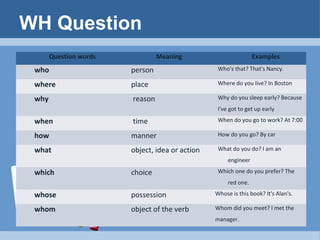
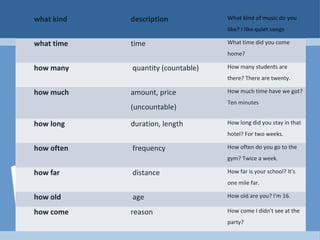
This document provides information and examples about forming yes/no questions and WH questions in English. For yes/no questions, the rules described include inverting the subject and verb when the verb is "to be" or adding an auxiliary verb when one is present. For verbs without an auxiliary, "do" or "does" is added. For WH questions, the document lists common question words like who, what, when, where and provides examples of how to form questions using those words by placing them at the start of questions about the subject or inverting verbs when asking about the predicate.