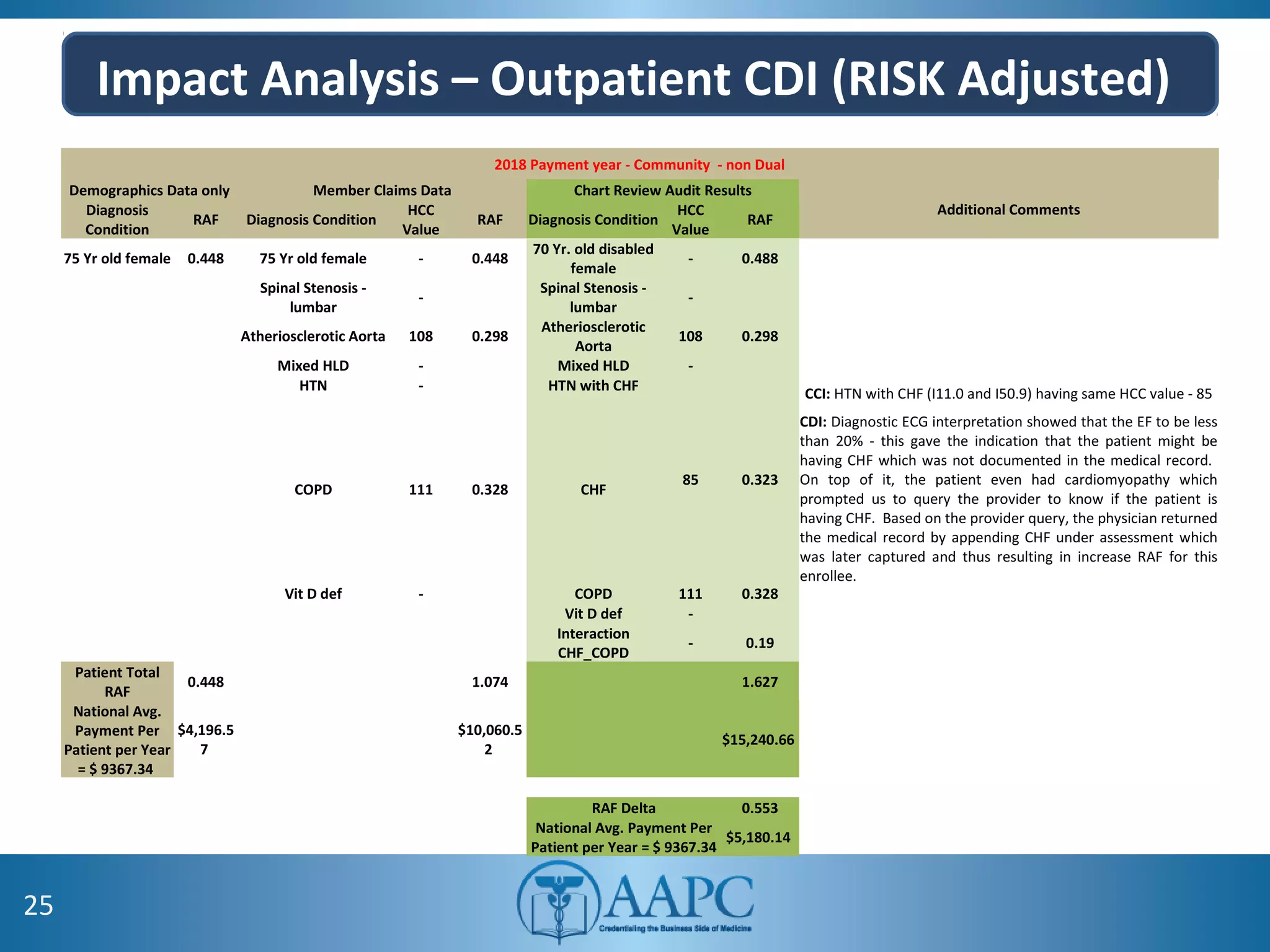
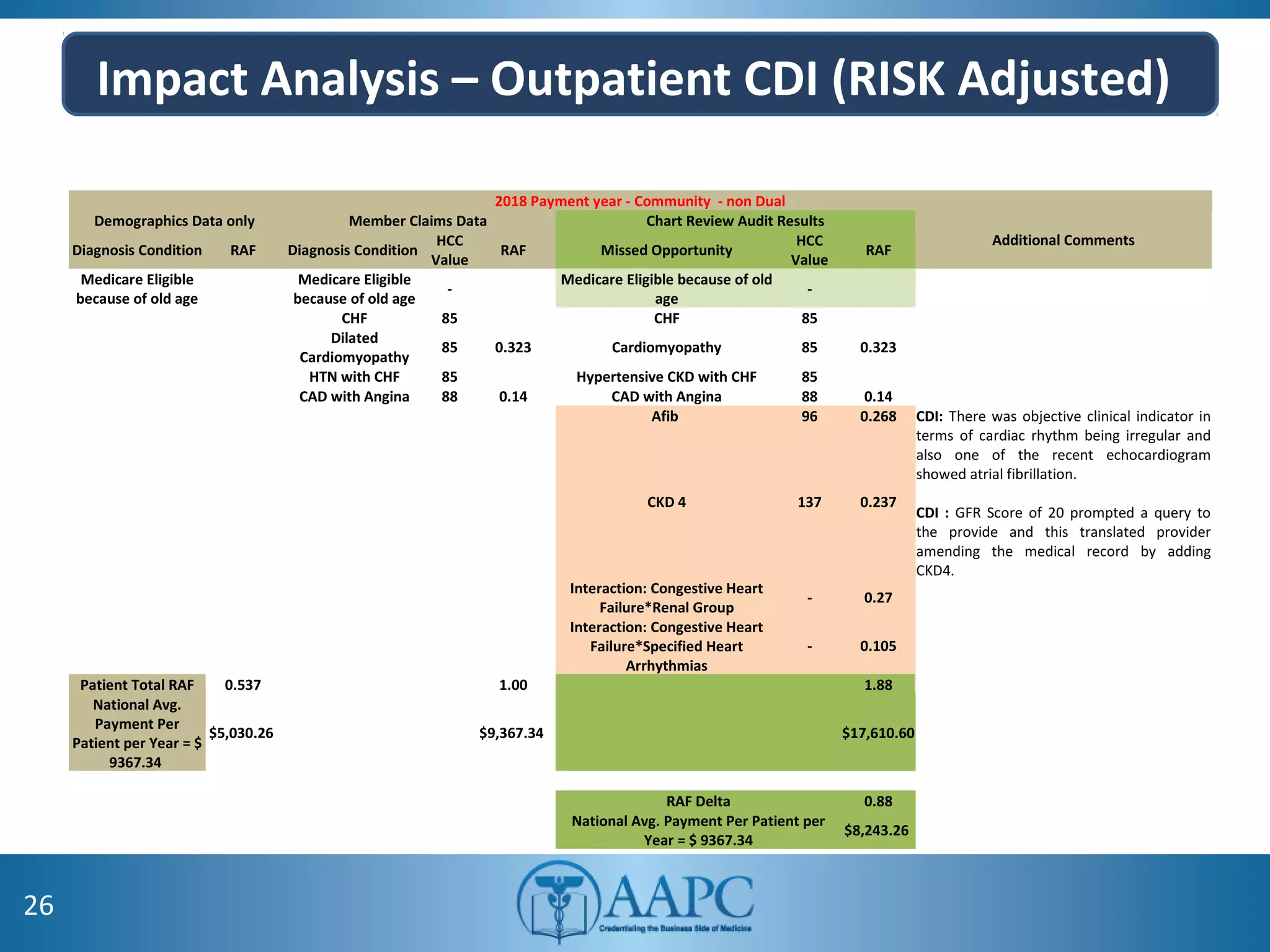
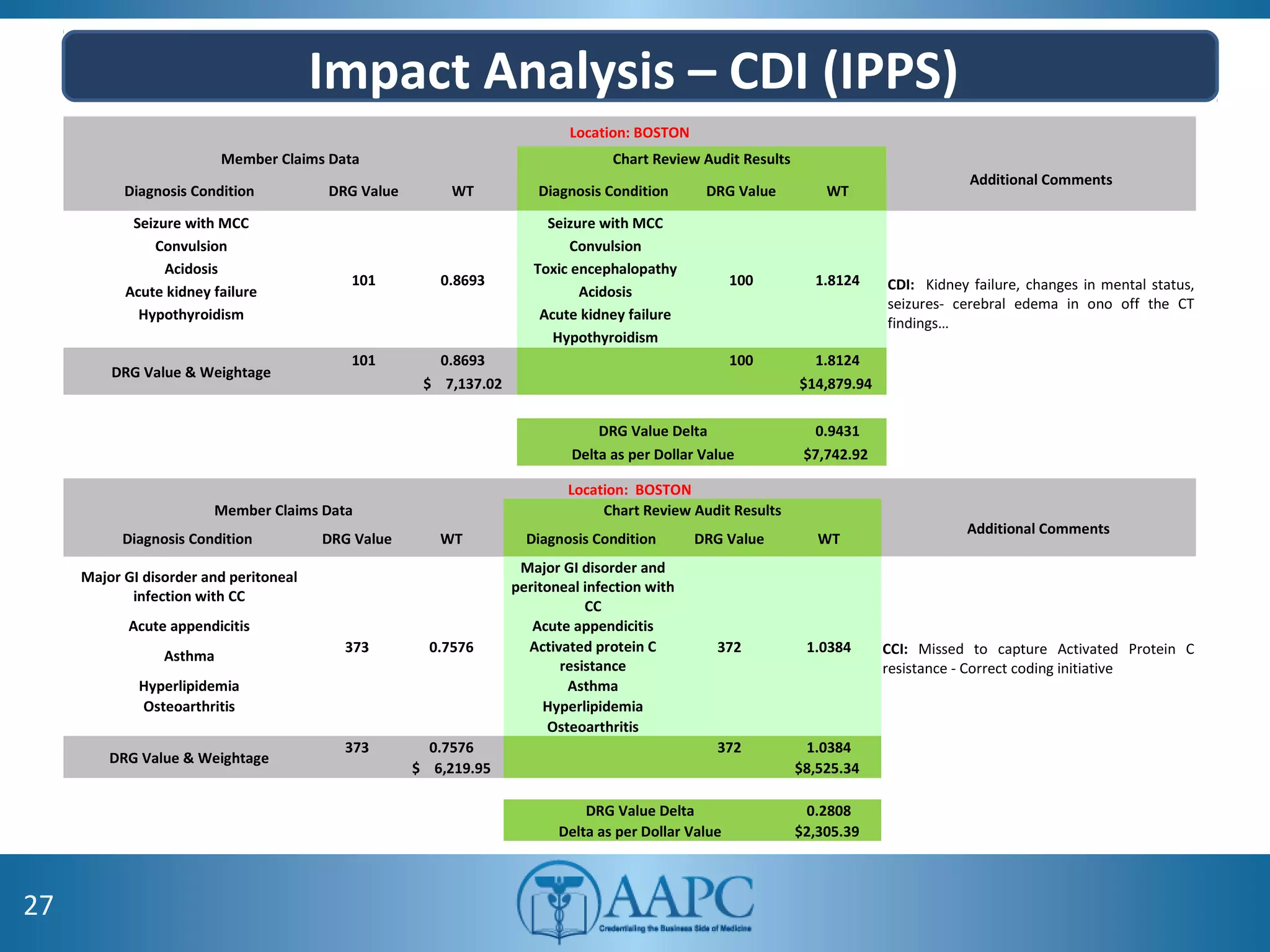
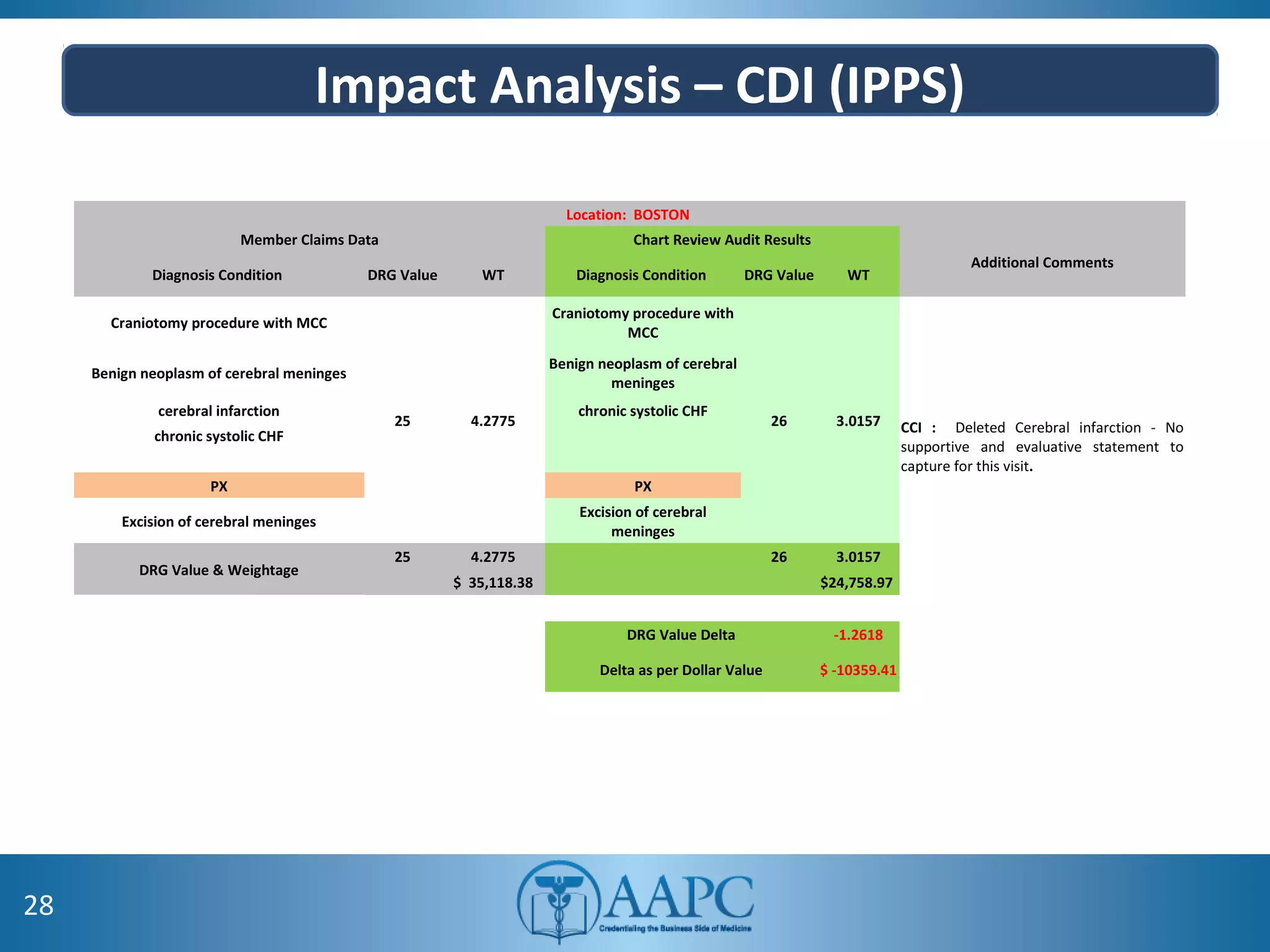
The value of clinical documentation improvement in a value-based reimbursement model is discussed. Physicians play a critical role in supporting the transition to value-based care through improved documentation. Value-based care combined with CDI can help achieve the goal of improved population health. CDI ensures accurate reimbursement under various models like IPPS, OPPS, FFS, and risk-adjusted models by capturing the right codes. It also impacts quality reporting programs like MIPS and helps achieve better health outcomes and cost savings. Examples are provided showing the impact of CDI on reimbursement through correcting coding at the outpatient level under different models.