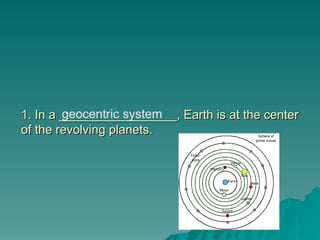
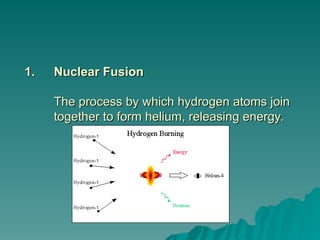
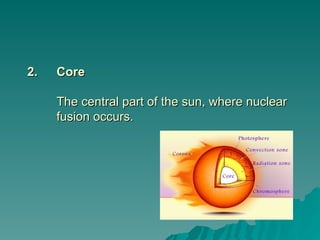
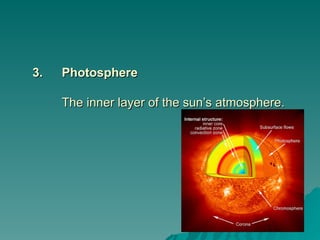
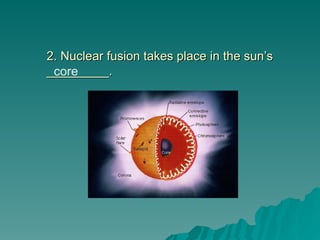
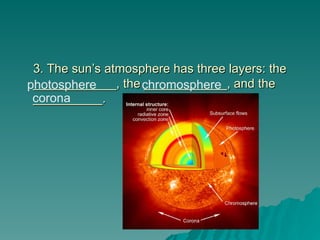
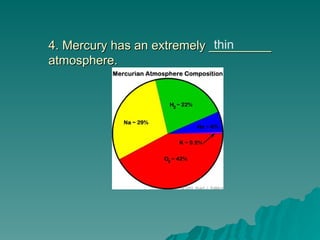
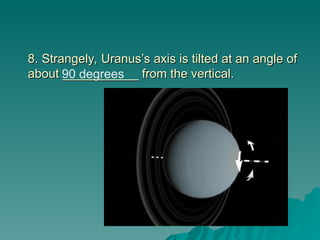
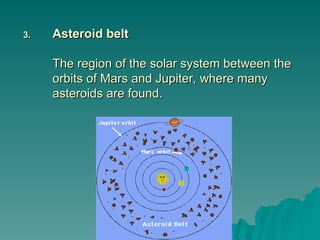
Chapter 2 discusses the solar system, including the differences between geocentric and heliocentric models, Kepler's discoveries related to planetary orbits, and Newton's factors that maintain these orbits. It describes the sun's structure, energy production through nuclear fusion, and the features of the inner and outer planets, including the characteristics of terrestrial and gas giant planets. The chapter also covers comets, asteroids, meteoroids, and the search for extraterrestrial life on Mars and Europa.