This document discusses the shift of businesses to cloud servers for their operations, highlighting the benefits like rapid deployment, cost efficiency, and scalability, while also addressing significant security concerns related to data stored on these platforms. It proposes a novel lightweight cryptographic algorithm for efficient data encryption and decryption that significantly reduces execution time compared to traditional methods like AES and RSA. Experimental results confirm the effectiveness of the proposed method in enhancing data security, achieving a notable performance improvement in encryption and decryption times.

![algorithm and encrypts the data [1]. The data is sent back to
the Gateway server after encryption which then sends the
encrypted data to another node containing Storage Manager
Gluster FS. This node in turn is connected to another node
containing many Docker containers, thus enabling the
distribution of the encrypted data in these containers. The
limitation is that an entire container is used for the
cryptographic purpose which is not advisable for data stored in
a mobile cloud platform.
File-based encryption is also incorporated as security
measures in the cloud. The file present on the device is
encrypted using password-based AES algorithm [2]. The user
has the provision to download the uploaded encrypted files.
Shortcomings of this framework are that the use of the
classical AES approach brings no novelty in the approach
proposed. Also, time taken for encryption and decryption is
more when applied to mobile cloud environment which is a
disadvantage and no comparison is made with respect to
throughput, time is taken for encryption and decryption.
There is also a scheme which first converts the plaintext
into their corresponding ASCII value and then the encryption
and decryption are performed using symmetric hybrid
approach [3]. But the scheme is only applicable for alphabets
and not for numbers and special characters. Also, there is no
comparison of time complexity with the existing methods like
AES and DES and incorporates the use of inverse matrix
operation in decryption algorithm which cannot be used in all
cases (i.e., the inverse of a matrix does not exist if the
determinant is zero).
The use of a secure encryption scheme using advanced
encryption scheme and fully homomorphic encryption in
cloud computing is also incorporated [4]. The user chooses a
passphrase which serves as a hint to the secret key that will be
used to encrypt the data. On entering the passphrase, the
system randomly generates a secret key from the chosen
passphrase. The first encryption process using AES of 128 bits
block size and a 256-bit key. After the first stage, the cipher
text and secret key are available. Next, an additive
homomorphic encryption is used to encrypt the cipher text
generated at the first stage and the secret key together. The
result of this stage generates another cipher text which is
stored in the cloud. But this method is not recommended for
large files because the homomorphic encryption process speed
is slow. The computations on large cipher texts are slower
than the computations on the plain text itself.
Achieving data privacy using the concept of division of
data through the use of Cloud Manager (CM) is one of the
ways to enhance the security in the cloud [5]. RSA is used to
encrypt the data. The encrypted data is then divided into
fragments and stored on different cloud servers. The Cloud
Manager (CM) manages the storage of the fragmented file on
a cloud server. But with the advancing technology, RSA is
subjected to various attacks and thus is not a reliable
cryptographic scheme due to its large computation time when
large prime numbers are involved in it.
Other data security methods such as homomorphic
encryption proposed by Rivest et al , wherein the cipher text
are much larger than the original plain text so system fails
drastically if the input is in the order of few Gigabytes or
Terabytes as it takes a considerable amount of time for
computation.
III. PROPOSED METHODOLOGY
The proposed method is as follows. The document
containing the confidential information is fed as the input
along with the key (secret key) for encryption. The algorithm
makes use of symmetric encryption model wherein the same
key should be used at the time of decryption the document (or
original message). The encrypted document is then stored in
cloud When the user wants to retrieve the document, the
document should be downloaded from the cloud servers and
decryption algorithm is used to get the original message
document, with the help of the same secret key used in
encryption. If the key is mismatched then the decrypted
message will not be same as original , thereby the intruder
cannot get to know which is the original message as for all the
combination of the keys some message will be shown after
decryption.
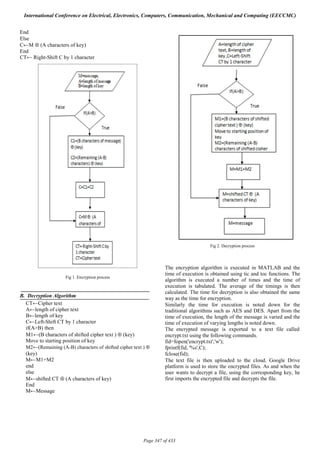
The proposed algorithm is explained as follows. The
encryption technique makes use of the length of the message,
say A, and the length of the key, say B, which is first
compared. If the length of the message is greater than the
length of the key, first B characters of the message are XORed
with the key. Then, the remaining (A-B) characters of the
message are XORed with the key. The two results are then
combined to get the intermediate message. If the length of the
message is less than the length of the key,the shifted cipher
text is XORed with first A characters of the key to get the
intermediate message. The intermediate message is then
shifted by one character to the right to get the encrypted
message.The decryption technique is as follows. The cipher
text is first shifted by one character to the left. The length of
the cipher text, say A, and the length of the key,say B, is then
compared. If the length of the cipher text is greater than the
length of the key, first B characters of the shifted cipher text
are XORed with the key. Then, the remaining (A-B)
characters of the shifted cipher text are XORed with the key.
