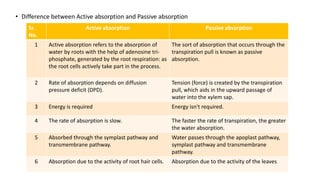
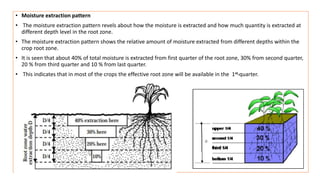
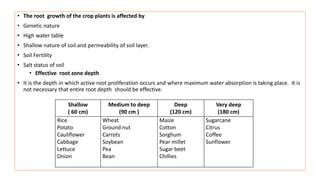
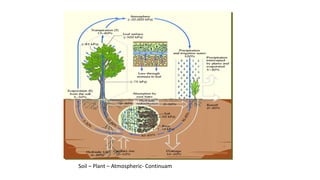
The document discusses the mechanisms and factors influencing water absorption in plants, emphasizing the role of root systems and moisture extraction patterns. It distinguishes between active and passive absorption processes, detailing how factors like soil type, water concentration, and temperature affect water uptake. Additionally, it highlights the importance of rooting characteristics in determining moisture availability and discusses the overall significance of water movement within the soil-plant-atmospheric system.