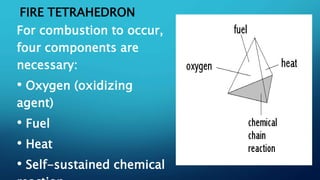
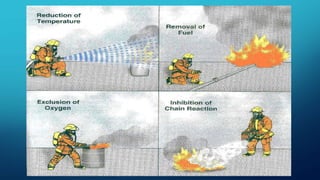
Fire requires oxygen, fuel, and heat to burn in a self-sustaining chemical reaction known as the fire tetrahedron. There are four stages of fire: ignition, growth, flashover, and fully developed. Fire can be extinguished by removing one of the elements of the fire tetrahedron such as oxygen, fuel, or heat. Wildfires are uncontrolled fires that burn vegetation and organic materials in remote areas. They can be caused by natural events like lightning or human activities like smoking. Controlling wildfires involves reducing flammable fuels through forest management and community participation in prevention.