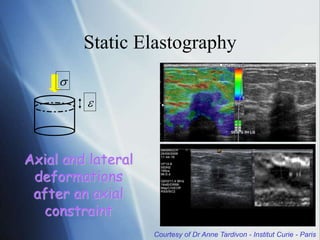
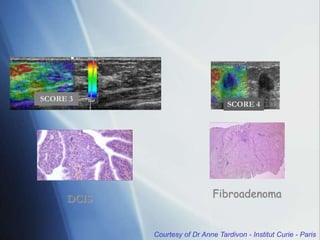
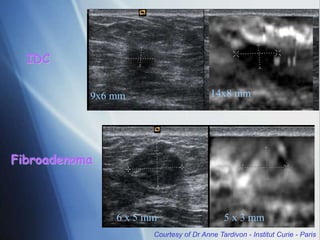
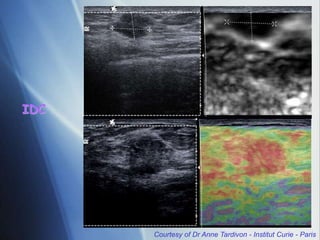
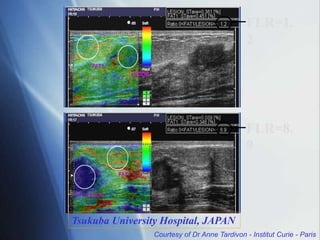
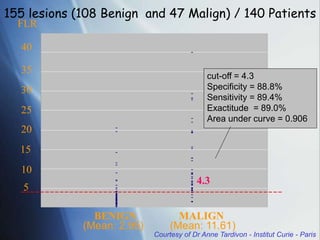
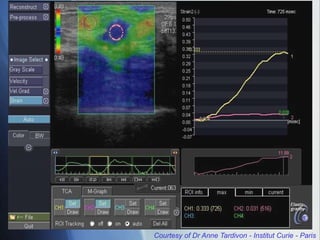
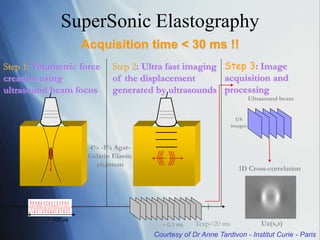
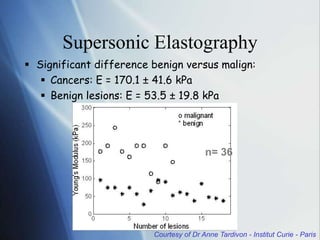
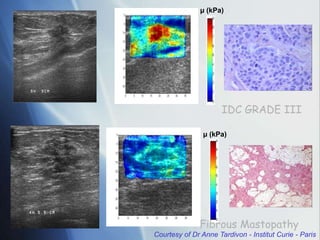
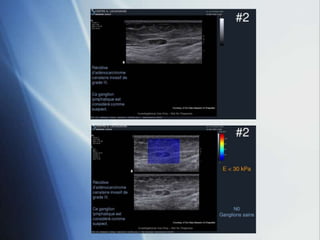
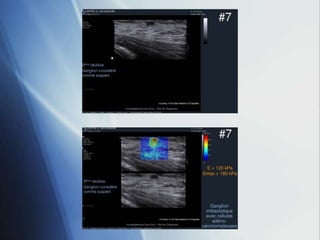
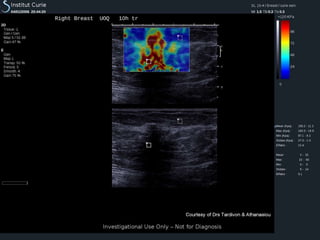
This document discusses a new ultrasound modality called elastography, which measures the stiffness of tissues. Elastography was developed to provide quantitative measurements of tissue elasticity, building on the ancient medical practice of palpation. Various methods are described, including static elastography using manual compression, shear wave elastography using focused ultrasound pulses, and potential applications in breast, thyroid, liver and prostate imaging. The document calls for including elastography data in DICOM to allow storage and sharing of these images and quantitative measurements as the technique gains clinical use.