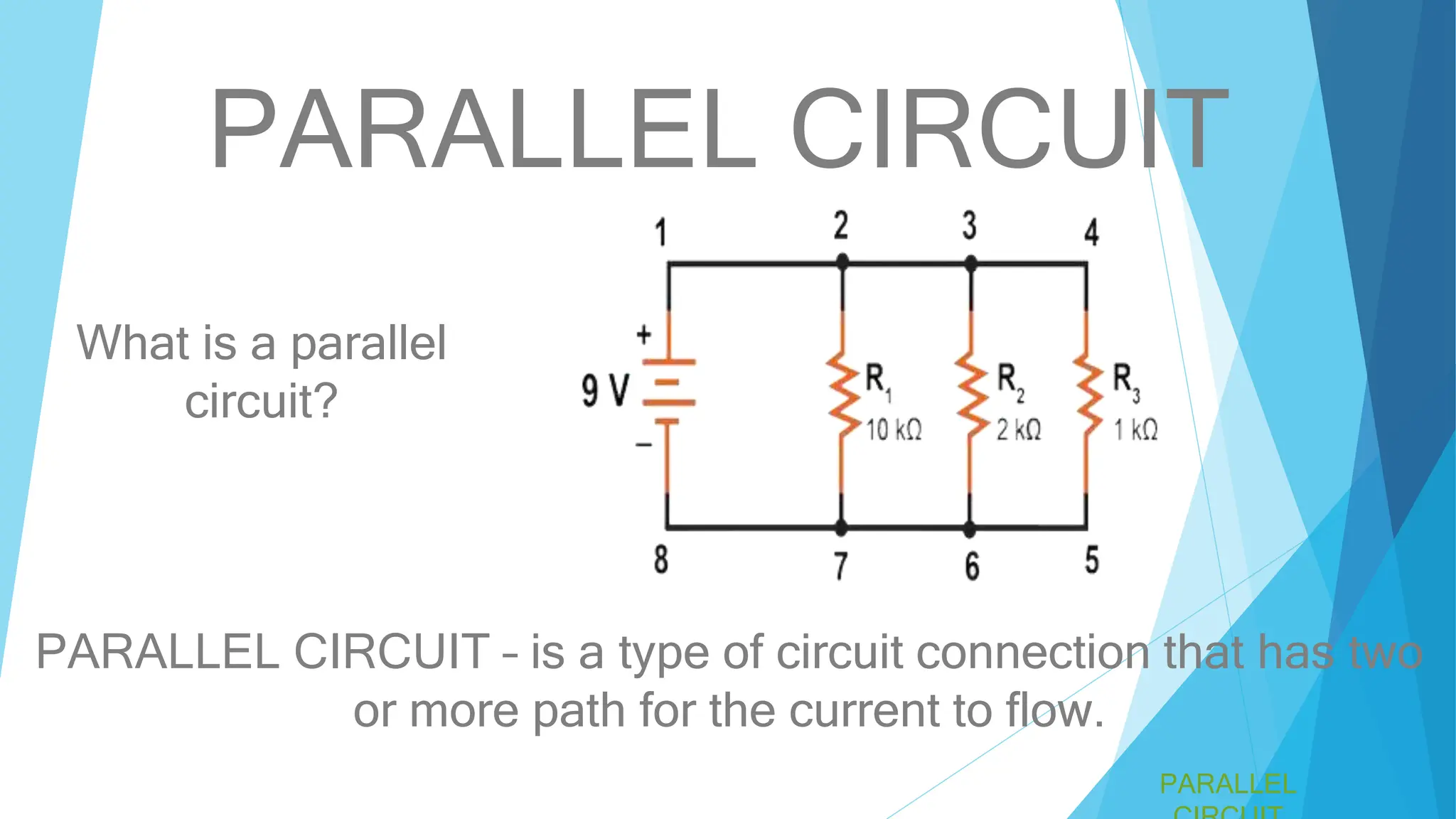
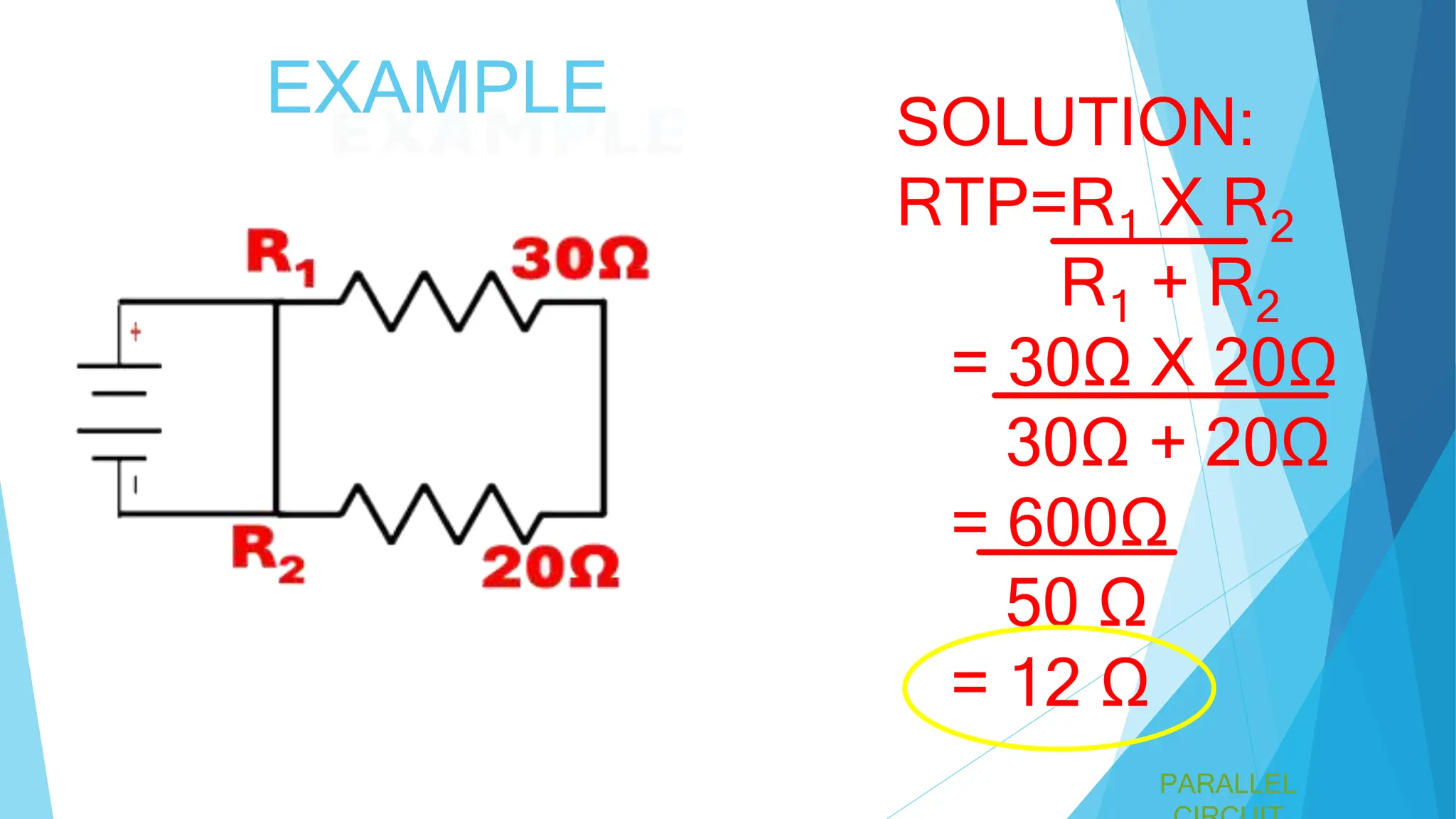
