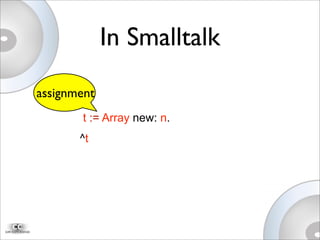
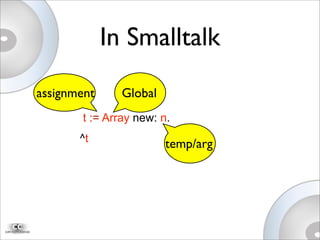
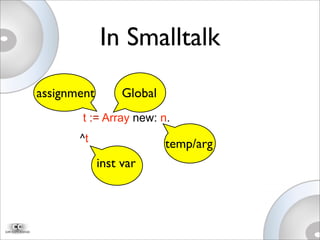
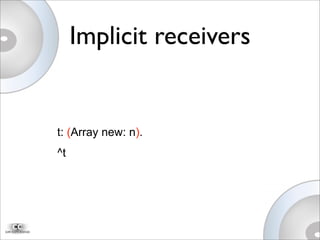
This document discusses Newspeak, an evolution of Smalltalk designed for the modern web. Newspeak aims to improve on Smalltalk's modularity, security, and interoperability using message-based programming and an object capability model without static state. It also aims to support cloud computing by enabling network-serviced applications that can run locally but sync seamlessly with server-hosted software and data.