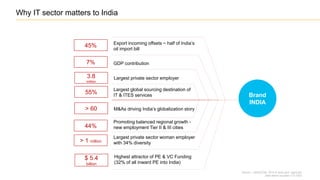
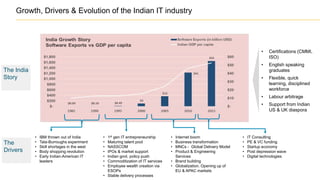
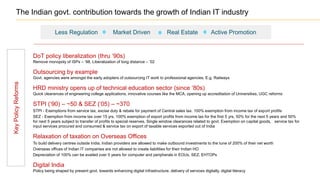
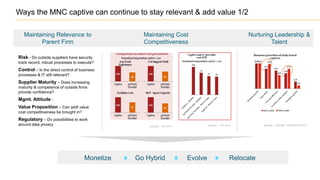
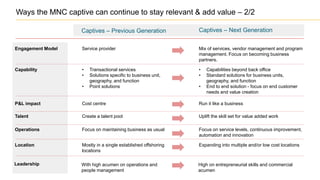
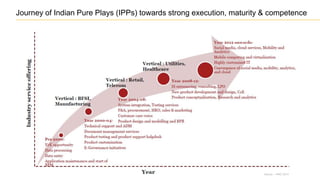
The document discusses the evolution of the Indian IT industry, emphasizing its significance as a major contributor to India's GDP and employment. It explores the opportunities and challenges faced by multinational IT captives and service providers in India, including evolving service models, cost pressures, and the need for innovation and skill development. Additionally, it highlights the impacts of government policies, market dynamics, and global trends on the industry's growth trajectory.