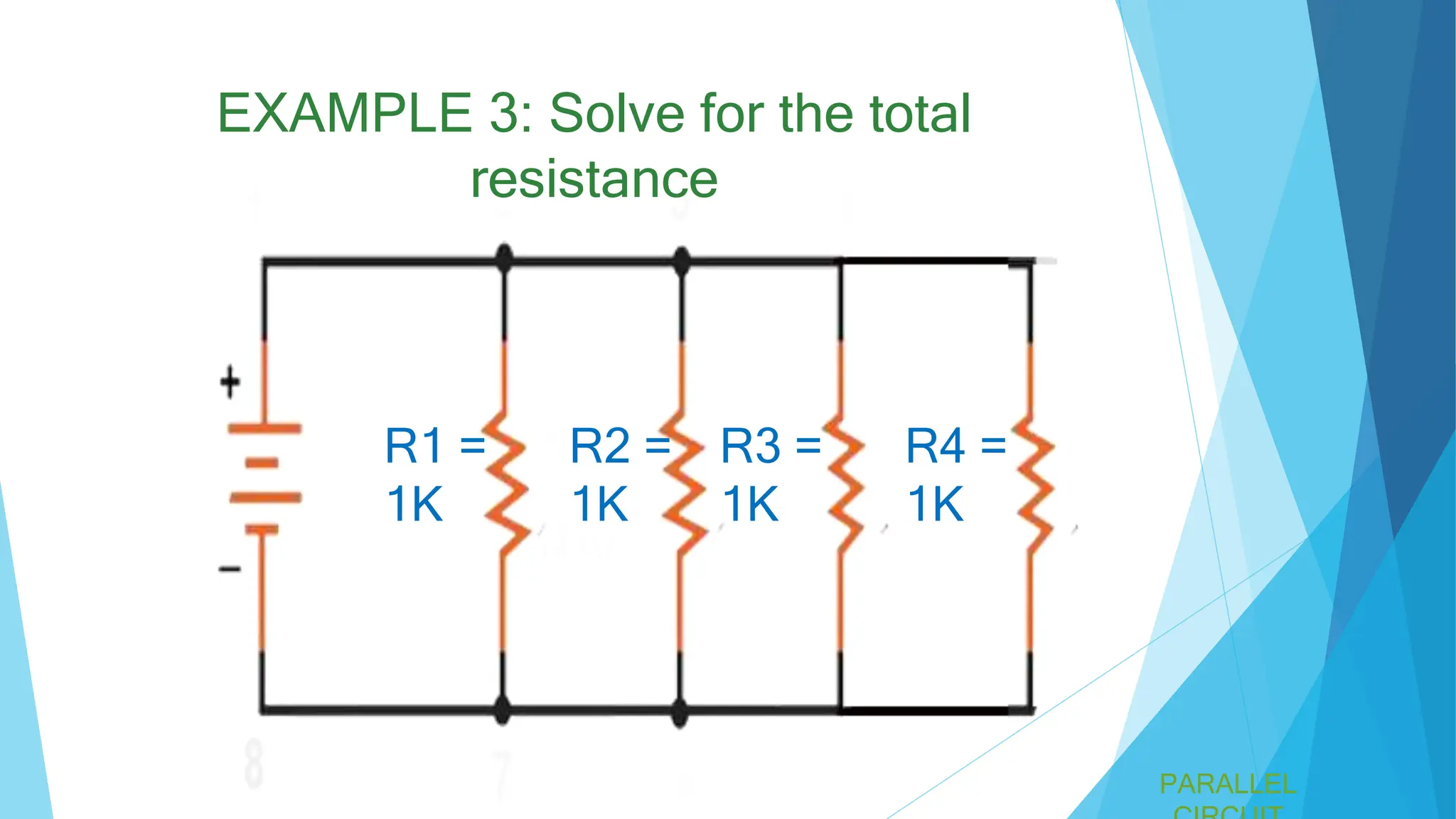
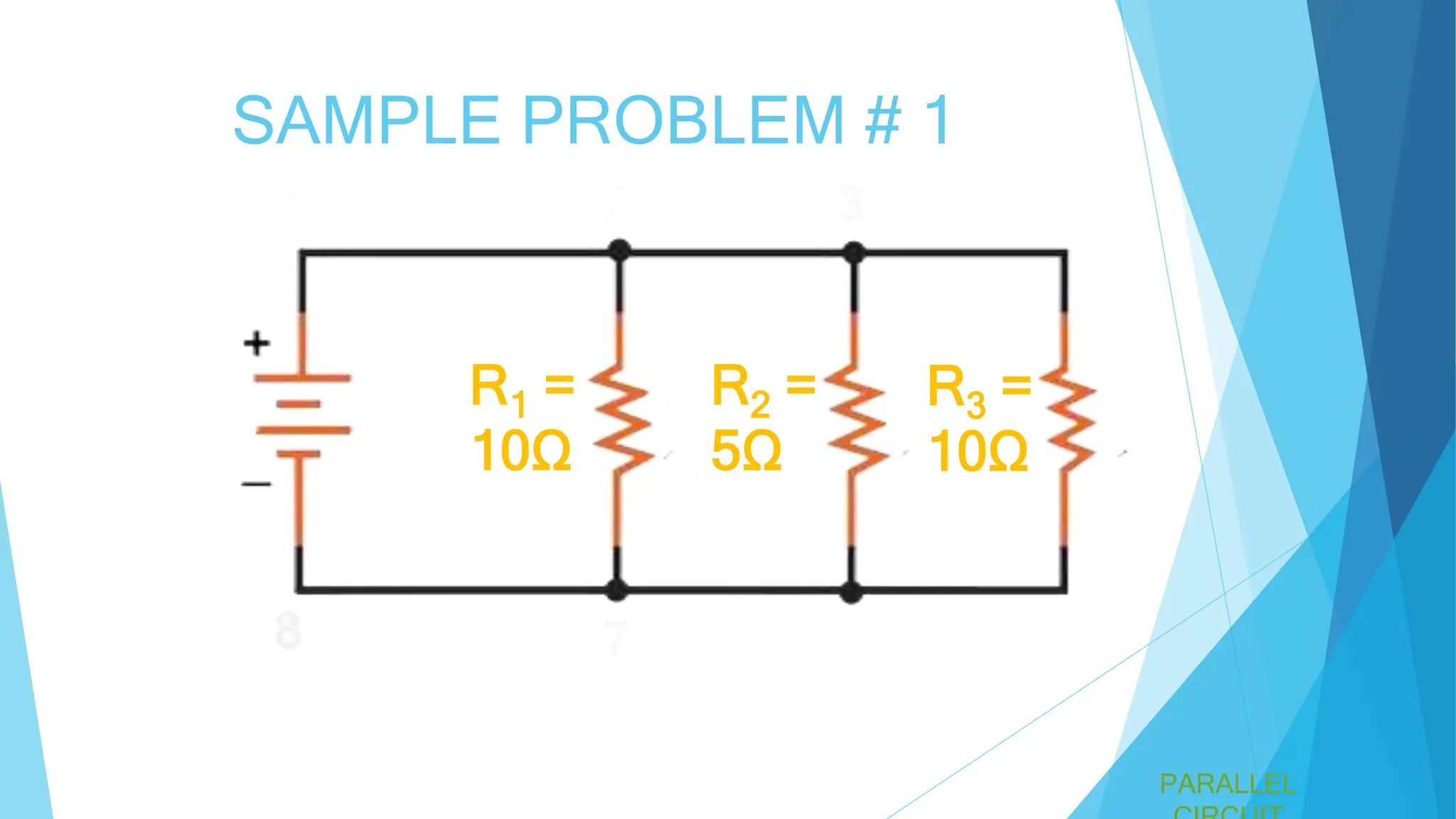
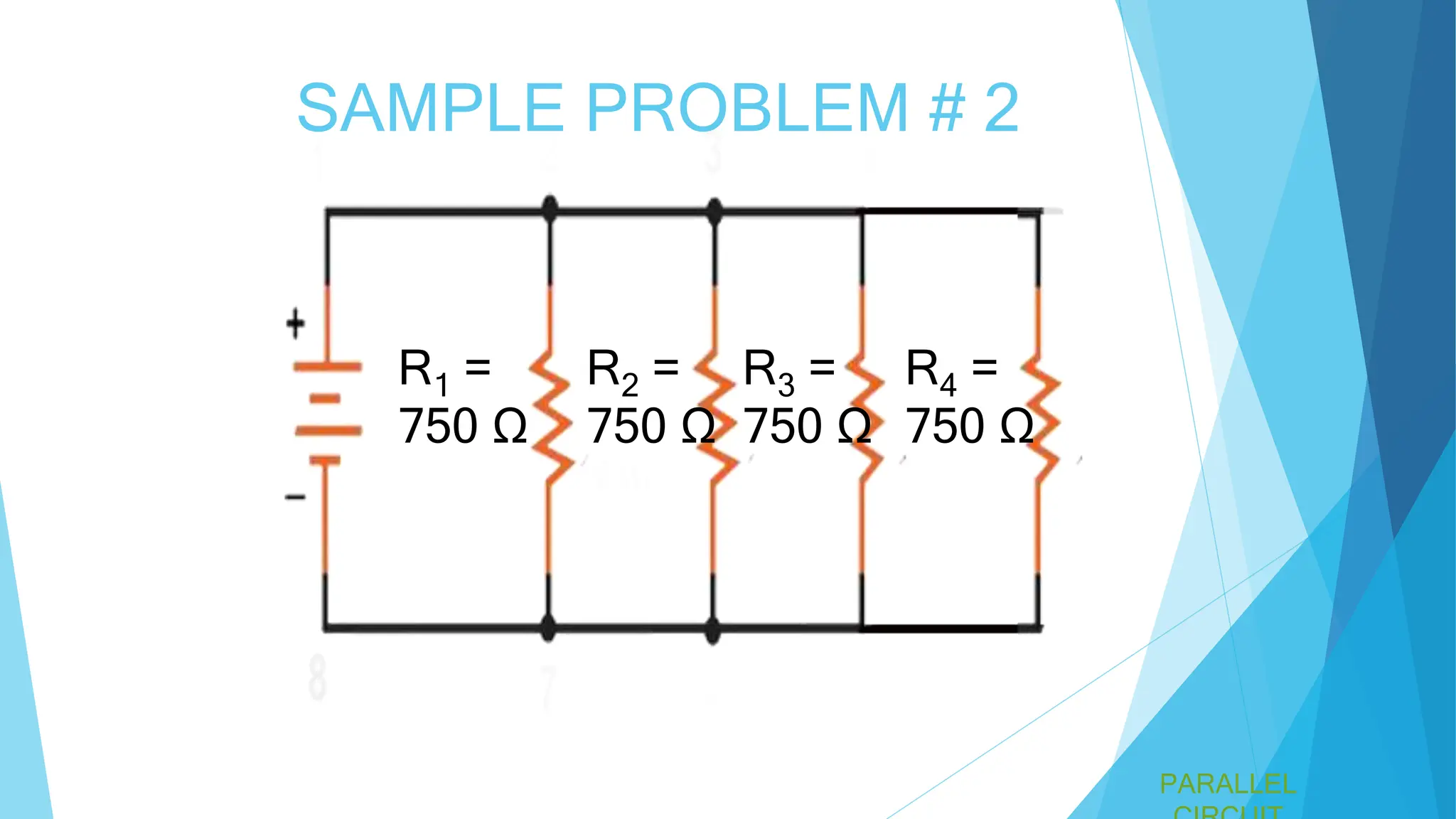
