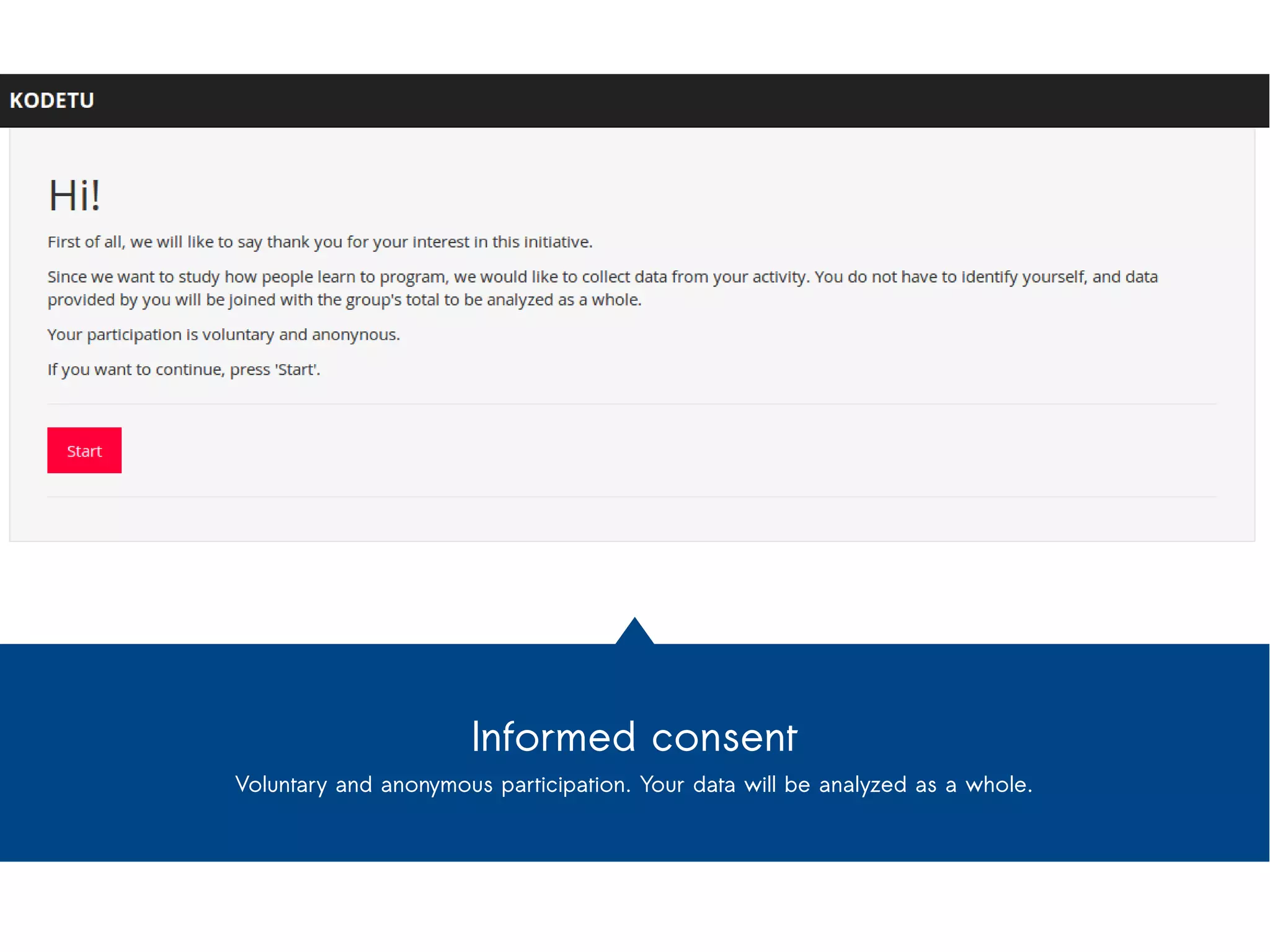
This document discusses the technical benefits and privacy risks of using HTML5 APIs for multimodal learning analytics on mobile devices. It describes how APIs that provide access to device sensors and information could provide insights about learning processes but also raise privacy issues if personal data is not properly anonymized and consent is not obtained. The document advocates for balancing these benefits and risks through practices like informed consent, voluntary and anonymous data collection, and ensuring data is only used to benefit students.