The two results are then combined to get the decrypted
message. If the length of the ciphertext is less than the length
of the key, the shifted cipher text is XORed with first A
characters of the key. The result of the XOR operation is
decrypted message. The encryption and the decryption flow
algorithm is shown in figure 1 and figure 2 respectively.
A. Encryption Algorithm
M←message
A←length of message
B←length of key
CT←Cipher Text
if(A>B) then
C1←(B characters of message) ⊕ (key)
Move to starting position of key
C2←(Remaining (A-B) characters) ⊕
(key)
C←C1+C2
International Conference on Electrical, Electronics, Computers, Communication, Mechanical and Computing (EECCMC)
Page 346 of 433](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/proceeding1700-200119065756/85/A-Novel-Approach-for-Data-Security-in-Cloud-Environment-2-320.jpg)
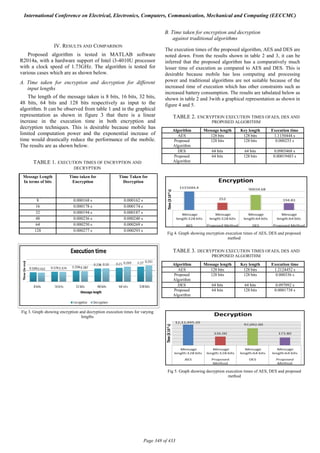
![C. Cryptanalysis strength against brute force attack
The plain text and the key is used to produce cipher text
using AES, DES, Blow Fish, and the proposed algorithm and
a brute force search space is analyzed.
TABLE 4. BRUTE FORCE SEARCH SPACE ANALYSIS
Key used
Brute force
Algorith [in Plain Cipher Text
Search space
m hexadecima Text produced
analysis
l]
0368945f11
AES[12 1d0cbfc8a1 Good 7Ucho3w+xc1zM 2.95 x 1047
8 bit] 3886fd6ebf Morning QspXUVPLw==
5d
0368945f11
DES 1d0cbfc8a1 Good T0DxqUAivx37R 2.95 x 1047
3886fd6ebf Morning 6YgnCCrEw==
5d
0368945f11
Blow 1d0cbfc8a1 Good nLWGjYn+W2ic 2.95 x 1047
Fish 3886fd6ebf Morning CcW4P2iEpA==
5d
Propose 0368945f11
d 1d0cbfc8a1 Good wY^YyZ^T_X_ 3.81 x 1043
Algorith 3886fd6ebf Morning ^C0cbf
m 5d
From the above analysis shown in table 4, it can be proved
that the proposed algorithm is comparatively strong and is
competent with the AES, DES and blowfish algorithm as
search space for attacking is very close.
V. CONCLUSION
Data Security and privacy are one of the major issues that
exist in all levels of cloud service. A new method for securing
data is proposed to increase the efficiency of storage and
retrieval in cloud .The proposed model is tested and the results
showcase that the proposed data security model is light weight
in terms of time taken for encryption and decryption and is
98.7% faster as compared existing methods such as AES and
DES. Brute force search space analysis shows that the search
space for attacking is considerably on par with AES and DES
algorithm hence time taken to crack the cipher text in
traditional methods and the proposed methods are same as
shown in the above results and comparisons.
REFERENCES
[1] R. R. Gupta et al., "Data storage security in cloud computing using
container clustering," 2016 IEEE 7th Annual Ubiquitous Computing,
Electronics & Mobile Communication Conference (UEMCON), New
York, NY, 2016, pp. 1-7.
[2] B. Thiyagarajan and R. Kamalakannan, "Data integrity and security in
cloud environment using AES algorithm," International Conference on
Information Communication and Embedded Systems (ICICES2014),
Chennai, 2014, pp. 1-5.
[3] S. Kaushik and C. Gandhi, "Cloud data security with hybrid symmetric
encryption," 2016 International Conference on Computational
Techniques in Information and Communication Technologies
(ICCTICT), New Delhi, 2016, pp. 636-640.
