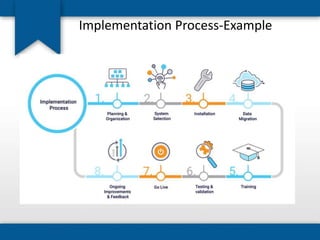
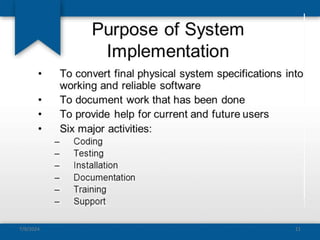
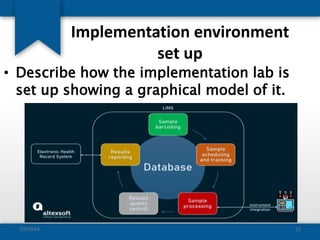
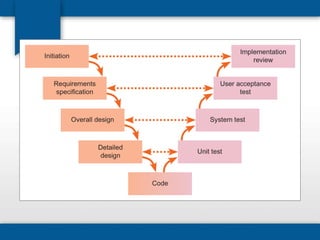
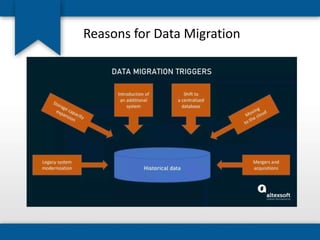
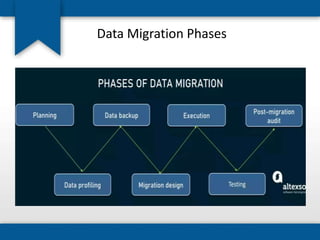
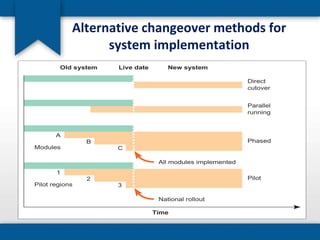
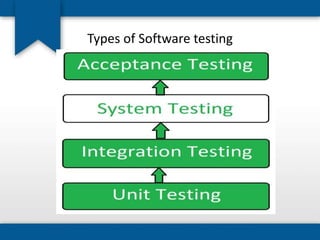
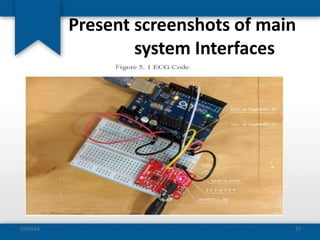
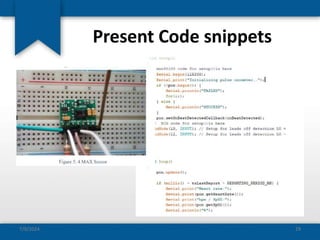
The document outlines the concepts of system build, implementation, maintenance, and change management within software development. It details steps for successful system implementation, including preparation, deployment, transition to organizational support, and data migration, as well as the importance of software quality and post-implementation review. Additionally, it covers the requirements for testing software to ensure functionality and suitability for users.