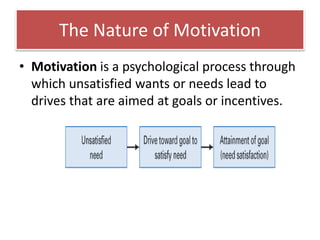
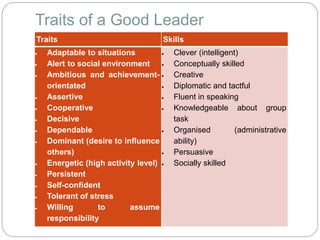
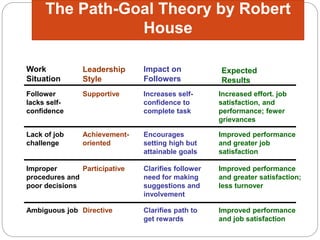
The document discusses motivation and leadership. It provides definitions of motivation and discusses various theories of motivation including Maslow's hierarchy of needs. It then discusses theories and models of leadership including trait theory, behavioral approaches, situational approaches, path-goal theory, and crisis leadership. It provides examples of leadership traits needed for crisis management and concludes with three case studies of companies that demonstrated effective leadership in times of crisis.