[4] K. B. P. Iyer, Manisha R, Subhashree R and Vedhavalli K, "Analysis of
data security in Cloud Computing," 2016 2nd International Conference
on Advances in Electrical, Electronics, Information, Communication and
Bio-Informatics (AEEICB), Chennai, 2016, pp. 540-543.
[5] S. Manjula, M. Indra and R. Swathiya, "Division of data in cloud
environment for secure data storage," 2016 International Conference on
Computing Technologies and Intelligent Data Engineering
(ICCTIDE'16), Kovilpatti, 2016, pp. 1-5.
[6] M. K. Sarkar and Trijit Chatterjee, “Enhancing Data Storage Security in
Cloud Computing Through Steganography”, ACEEE Int. J. on Network
Security, Vol. 5, No. 1, Jan 2014, pp. 13-19.
[7] Sidhu, Aparjita, and Rajiv Mahajan. "Research Article Enhancing
Security In Cloud Computing Structure By Hybrid Encryption."
International Journal of Recent Scientific Research 5 (2014): 128-132.
[8] A. Bhagat and R. Kant Sahu, "Cloud Data Security While using Third
Party Auditor", International Journal of Computer Applications, vol. 70,
no. 16, , 2013, pp. 9-13.
[9] Dastjerdi, Amir Vahid, Kamalrulnizam Abu Bakar, and Sayed Gholam
Hassan Tabatabaei. "Distributed intrusion detection in clouds using
mobile agents." Advanced Engineering Computing and Applications in
Sciences, 2009. ADVCOMP'09. Third International Conference on.
IEEE, 2009
[10] Singla, Sanjoli, and Jasmeet Singh. "Cloud data security using
authentication and encryption technique." Global Journal of Computer
Science and Technology 13.3 (2013).
[11] V .Yadav and P. Aggarwal, “Fingerprinting Based Recursive
Information Hiding Strategy in Cloud Computing Environment”
International Journal of Computer Science and Mobile Computing,
Vol.3 Issue.5, May- 2014, pg. 702-707
[12] Rishav Ray, Jeeyan Sanyal, Debanjan Das, Asoke Nath. “A new
Challenge of hiding any encrypted secret message inside any
Text/ASCII file or in MS word file: RJDA Algorithm”. 2012 IEEE
International Conference on Communication Systems and Network
Technologies
[13] Nath, Joyshree, et al. "New Steganography algorithm using encrypted
secret message." Proceedings of Worldcomp 2011 Held at Las Vegas
(USA), 18-21 Jul, 2011 (2011).
[14] Nath, Joyshree. "A challenge in hiding encrypted message in LSB and
LSB+ 1 bit positions in various cover files." Journal of global research
in computer science 2.4 (2011): 180-185.
[15] S. Manjula, M. Indra and R. Swathiya, "Division of data in cloud
environment for secure data storage," 2016 International Conference on
Computing Technologies and Intelligent Data Engineering
(ICCTIDE'16), Kovilpatti, 2016, pp. 1-5.
[16] M. Ahmadi, F. Fatemi Moghaddam, A. J. Jam, S. Gholizadeh and M.
Eslami, "A 3-level re-encryption model to ensure data protection in
cloud computing environments," 2014 IEEE Conference on Systems,
Process and Control (ICSPC 2014), Kuala Lumpur, 2014, pp. 36-40.
[17] K. V. Raipurkar and A. V. Deorankar, "Improve data security in cloud
environment by using LDAP and two way encryption algorithm," 2016
Symposium on Colossal Data Analysis and Networking (CDAN),
Indore, 2016, pp. 1-4.
[18] Jayapandian, A. M. J. M. Z. Rahman, M. Koushikaa and S.
Radhikadevi, "A novel approach to enhance multi level security system
using encryption with fingerprint in cloud," 2016 World Conference on
Futuristic Trends in Research and Innovation for Social Welfare
(Startup Conclave), Coimbatore, 2016, pp. 1-5.
[19] Nath, Joyshree, and Asoke Nath. "Advanced Steganography Algorithm
using encrypted secret message." International journal of advanced
computer science and applications 2.3 (2011).
[20] Gampala, Veerraju, Srilakshmi Inuganti, and Satish Muppidi. "Data
security in cloud computing with elliptic curve cryptography."
International Journal of Soft Computing and Engineering (IJSCE) 2.3
(2012): 138-141.
International Conference on Electrical, Electronics, Computers, Communication, Mechanical and Computing (EECCMC)
Page 349 of 433](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/proceeding1700-200119065756/85/A-Novel-Approach-for-Data-Security-in-Cloud-Environment-5-320.jpg)