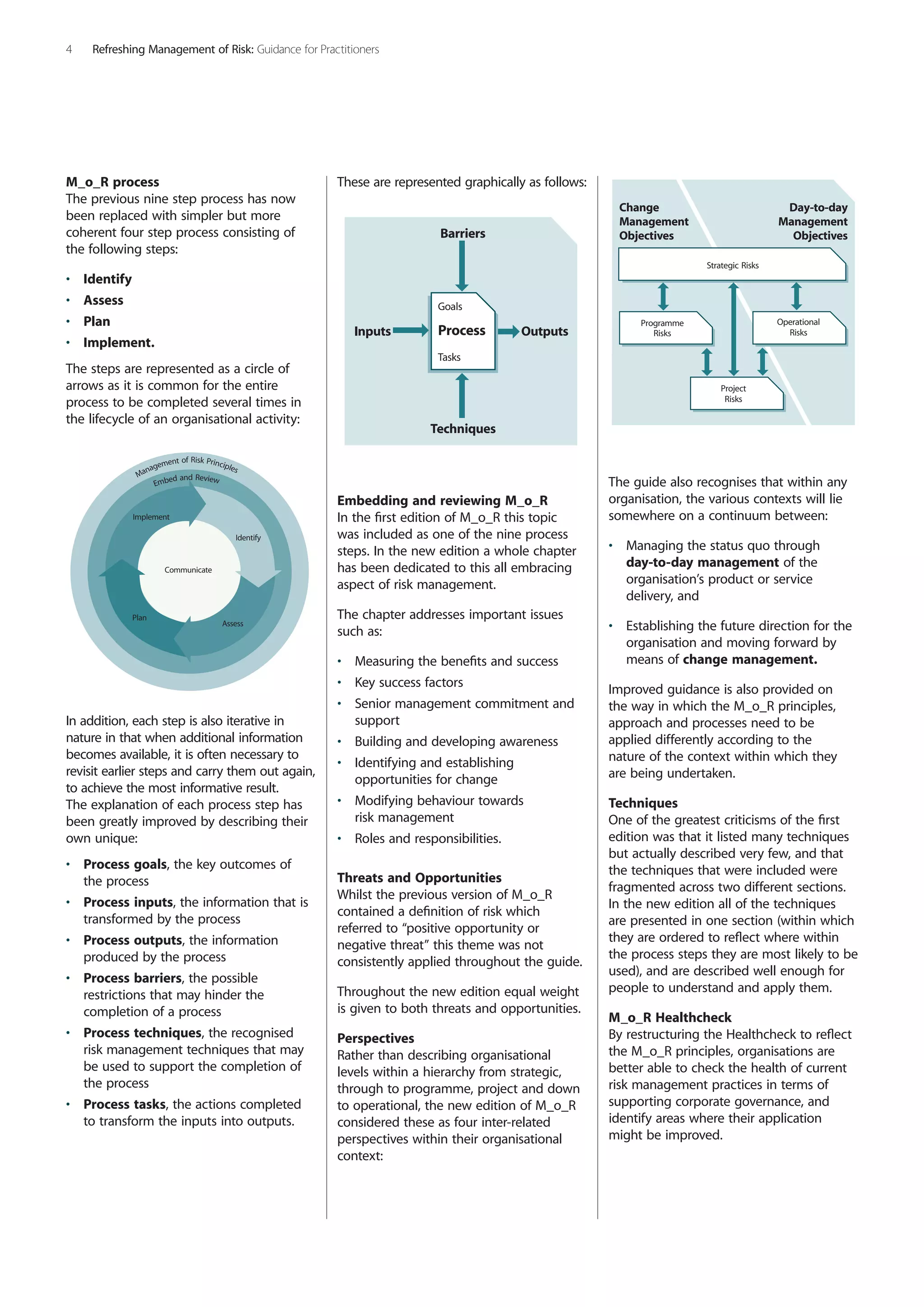
The document summarizes the refresh of the Management of Risk (M_o_R) guidance. Some key changes include:
1) Structuring the guide around a new M_o_R framework based on principles, approach, process, and embedding/reviewing.
2) Emphasizing both threats and opportunities.
3) Simplifying the risk management process to four steps: identify, assess, plan, and implement.
4) Providing improved guidance on risk concepts, techniques, and embedding risk management practices.
5) Maintaining the core framework while updating content to align with current best practices.