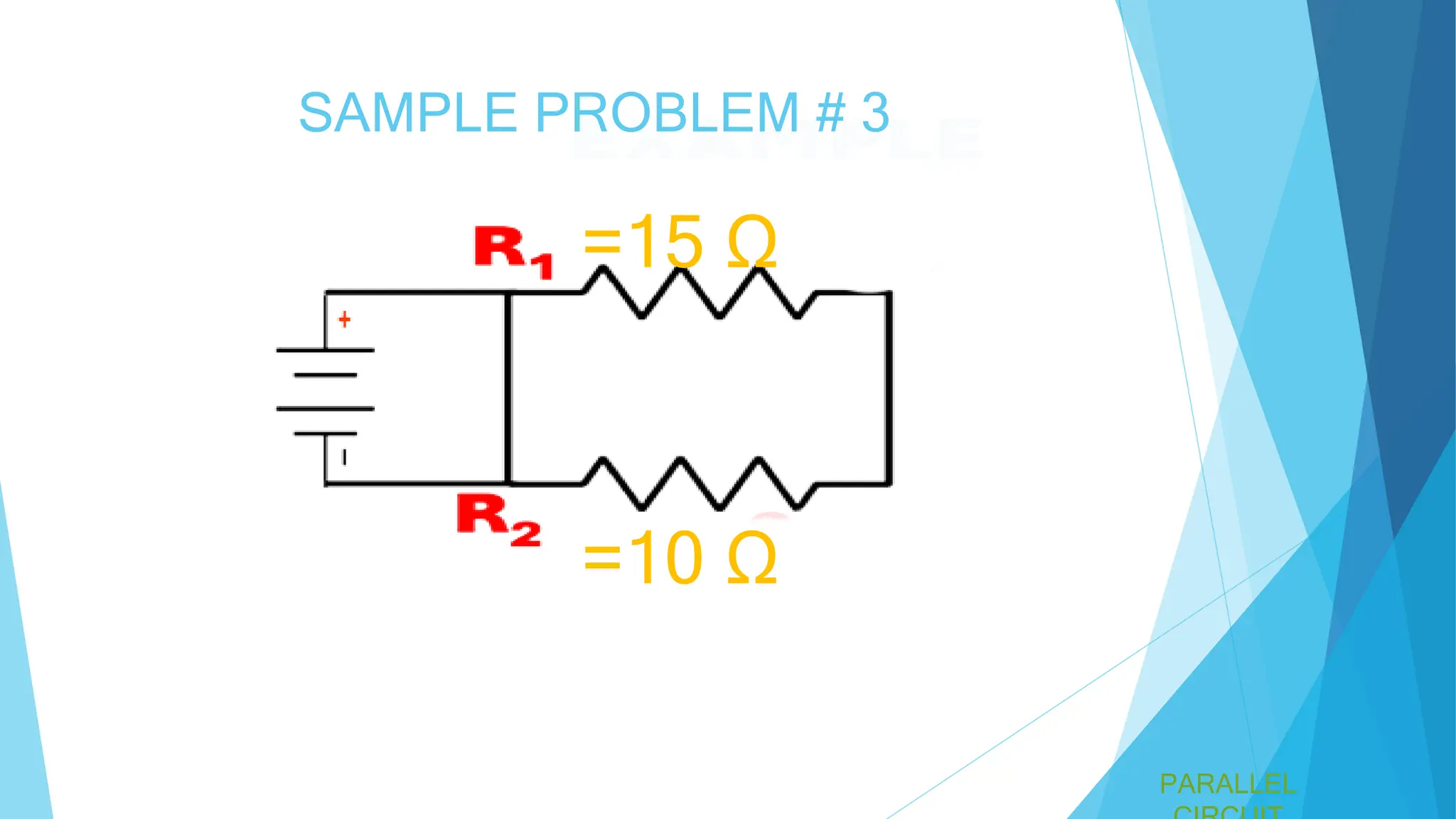
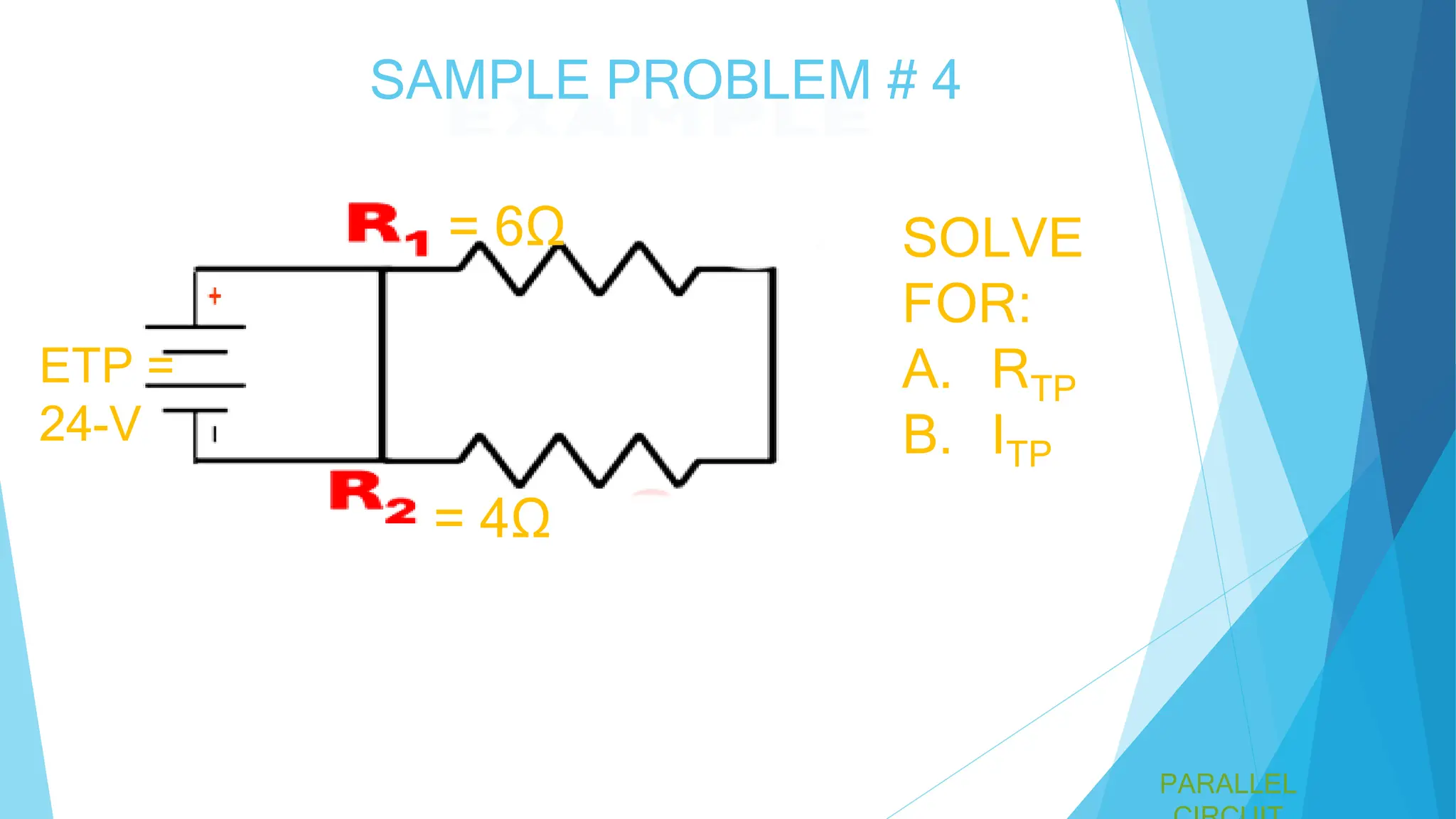
A parallel circuit involves multiple paths for current, with all components operating at the same voltage. The total current is the sum of the currents through each component, and the total resistance is less than the smallest individual resistance. Specific formulas and examples, including calculations for total resistance in various configurations, are provided.