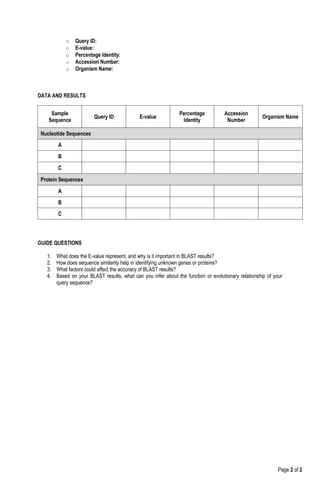
This is an activity for BLAST. The Basic Local Alignment Search Tool (BLAST) is a widely used bioinformatics tool for comparing biological sequences such as DNA, RNA, and proteins. It allows researchers to identify similarities between sequences, infer evolutionary relationships, and annotate genes.
In this laboratory activity, you will learn how to use BLAST to analyze a given sequence and compare it with known sequences in the NCBI database.
By the end of this activity, you should be able to:
• Understand the basic principles and applications of BLAST.
• Learn how to retrieve and analyze DNA and protein sequences.
• Perform a sequence alignment using the NCBI BLAST tool.
• Interpret BLAST search results.